A high performance authority-only dns server implemented with DPDK
- support storing zone data in mongodb
- high performance
NIC: Intel Corporation 82599ES 10-Gigabit SFI/SFP+ Network Connection
CPU: Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-2650 0 @ 2.00GHz
Memory: 64GB
OS: Ubuntu 16.04.1 LTS
Kernel: 4.4.0-81-generic
-
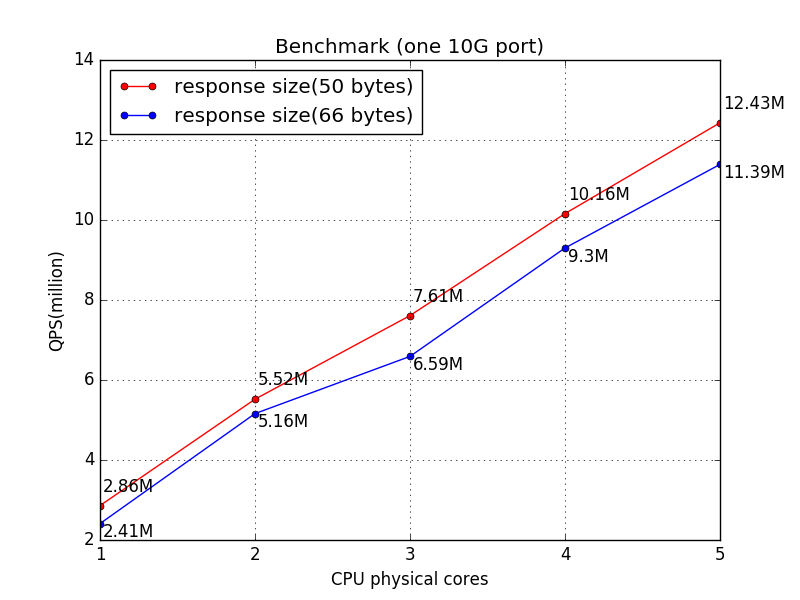
one 10G port
pls note when test with 5 cores, shuke actually processed 12.43M and 11.39M requests per second, but the client reports 10.7M and 9.46M, this is because the NIC doesn't have enough bandwidth.
-
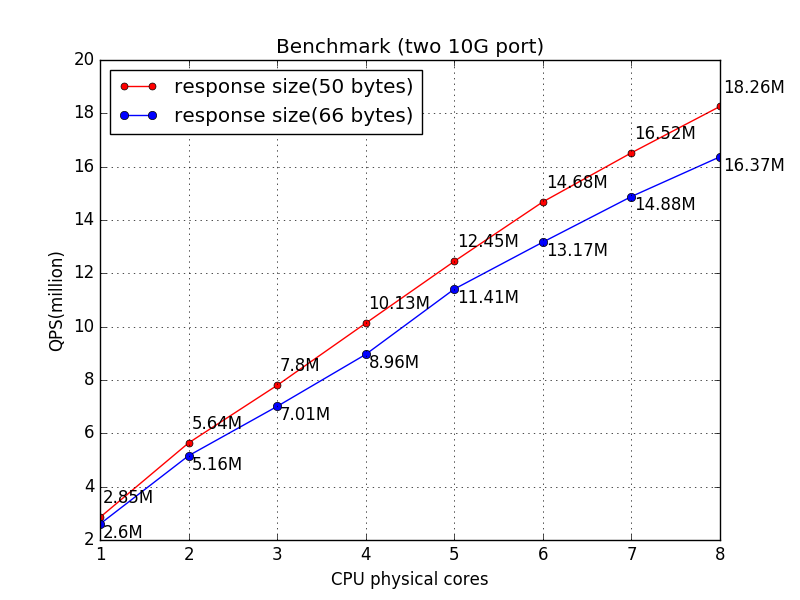
two 10G port
if you use vagrant, it is very simple to try shuke
-
install virtualbox and vagrant
-
run
cd vagrant && vagrant up -
ssh to the guest machine, then run the following command:
cd /shuke sudo build/shuke-server -c vagrant/test.toml -
in the host machine, run
dig www1.example.com. @172.28.128.10 -p 19899 -t A
tips: vagrant/setup.sh is a good place to figure out how to build this project
and prepare the running environment.
-
clone source code:
git clone --recursive https://github.com/yuyang0/shuke.git -
build dpdk, shuke is only tested on dpdk-17.05.2. if you use linux x86-64, you can run
bash 3rd/dpdk/usertools/dpdk-setup.sh, then perform the following instructions.- press
[12]to compile dpdk for linux x86-64 target. - press
[15]to insert UIO - press
[17]to insert KNI - press
[19]([18]for non-NUMA systems) to setup huge pages, since shuke uses huge page heavily, so allocate as large as possible - press
[21]to bind NIC device - press
[32]to quit
- press
-
install autoconf and libtool
-
run
makeat the top of source tree, then you will get a binary file namedbuild/shuke-server.
- if you use ubuntu, you can just run
bash ./bootstrap.shto build shuke - if you want to build shuke in DEBUG mode, just run
make DEBUG=1 - if you want to see the compiler command, just run
make V=1 - if you want to support ip fragmentation, just run
make IP_FRAG=1.
just run build/shuke-server -c conf/shuke.toml,
you may need to change the config in the config file.
every zone should have a collection in mongodb. you can use
tools/zone2mongo.py to convert zone data from zone file to mongodb
this collection used to track the RR of a zone, the collection name is the domain of the zone, since mongodb's collection name can't end with dot, so the domain should be the absolute domain name except the last dot. the collection should contain the following fields
{
name: "the absulute owner name,
ttl: 1234567,
type: "DNS type",
rdata: "rdata"
}
the meaning of fields is clear. just like the zone file.
SHUKE has a tcp server used to execute admin operations,
tools/admin.py is the client. it supports several commands:
zone: this command used to manipulate the zone data in memory, it has many subcommands.get: get a zonegetall: get all zonesreload: reload multiple zonereloadall: reload all zoneget_numzones: return the number of zones in memory cache.
config: this command is used to manipulate the config of server.version: return version of shukedebug: mainly for debugsegfault: cause a segement faultoom: trigger a OOM error.
info: print information of server, including statistics. subcommandsallordefaultor empty: return all informationserver: return the server informationmemory: return memory usage informationcpu: return cpu usage informationstats: statistics information
- support EDNS, DNSSEC and PTR (currently only support A,AAAA,NS,CNAME,SOA,SRV,TXT,MX.).
- support mysql (currently only support mongodb).
- plugin system
- some anti-attack mechanisms such as white list, black list, response rate limit(RRL), etc.
- HTTP api