Leopard: fast decoding cell type-specific transcription factor binding landscape at single-nucleotide resolution
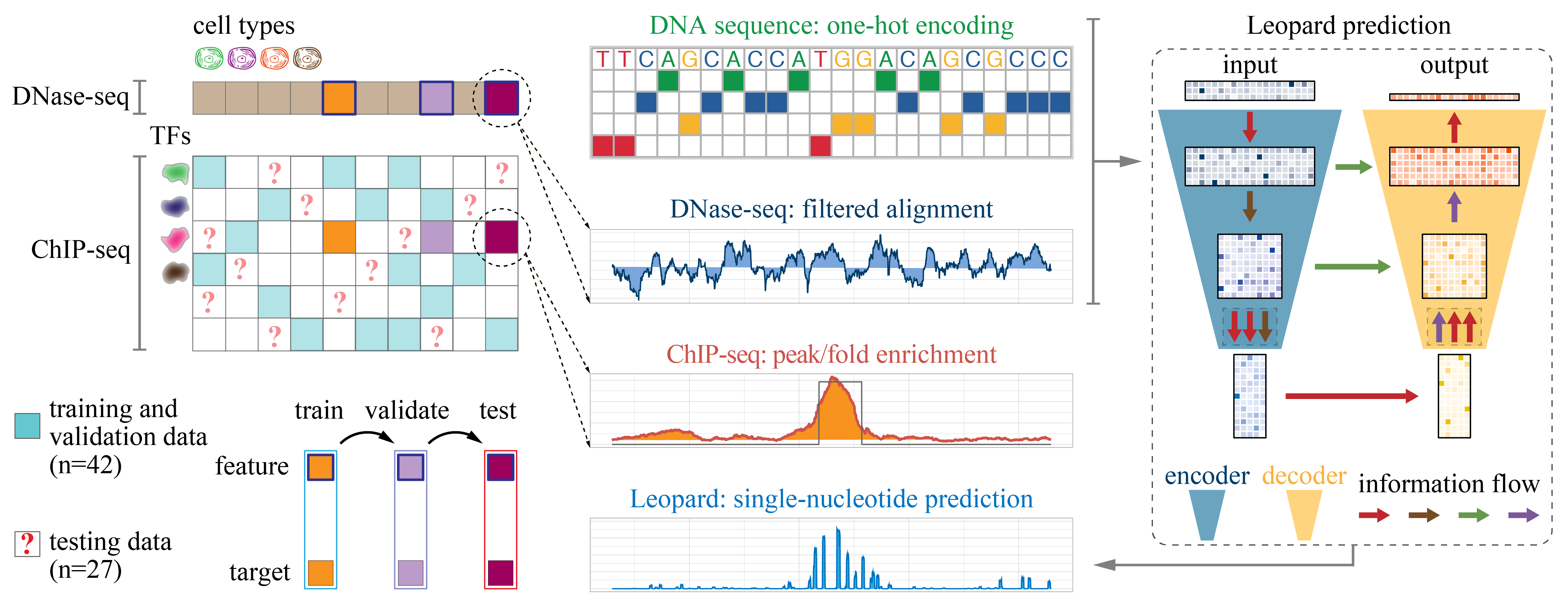
Leopard is a deep learning approach to predict cell type-specific in vivo transcription factor binding sites with high accuracy, speed and resolution Hongyang Li, Yuanfang Guan - bioRxiv, 2019, doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/856823. Please contact (hyangl@umich.edu or gyuanfan@umich.edu) if you have any questions or suggestions.
Git clone a copy of code:
git clone https://github.com/GuanLab/Leopard.git
- python (3.6.5)
- numpy (1.13.3). It comes pre-packaged in Anaconda.
- pyBigWig A package for quick access to and create of bigwig files. It can be installed by:
conda install pybigwig -c bioconda
- tensorflow (1.14.0) A popular deep learning package. It can be installed by:
conda install tensorflow-gpu
- keras (2.2.5) A popular deep learning package using tensorflow backend. It can be installed by:
conda install keras
The data in bigwig format can be directly downloaded from our web server:
Before running Leopard, please download the above data (30GB) and deposit them in the "Leopard/data/" folder. The DNA sequence bigwig files are always needed. If you only need to make predictions on one cell type, you only need to download the "avg.bigwig" and the correpsonding DNase-seq file for this specific cell type. The ChIP-seq data are optional. You only need them if you want to re-train/adapt our models or compare predictions with experimental observations.
The original data can be found as follows:
The DNase-seq data were downloaded from the ENCODE-DREAM challenge website: filtered alignment
The ChIP-seq data were downloaded from the ENCODE-DREAM challenge website: conservative peaks and fold enrichment and the ENCODE project(The accession numbers are provided in Supplementary Table 4.)
Once the required input files are put in the correpsonding directories, Leopard is ready to go (fast mode):
python Leopard.py -tf E2F1 -te K562 -chr chr21 chr22
Or you can run the complete mode with higher accuracy and longer runtime:
python Leopard.py -tf E2F1 -te K562 -chr chr21 -m complete
The prediction npy files are saved in the ./output/ folder