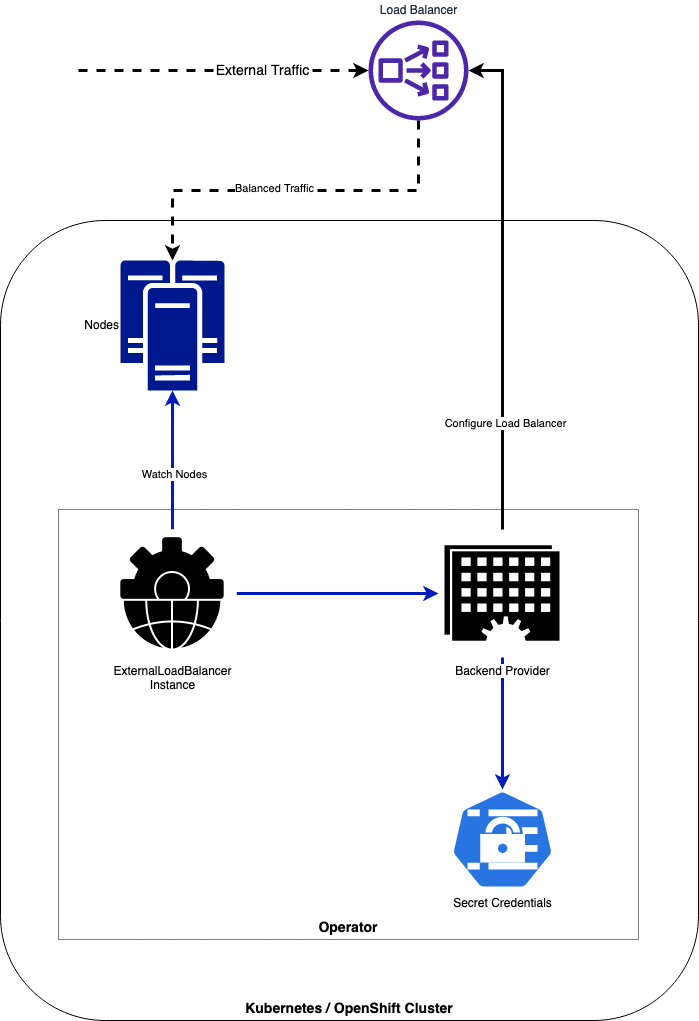
The LBConfig Operator, manages the configuration of External Load Balancer instances (on third-party equipment via it's API) and creates VIPs and IP Pools with Monitors for a set of OpenShift or Kubernetes nodes like Master-nodes (Control-Plane), Infra nodes (where the Routers or Ingress controllers are located) or based on it's roles and/or labels.
The operator dynamically handles creating, updating or deleting the IPs of the pools in the Load Balancer based on the Node IPs for each role or label. On every change of the operator configuration (CRDs) or addition/change/removal or cluster Nodes, the operator updates the Load Balancer properly.
The objective is to have a modular architecture allowing pluggable backends for different load balancer providers.
To use the operator, you will need a Kubernetes cluster to run against. You can use KIND to get a local cluster for testing, or run against a remote cluster.
Note: Your controller will automatically use the current context in your kubeconfig file (~/.kube/config) (i.e. whatever cluster kubectl cluster-info shows).
Quick demo:
The main users for this operator is enterprise deployments or clusters composed of multiple nodes having an external load-balancer providing the balancing and high-availability to access the cluster in both API and Application levels.
Apply the operator manifest into the cluster:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/carlosedp/lbconfig-operator/main/manifests/deploy.yamlThis creates the operator Namespace, CRD and deployment using the latest container version. The container image is built for amd64, arm64 and ppc64le architectures.
Create the instances for each Load Balancer instance you need (for example one for Master Nodes and another for the Infra Nodes).
The provider vendor field can be (case-insensitive):
- F5_BigIP - Tested on F5 BigIP version 15
- Citrix_ADC - Tested on Citrix ADC (Netscaler) version 13
- Dummy - Dummy backend used for testing to only print log messages on operations
Create the secret holding the Load Balancer API user and password:
oc create secret generic f5-creds --from-literal=username=admin --from-literal=password=admin123 --namespace lbconfig-operator-systemMaster Nodes using a Citrix ADC LB:
apiVersion: lb.lbconfig.carlosedp.com/v1
kind: ExternalLoadBalancer
metadata:
name: externalloadbalancer-master-sample
namespace: lbconfig-operator-system
spec:
vip: "192.168.1.40"
type: "master"
ports:
- 6443
monitor:
path: "/healthz"
port: 6443
monitortype: "https"
provider:
vendor: Citrix_ADC
host: "https://192.168.1.36"
port: 443
creds: netscaler-creds
validatecerts: noInfra Nodes using a F5 BigIP LB:
apiVersion: lb.lbconfig.carlosedp.com/v1
kind: ExternalLoadBalancer
metadata:
name: externalloadbalancer-infra-sample
namespace: lbconfig-operator-system
spec:
vip: "192.168.1.45"
type: "infra"
ports:
- 80
- 443
monitor:
path: "/healthz"
port: 1936
monitortype: http
provider:
vendor: F5_BigIP
host: "https://192.168.1.35"
port: 443
creds: f5-creds
partition: "Common"
validatecerts: noTo choose the nodes which will be part of the server pool, you can set either type or nodelabels fields. The yaml field type: "master" or type: "infra" selects nodes with the role label "node-role.kubernetes.io/master" and "node-role.kubernetes.io/infra" respectively. If the field nodelabels array is used instead, the operator will use nodes which match all labels.
Clusters with sharded routers or using arbitrary labels to determine where the Ingress Controllers run can be configured like:
spec:
vip: "10.0.0.6"
ports:
- 80
nodelabels:
"node.kubernetes.io/ingress-controller": "production"
"kubernetes.io/region": "DC1"
...Some fields inside providers are optional and depend on the used backend. Check the API docs which fields are backend-specific.
CRD Fields:
apiVersion: lb.lbconfig.carlosedp.com/v1 # This is the API used by the operator (mandatory)
kind: ExternalLoadBalancer # This is the object the operator manages (mandatory)
metadata:
name: externalloadbalancer-master-sample # Load Balancer instance configuration name (mandatory)
namespace: lbconfig-operator-system # The instance namespace (same as the operator runs) (mandatory)
spec:
vip: "192.168.1.40" # This is the VIP that will be created on the Load Balancer for this instance (mandatory)
type: "master" # Type could be "master" or "infra" that maps to OpenShift labels (optional)
nodelabels: # List of labels to be used instead of "type" field (optional)
- "node.kubernetes.io/ingress": "production" # Example label used to fetch the Node IPs by this instance (optional)
ports:
- 6443 # Port list which the Load Balancer will be forwarding the traffic (mandatory)
monitor:
path: "/healthz" # Monitor URL to be configured in the Load Balancer instance
port: 6443 # Monitor port to be configured in the Load Balancer instance
monitortype: "https" # Monitor protocol to be configured in the Load Balancer instance
provider: # This section defines the backend provider or vendor of the Load Balancer
vendor: F5_BigIP # See supported vendors in the section above (mandatory)
host: "192.168.1.35" # The IP of the API for the Load Balancer to be managed (mandatory)
port: 443 # The port of the API for the Load Balancer to be managed (mandatory)
creds: f5-creds # The name of the Kubernetes Secret created with username and password to the API (mandatory)
partition: "Common" # The partition for the F5 Load Balancer to be used (optional, only for F5_BigIP provider)
validatecerts: no # Should check the certificates if API uses HTTPS (optional)For more details, check the API documentation at https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/carlosedp/lbconfig-operator/api/v1?utm_source=gopls#pkg-types.
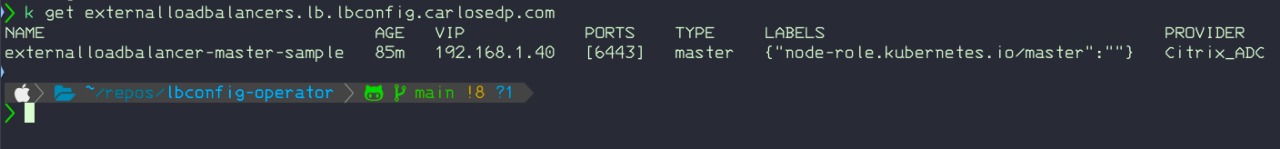
The kubectl get output shows each ExternalLoadBalancer instance details:
The operator exports two metrics. One counts the amount of ExternalLoadBalancers the operator is currently managing and another exposes the amount of nodes managed by each instance of ExternalLoadBalancer with appropriate metric labels.
# HELP externallb_total Number of external load balancers configured
# TYPE externallb_total gauge
externallb_total 1
# HELP externallb_nodes Number of nodes for the load balancer instance
# TYPE externallb_nodes gauge
externallb_nodes{ip="192.168.1.40",name="externalloadbalancer-master-sample",namespace="lbconfig-operator-system",port="6443",type="master"} 3This project aims to follow the Kubernetes Operator pattern
It uses Controllers which provides a reconcile function responsible for synchronizing resources untile the desired state is reached on the cluster
There are multiple make targets available to ease development.
- Build binary:
make - Install CRDs in the cluster:
make install - Deploy the operator manifests to the cluster (CRDs + Namespace + Operator Container):
make deploy - Create CRs in cluster (secret and Load Balancer instance)
To run the operator in your dev machine without deploying it to the cluster (using configurations use the defined in the $HOME/.kube/config), do not use make deploy, instead do:
- Run
make installto create the CRDs as above; - Create the operator namespace with
kubectl create namespace lbconfig-operator-system; - Create CRs (secret, backend, LB) as before in the same namespace.
- Use
make runto run the operator locally;
To remove the manifests to the cluster: make undeploy
Building the manifests and docker images: make dist.
Operator deployment manifest bundle is created at ./manifests/deploy.yaml.
The sample manifests for LoadBalancer instances and backends are in ./config/samples folder.
- Create a package directory at
controllers/backendwith provider name - Create the provider code with CRUD matrix of functions implementing the
Providerinterface - Create the test file using Ginkgo
- Add the new package to be loaded by the
controllers/backend/backend_loader/backend_loader.goas an_import
- Add Multiple backends (not in priority order)
- F5 BigIP
- Citrix ADC (Netscaler)
- HAProxy
- NGINX
- NSX
- Dummy backend
- Dynamic port configuration from NodePort services
- Check LB configuration on finalizer
- Add tests
- Add Metrics/Tracing/Stats
- Upgrade to go.kubebuilder.io/v3 - https://master.book.kubebuilder.io/migration/v2vsv3.html
- The operator does not check if the requested configuration (names, IPs) already exists and/or conflicts with existing configuration in the Load Balancer. The user is responsible for these checks before deployment;
- I am not responsible if the operator changes/deletes existing configuration on the Load Balancer if existing names are already configured.