A course designed to understand:
- the challenges of data exchange in microservices
- best practices with sync and async patterns to communicate between microservices
- implement an Event Bus, and then used common industry tooling to handle communications
- JavaScript & TypeScript
- ReactJs / NextJs (server-side rendering) + Bootstrap
- NodeJs, Express, MongoDb/Mongoose
- Jest for testing
- Docker, Kubernetes, Skaffold
- Google Cloud Platform (nitrous developments account) - Kubernetes, Google Cloud Build, Google Cloud VM,
- custom NPM module/library called
common - NATS streaming event-bus
- Redis
Each project represents a discrete chunk of code, and stages in the learning journey.
Each stage of the course is also reflected in a branch, whose name should correlate with the folder associated with each stage in the course.
- ensure Skaffold is installed - so you can run
skaffold dev - ensure ingress-nginx is installed by running the following:
docker ps --allorkubectl get namespaceand see if ingress-nginx is there. Shortcut to list all pods in all namespaces iskubectl get pods -A. Otherwise install it fromkubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx. REMEMBER TO WAIT UNTIL THIS POD IS RUNNING. check withkubectl get pods -n ingress-nginx - if Kubernetes on Docker Desktop is erroring, reset it. you will then need to re create the Kubernetes secrets service for the env variable for the
/authservice. This can be set using the following command:kubectl create secret generic <<name of secret>> --from-literal=<KEY_NAME>=<KEY VALUE>.
The actual command for this project will bekubectl create secret generic auth-jwt --from-literal=JWT_KEY=<INSERT RANDOM STRING>. Use the random string from the test setup if needed.
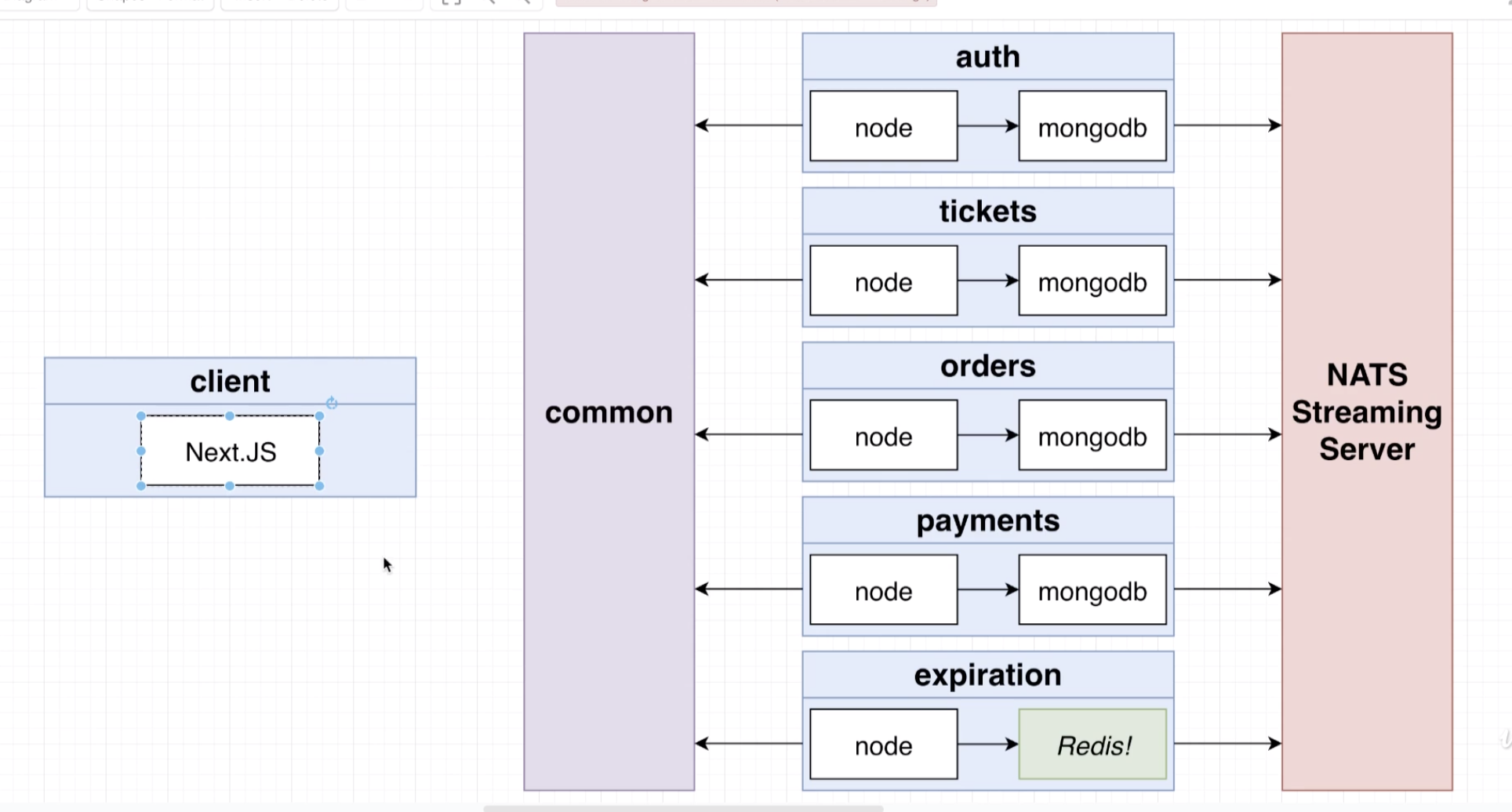
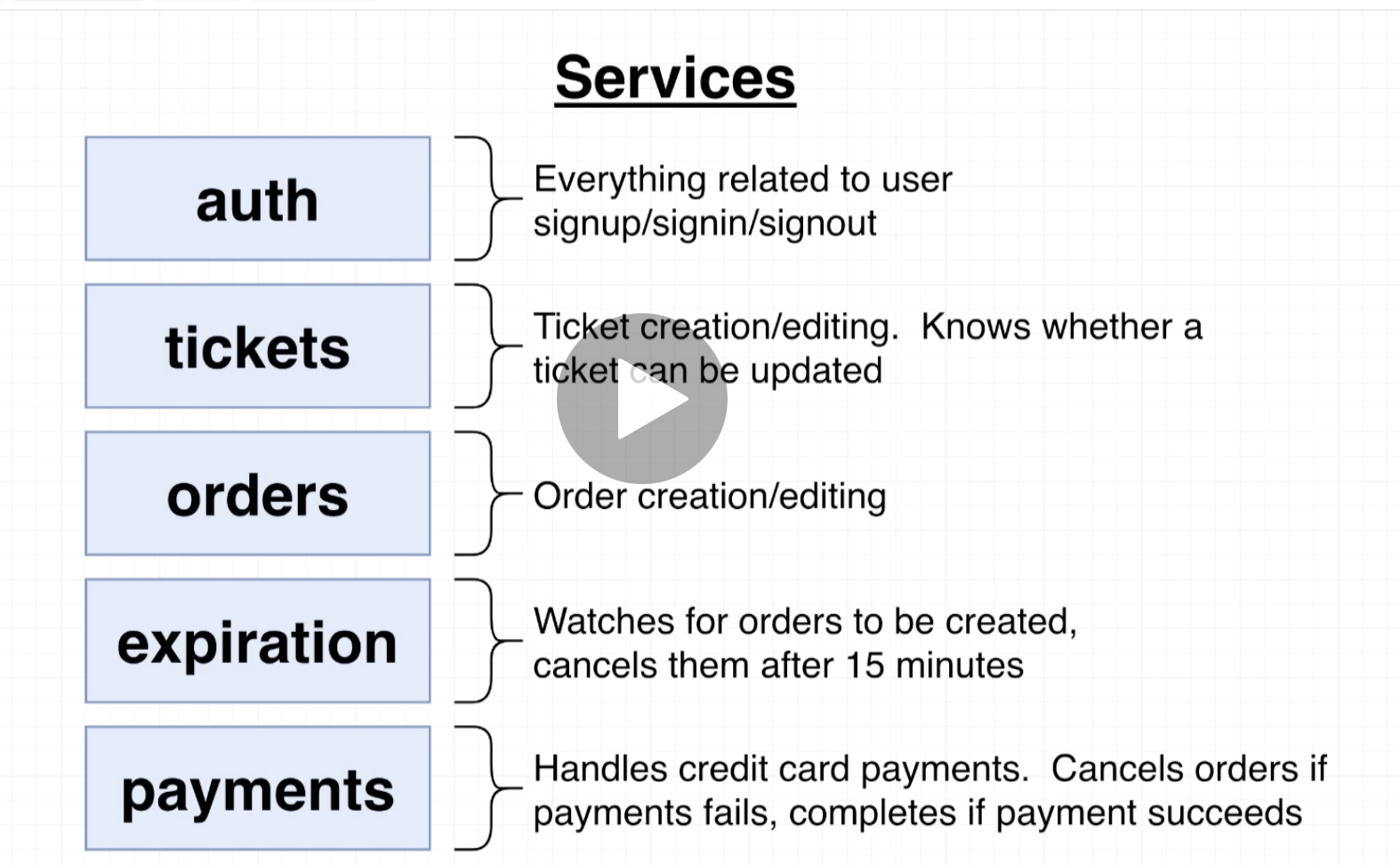
This is a made-from-scratch react front end, with multiple backend services (separated out to mimic microservices). The app is meant to simulate a blog/NewsFeed type scenario with Posts and Comments. It is extremely basic and crude, and only intended to illustrate the challenges in true production-grade challenges presented by microservices.
- the
Reactfront end app is on port3000 - the
Postsservice is on port5001. It receives posts and it emits events into the event bus. It also receives events from the event bus. - the
Commentsservice is on port5002. It receives comments and emitsCommentCreatedevents into the event bus. It also receives events from the event bus. Comments are sent to theModeratorservice, which moderates it and emits it back withstatustoCommentModerated. Then theCommentsservice updates its database, and emits withCommentUpdatedthrough the event bus, to be picked up by theQueryService. - the
Queryservice is on port5004. It fetches data for the Front End. It joinsPostsandCommentsand returns them. It receives events from the event bus. - the
Comment Moderatorservice is on port5003. It receives events from the event bus. It moderates thestatusflag onCommentsand emits an event that notifies subscribers that comments have been updated. TheQueryservice listens for this update to update the presentation layer with updated comment data. - the
Event Busservice is on port5005. Event objects havfe two properties :typeanddata. The event data also publishes events to the other 3 services.
All services that recieve post requests emit events into the Event Bus. The event bus then emits it out to all subscribing services.
The Query service protects against failures of the Posts and Comments service by receiving all relevant events, and persisting in its own database.
The Front End queries all posts and attached comments from the Query service, rather than directly from the Post and Comments service; however, the actual posting of new comments goes into those services directly. Thus reads and writes are handled by different services.
Containerizes Project 1. Adds kubernetes and ends with adding Skaffold as a dev tool.
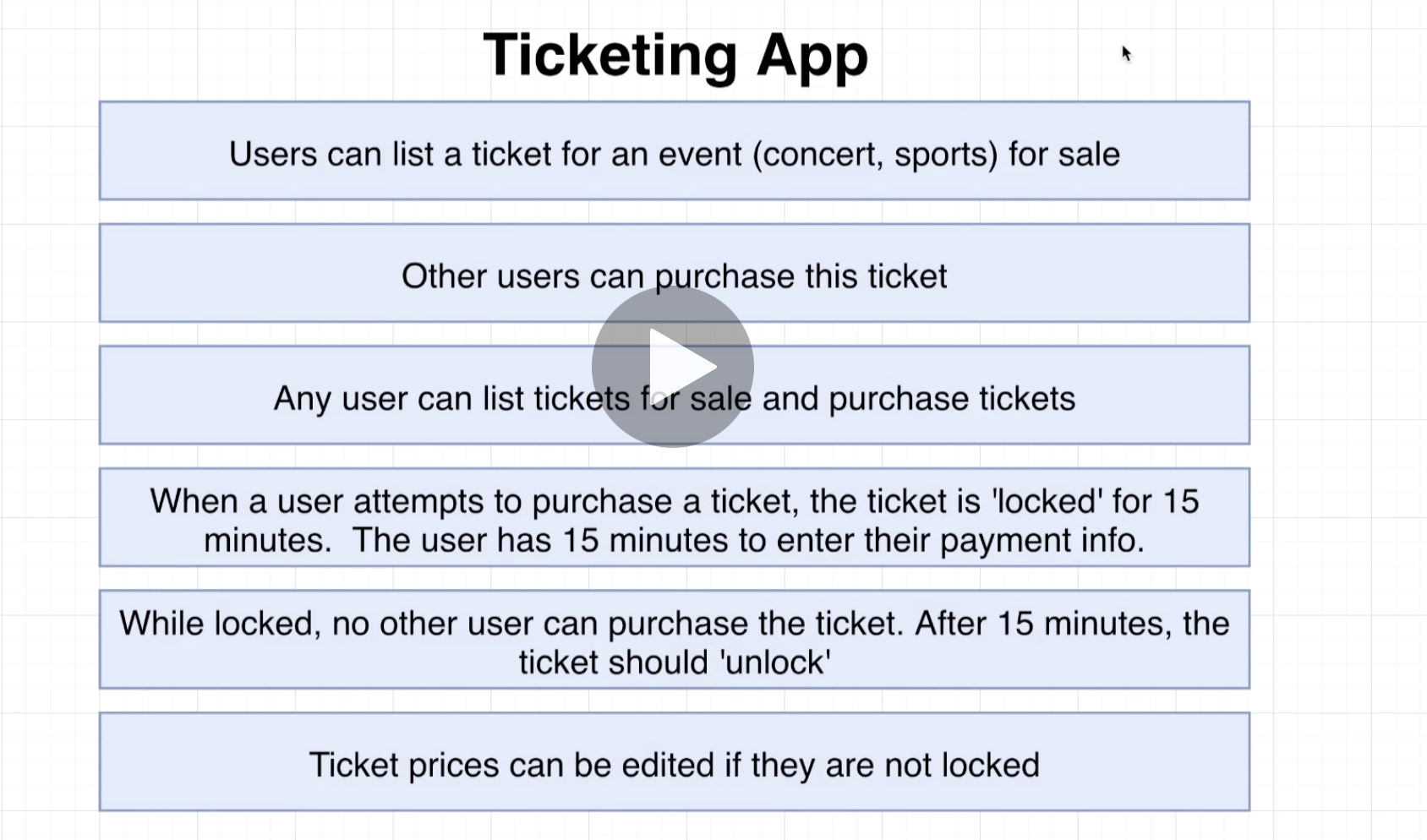
Build a stubhub.com clone using microservices and event-driven architecture.
To run the app, in the root folder for Project 3, run skaffold dev
IMPORTANT The app is served on a custom host address mystubhub.dev. This is set via the /etc/hosts file on the mac. This host is also set in the ingress-nginx-srv.yaml file which handles the routing and ingress into the Kube cluster.
To set up Docker and Kube for a given (auth, by example) service follow these steps:
Docker
- You need a Docker image for the service. So create a
Dockerfilein the root of the service folder - Create the
dockerignoreand ignorenode_modulesand others - run
docker build -t zeuslawyer/<image name> .- dont forget the.at the end. Then rundocker push zeuslawyer/<docker-image name> - Check that you have the
ingress-nginxcontroller for network i/o running on docker. you can rundocker ps --allto check if its running. Otherwise install it fromkubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx
Kubernetes
- Create a Kube Deployment (which creates a set of pods that runs the auth service.)
- create an
infra/k8spath inside the projectroot folderand inside there create the config fileauth-depl.yaml - In the project
root foldercreate theskaffold.yamlconfiguration file to use Skaffold devtools. Point it to the necessary deployments that skaffold must monitor and manage. - run
skaffold devfrom the projectroot folderand check terminal outputs. Skaffold will monitor the synced files for changes and push them directly into the pod. Unsynced file changes will cause the image to rebuild. - Consider the two ways to allow an outside network request (from browser) to get inside the Kube pod and hit the service. The two ways to do this are using a Kube NodePort service object or a service like the
ingress-nginx. If theingress-nginxinstance is still running in docker, then create a newingress-nginx-srv.yamlfile - In this file if you're changing the host, then update
/etc/hostson the machine to enable redirects to that host domain that you've chosen. - Upon navigation there will be a security error in chrome because
ingress-nginxexpects https by default. Get around this by typing anywhere in browserthisisunsafe
Google Kubernetes Engine
-
CReate a new project in console.cloud.google.com and create a new GKE instance, an associate it with region closest. choose the lowest configurations and from Node Pool choose a share GPU low end machine.
-
Login via terminal using gcloud, and choose the right account using
gcloud auth login. ensure the region is set to match the one chosen on cloud.console. -
Strategy is to retain use of Docker Desktop, while spinning up cluster in GCP. So set the context (folder context) for the cluster in GKE by using
gcloud container clusters get-credentials <Cluster Name (NOT project name or project id)>. You can get the project Id by listing out the configurations usinggcloud config configurations list -
verify that the cluster contexct has been set on GKE by clicking the docker desktop taskbar icon, clicking Kubernetes and checking whether a GKE context is there.
-
Enable Google cloud build to build images using the Dockerfile in codebase
-
update the
skaffold.yamlfile to configure it with Google Cloud Build / gcloud. It should now have this under the build section:build: # local: # push: false # auto-push changes to image to dockerhub? googleCloudBuild: projectId: eastern-team-278907 artifacts: # names of the image that Skaffold must maintain # standard google cloud project name + project directory to replace zeuslawyer/<image name> - image: us.gcr.io/<project Id>/<Dockerfile folder>
Use this image name to update the relevant
*-depl.yamlfile's image reference too. -
configure ingress-nginx as the ingress controller + loadbalancer in the GKE cluster. Follow the deployment instructions in https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx/deploy/#gce-gke. Ensure your local Docker context is set to GKE! Running this command will also provision a GCP Load Balancer for the cluster. In Cloud Console go to Networking > Network Services > Load Balancing and see the instance. Click on the Load Balancer to get the IP Address and Port for the Load Balancer.
-
update
/etc/hoststo point to GKE cluster - using the IP address of the Load Balancer from the previous setp. -
restart skaffold. This will take the
*-depl.yamlconfig files and deploy them to GKE. If working, the terminal should show the deployments being started, and the services' console.logs should show up.
**_NOTE_** if you get an error message like this from running skaffold
exiting dev mode because first build failed: couldn't build "us.gcr.io/eastern-team-278907/auth": creating bucket if not exists: getting bucket "eastern-team-278907_cloudbuild": Get "https://storage.googleapis.com/storage/v1/b/eastern-team-278907_cloudbuild?alt=json&prettyPrint=false&projection=full": oauth2: cannot fetch token: 400 Bad Request
Response: {
"error": "invalid_grant",
"error_description": "Bad Request"
}
then run the following two commands, as this error happens without using a service account
gcloud auth application-default revoke
gcloud auth application-default login
// source : https://thornelabs.net/posts/resolve-google-cloud-api-oauth2-cannot-fetch-token-invalid-grant-error.html
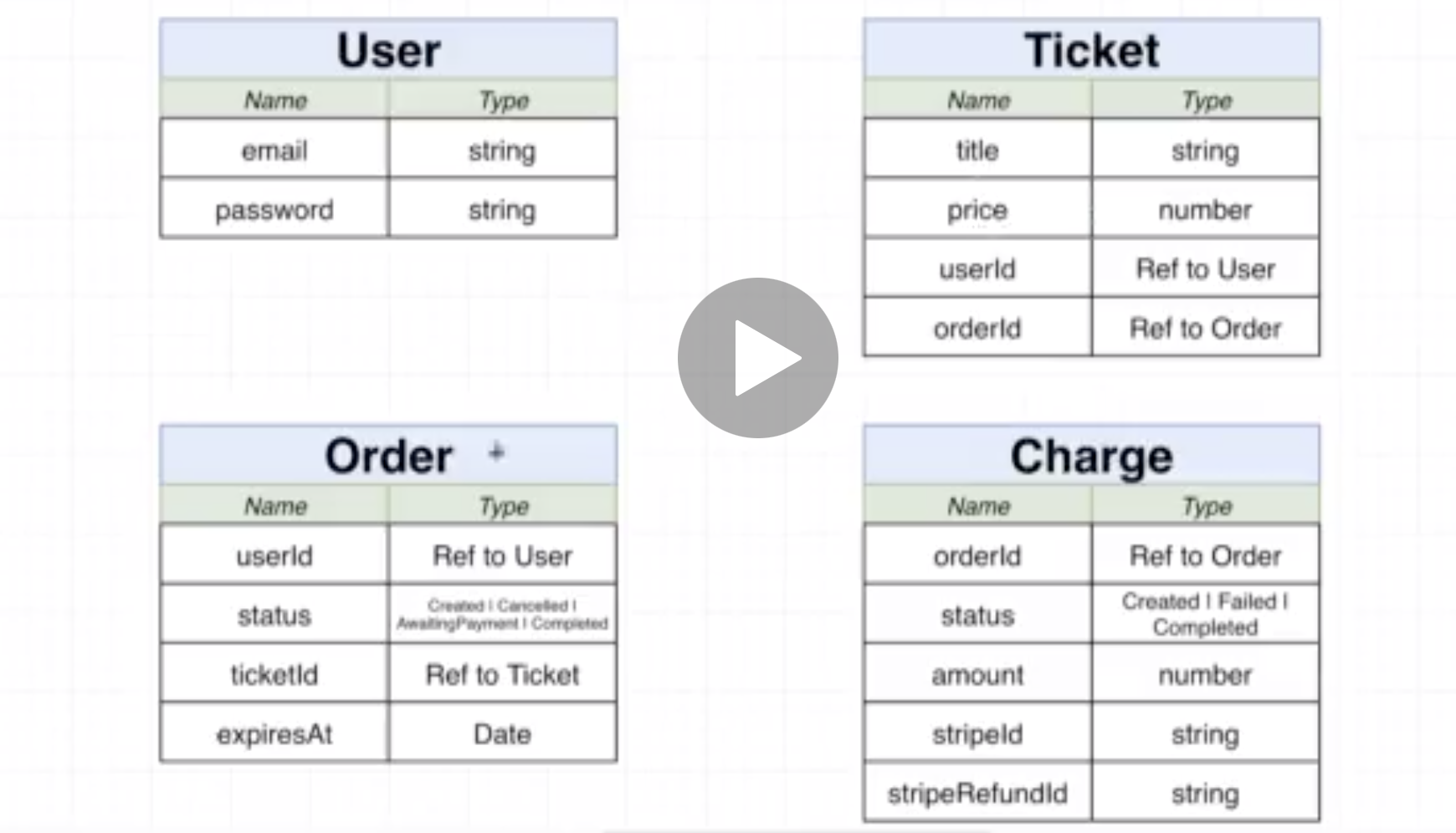
** Mongo Db ** Each service in this app gets its own mongo db instance to avoid sync communication between services (refer to App Design). To set up Mongo DB, it will need to be in its own service which means its got to have its own pod (created and configured as a Kube Deployment).
const connect = async () =>{ mongoose.connect("mongodb://auth-mongo-clusterip:27017/auth", options, callback) }, where /auth is the name of the db and mongoose will create that automatically. The uri includes the port specified in the -depl.yaml config file for the mongo db service attached to the auth service.
sample mini project to play with nats-streaming and the nats streaming node client. Does not use Kube initially. but does access services inside of Kube. Specifically we need to access the nats-depl service.
We do this ** strictly in development mode ** by running a kube port forward command: kubectl port-forward <deployment name> fromport1 : toport 2 where port 1 is the local machine port, and port 2 is target port on the pod.