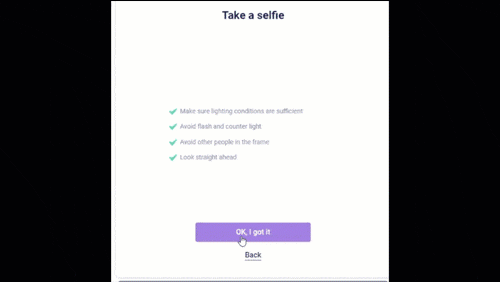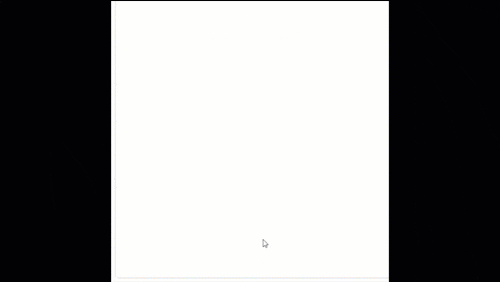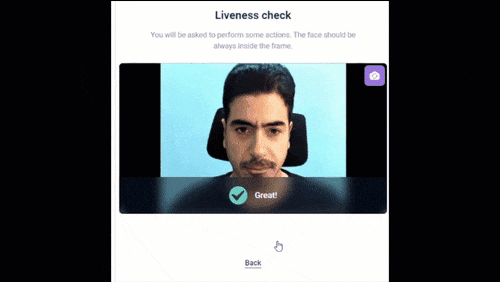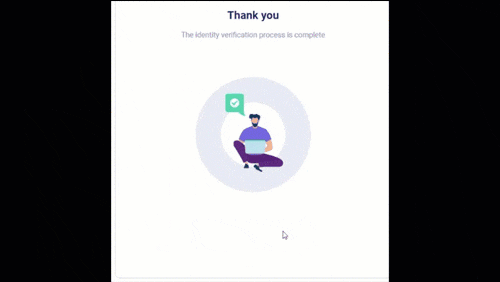
dot (aka Deepfake Offensive Toolkit) makes real-time, controllable deepfakes ready for virtual cameras injection. dot is created for performing penetration testing against e.g. identity verification and video conferencing systems, for the use by security analysts, Red Team members, and biometrics researchers.
If you want to learn more about dot is used for penetration tests with deepfakes in the industry, read these articles by The Verge and Biometric Update
dot is developed for research and demonstration purposes. As an end user, you have the responsibility to obey all applicable laws when using this program. Authors and contributing developers assume no liability and are not responsible for any misuse or damage caused by the use of this program.
In a nutshell, dot works like this
__________________ _____________________________ __________________________
| your webcam feed | -> | suite of realtime deepfakes | -> | virtual camera injection |
------------------ ----------------------------- --------------------------
All deepfakes supported by dot do not require additional training. They can be used in real-time on the fly on a photo that becomes the target of face impersonation. Supported methods:
- face swap (via SimSwap), at resolutions
224and512- with the option of face superresolution (via GPen) at resolutions
256and512
- with the option of face superresolution (via GPen) at resolutions
- lower quality face swap (via OpenCV)
- FOMM, First Order Motion Model for image animation
-
Linux
sudo apt install ffmpeg cmake
-
MacOS
brew install ffmpeg cmake
The instructions assumes that you have Miniconda installed on your machine. If you don't, you can refer to this link for installation instructions.
conda env create -f envs/environment-gpu.yaml
conda activate dotInstall the torch and torchvision dependencies based on the CUDA version installed on your machine:
- Install
cudatoolkitfromconda:conda install cudatoolkit=<cuda_version_no>(replace<cuda_version_no>with the version on your machine) - Install
torchandtorchvisiondependencies:pip install torch==1.9.0+<cuda_tag> torchvision==0.10.0+<cuda_tag> -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html, where<cuda_tag>is the CUDA tag defined by Pytorch. For example,pip install torch==1.9.0+cu111 torchvision==0.10.0+cu111 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.htmlfor CUDA 11.1. See here for a list of all availabletorchandtorchvisionversions.
To check that torch and torchvision are installed correctly, run the following command: python -c "import torch; print(torch.cuda.is_available())". If the output is True, the dependencies are installed with CUDA support.
conda env create -f envs/environment-cpu.yaml
conda activate dotpip install -e .-
Download GitHub Release binaries from here or use the following
wgetcommands:wget https://github.com/sensity-ai/dot/releases/download/1.0.0/dot_model_checkpoints.z01 \ && wget https://github.com/sensity-ai/dot/releases/download/1.0.0/dot_model_checkpoints.z02 \ && wget https://github.com/sensity-ai/dot/releases/download/1.0.0/dot_model_checkpoints.zip
-
Unzip the binaries and place them in the root directory of the repository:
zip -s 0 dot_model_checkpoints.zip --out saved_models.zip \ && unzip saved_models.zip -
Clean up the downloaded binaries:
rm -rf *.z*
Run dot --help to get a full list of available options.
-
Simswap
dot \ -c ./configs/simswap.yaml \ --target 0 \ --source "./data" \ --show_fps \ --use_gpu -
SimSwapHQ
dot \ -c ./configs/simswaphq.yaml \ --target 0 \ --source "./data" \ --show_fps \ --use_gpu -
FOMM
dot \ -c ./configs/fomm.yaml \ --target 0 \ --source "./data" \ --show_fps \ --use_gpu -
FaceSwap
dot \ -c ./configs/faceswap.yaml \ --target 0 \ --source "./data" \ --show_fps \ --use_gpu
Note: To enable face superresolution, use the flag --gpen_type gpen_256 or --gpen_type gpen_512. To use dot on CPU (not recommended), do not pass the --use_gpu flag.
Disclaimer: We use the
SimSwaptechnique for the following demonstration
Running dot via any of the above methods generates real-time Deepfake on the input video feed using source images from the data/ folder.
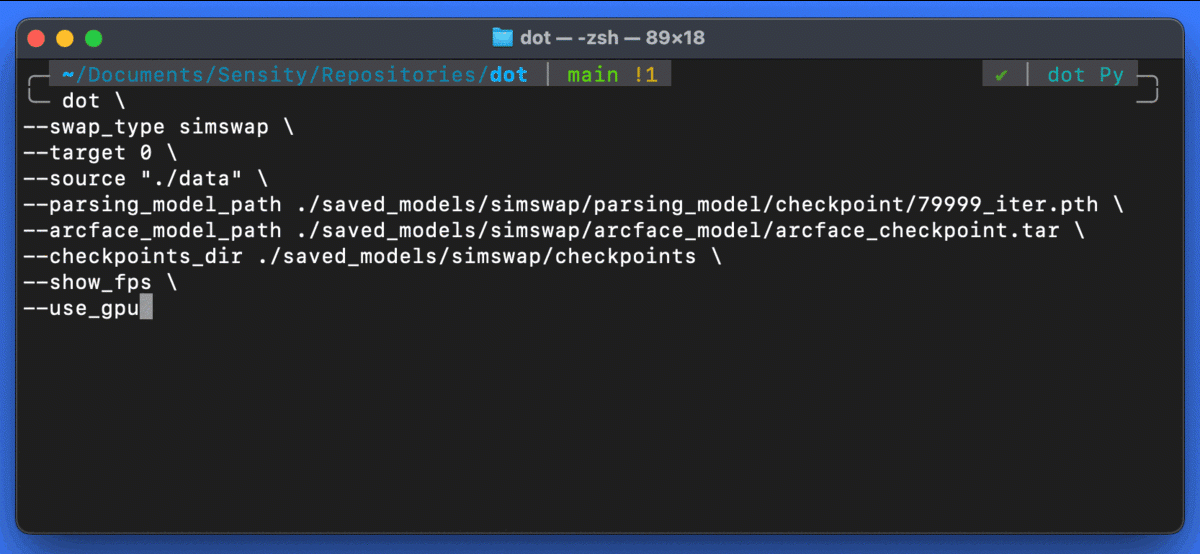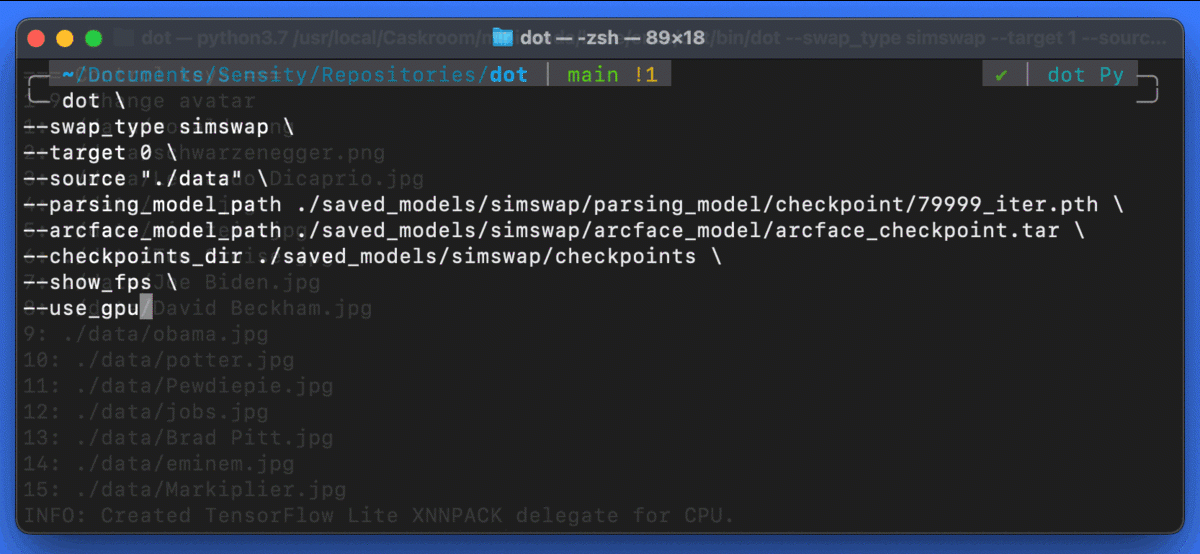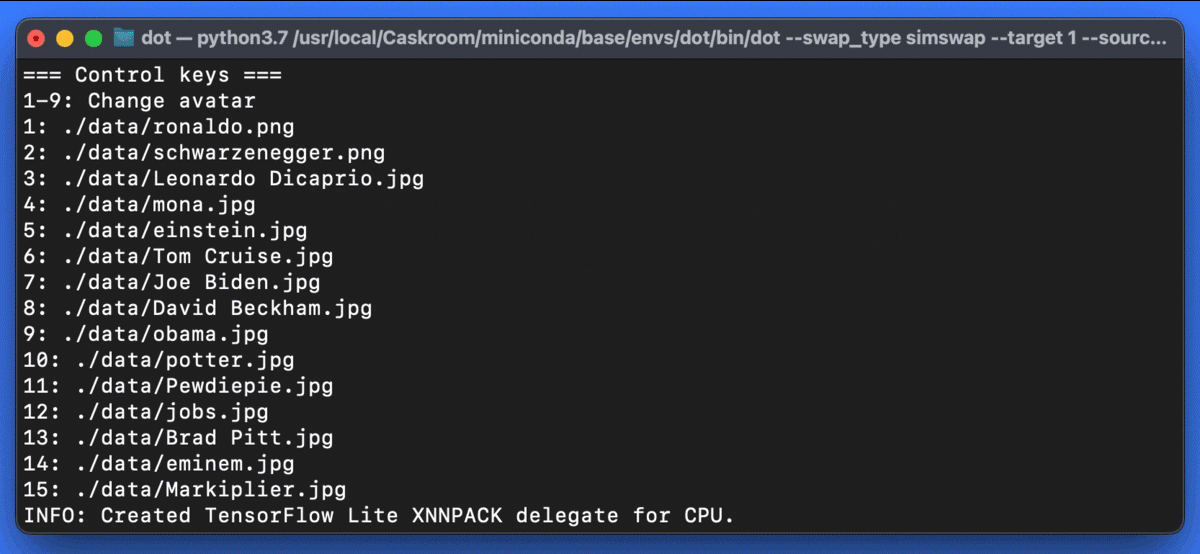
When running dot a list of available control options appear on the terminal window as shown above. You can toggle through and select different source images by pressing the associated control key.
Watch the following demo video for better understanding of the control options:
Instructions vary depending on your operating system.
-
Install OBS Studio.
-
Install VirtualCam plugin.
Choose Install and register only 1 virtual camera.
-
Run OBS Studio.
-
In the Sources section, press on Add button ("+" sign),
select Windows Capture and press OK. In the appeared window, choose "[python.exe]: fomm" in Window drop-down menu and press OK. Then select Edit -> Transform -> Fit to screen.
-
In OBS Studio, go to Tools -> VirtualCam. Check AutoStart,
set Buffered Frames to 0 and press Start.
-
Now
OBS-Cameracamera should be available in Zoom(or other videoconferencing software).
sudo apt update
sudo apt install v4l-utils v4l2loopback-dkms v4l2loopback-utils
sudo modprobe v4l2loopback devices=1 card_label="OBS Cam" exclusive_caps=1
v4l2-ctl --list-devices
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:obsproject/obs-studio
sudo apt install obs-studioOpen OBS Studio and check if tools --> v4l2sink exists.
If it doesn't follow these instructions:
mkdir -p ~/.config/obs-studio/plugins/v4l2sink/bin/64bit/
ln -s /usr/lib/obs-plugins/v4l2sink.so ~/.config/obs-studio/plugins/v4l2sink/bin/64bit/Use the virtual camera with OBS Studio:
- Open
OBS Studio - Go to
tools --> v4l2sink - Select
/dev/video2andYUV420 - Click on
start - Join a meeting and select
OBS Cam
- Download and install OBS Studio for MacOS from here
- Open OBS and follow the first-time setup (you might be required to enable certain permissions in System Preferences)
- Run dot with
--use_camflag to enable camera feed - Click the "+" button in the sources section → select "Windows Capture", create a new source and enter "OK" → select window with "python" included in the name and enter OK
- Click "Start Virtual Camera" button in the controls section
- Select "OBS Cam" as default camera in the video settings of the application target of the injection
This is not a commercial Sensity product, and it is distributed freely with no warranties
The software is distributed under BSD 3-Clause. dot utilizes several open source libraries. If you use dot, make sure you agree with their licenses too. In particular, this codebase is built on top of the following research projects:
- https://github.com/AliaksandrSiarohin/first-order-model
- https://github.com/alievk/avatarify-python
- https://github.com/neuralchen/SimSwap
- https://github.com/yangxy/GPEN
This repository follows the Google Python Style Guide for code formatting.
If you have ideas for improving dot, feel free to open relevant Issues and PRs. Please read CONTRIBUTING.md before contributing to the repository.
If you are working on improving the speed of dot, please read first our guide on code profiling.
Visit CHANGELOG.md to track changes in the repository.
-
Install Dev Requirements
pip install -r requirements-dev.txt
-
Install Pre-Commit Hooks
pre-commit install
-
Run Unit Tests (with coverage)
pytest --cov=dot --cov-report=term --cov-fail-under=10