Css-specs 
What ?
It's a tool that reports the differences from a very big stylesheet based on previous versions. It's based on selector and rule specifications that are being saved automatically from any given local html.
Why ?
This tool has emerged from the frustration of manually testing the result of a very large css codebase. Most likely emerging from a compiled language such as SASS, LESS or custom css builder.
It can be usefull to
- make sure the css rules realy apply or make sense
- detect unwanted changes from an other rule
- deeply report the difference between two states
Features
- Create a snapshot from existing compiled style
- Compare compiled styles to last valid snapshot for that css build
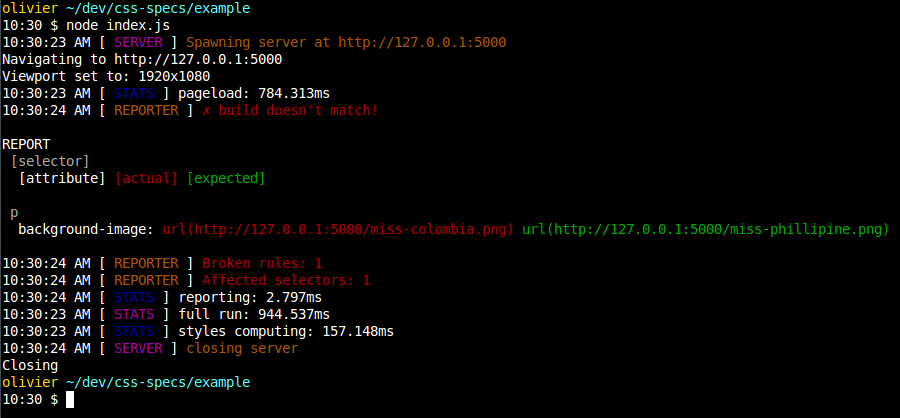
- Report differences displaying actual and expected css values
- JSON format output (can be converted to XML for jenkins report and such)
- can be pointed to any html template (remote or local)
- can load any stylesheet file that is local to your computer
- load remote stylesheets if present in the template or the remote server
Pictures
How to use
add in you project
npm install --save css-specs
create a config file named css-specs.conf.js
module.exports = {
prettySnapshots: false,
snapshotPath: 'snapshots',
port: 5000
};When you require it, you have a few methods exposed to handle different use cases.
var cs = require('..'); // that's our css-specs lib
var fs = require('fs');
var cssBuildPath = 'example.css'; // can be any local path
var url = './example.html'; // can be external urls as well
// get css as a string
var css = fs.readFileSync(cssBuildPath, 'utf-8');.renderer(url, css, callback) is used to render the current page with the specified style and return computed values.
cs.renderer(url, css, function(result) {
/* do something with the results... */
});.snapshot.save(cssBuildPath, result.styles) is used to save a result after being rendered.
cs.renderer(url, css, function(result) {
cs.snapshot.save(cssBuildPath, result.styles);
});.comparator.compare(cssBuildPath, result.styles) is used to compare two different results.
cs.renderer(url, cssToCheck, function(result) {
var snapshot = require(cs.utils.snapshotPath(cssBuildPath));
var diff = cs.comparator.compare(snapshot, result.styles);
});Lastlyl, .reporter(diffTree) is used to output differences in the console in a nice way
cs.renderer(url, cssToCheck, function(result) {
var snapshot = require(cs.utils.snapshotPath(cssBuildPath));
var diff = cs.comparator.compare(snapshot, result.styles);
cs.reporter(diff); // <------
});Refer to the example that you might run with node index.js for "real-life" usage.
API
We encourage reading the source code from the entry point and the config defaults