Lane finding is crucial for developing algorithms for self-driving cars.
The lane-finding algorithm should be robust to changing lighting conditions, weather conditions, other cars/vehicles on the road, curvature of road and type of road itself.
In this project, I will use the computer vision techniques and tools to identify lane lines on the road in an advance way. I will develop pipelines on a series of individual images, and later apply the result to a video stream.
- Compute the camera calibration matrix and distortion coefficients given a set of chessboard images.
- Apply a distortion correction to raw images.
- Use color transforms, gradients, etc., to create a thresholded binary image.
- Apply a perspective transform to rectify binary image ("birds-eye view").
- Detect lane pixels and fit to find the lane boundary.
- Determine the curvature of the lane and vehicle position with respect to center.
- Warp the detected lane boundaries back onto the original image.
- Output visual display of the lane boundaries and numerical estimation of lane curvature and vehicle position.
This project requires Python 3.5 and the following Python libraries installed:
- numpy
- opencv
- moviepy
- pickle
The easiest way to do this is to investigate an image where the lane lines are straight, and find four points lying along the lines that, after perspective transform, make the lines look straight and vertical from a bird's eye view perspective(top down view).
Using HSV color space instead of RGB is easier for us to identify yellow and white lanes in different lighting conditions in the images.
The Sobel operator is at the heart of the Canny edge detection algorithm. Here we use the Sobel operator to an image is a way of taking the derivative of the image in the x or y direction.
Combine several masks from different sources (color, Sobel, thresholding) with different weight together allow us to extract more useful lane image information while filtering out irrelevant parts.
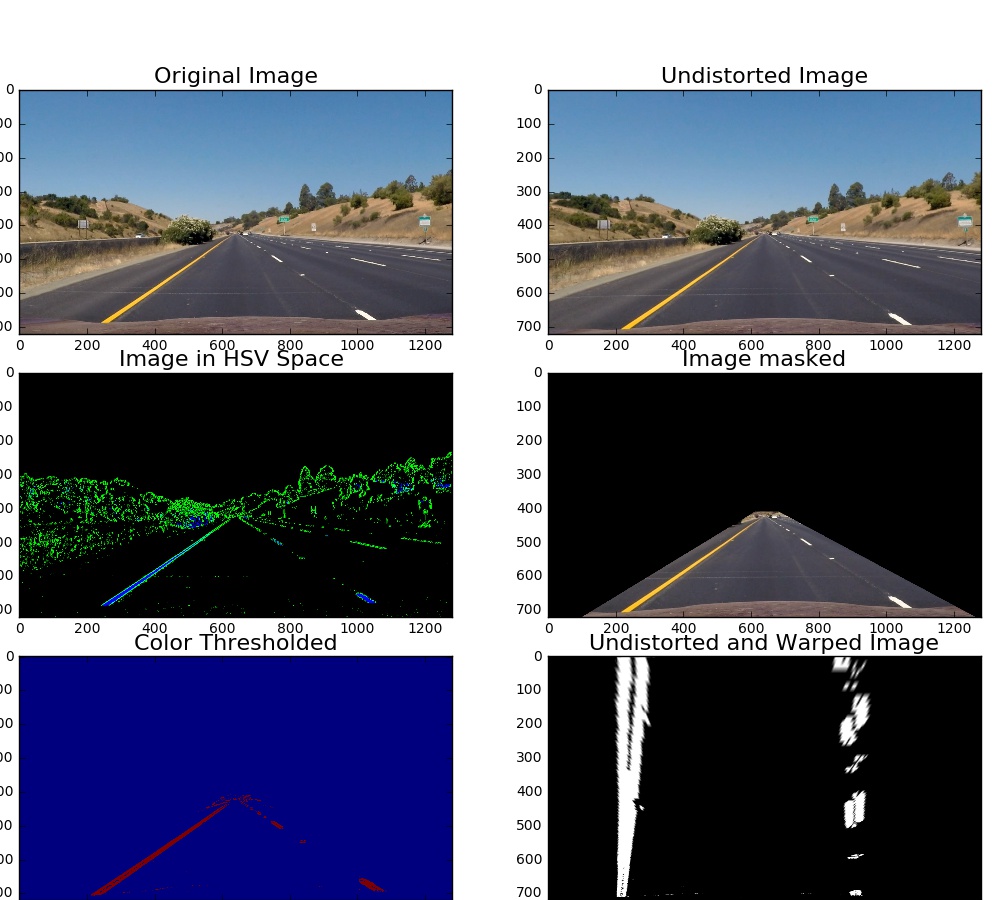
Look at the histogram of the extracted and converted lane images in gray scale, there are clearly two peaks which generated by line. Setting up a threshold will allow us to detect the line and points on the line.
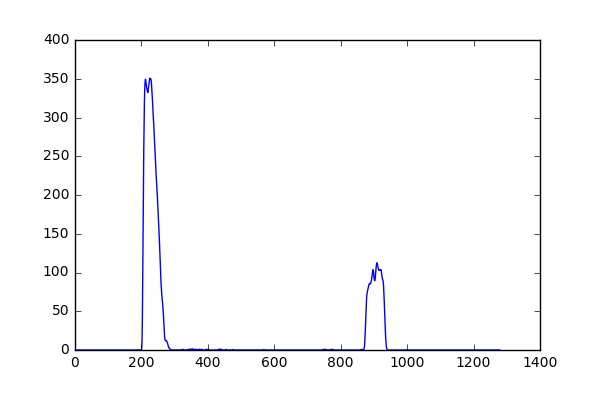
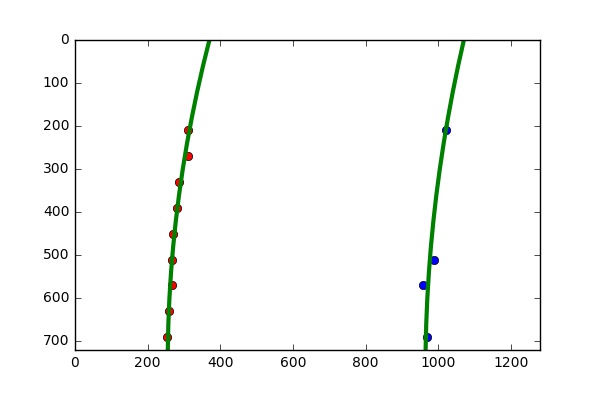
6. Apply polynomial regression to compute the left and right lanes (identify the peak of histogram horizontally from button up)
Fit a second order polynomial to get the curving lane approximation.
f(y) = Ay^2 +By +C
The equation for radius of curvature is based on the best fitted second order polynomial model. R_{curve} = \frac{(1+(2Ay+B^2)^{3/2})}{|2A|}
8. Wrap the fitted rectified image back onto the original image and plot to identify the lane boundaries
Scale the fitted polynomial line in bird view and put it back to the front-camera image, where the green shaded area denotes the current found lane.
9. Build pipeline to process the live stream of road videos from the front camera of the car to identify and analyze lane in real time
Basically all the procedures (1-8) described above are combined to build a lane-finding pipeline to detect the lane in real time video stream.
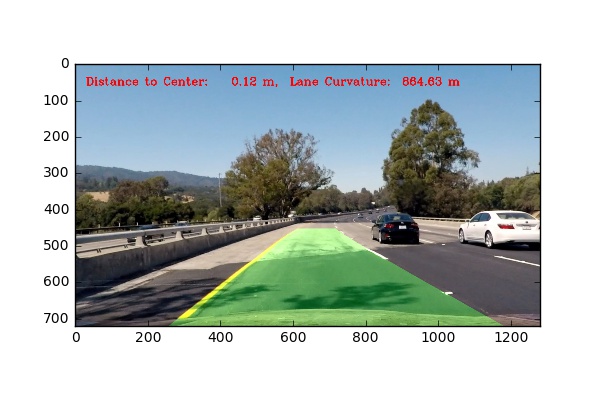
The final output lane finding image includes the following information:
- Detected region of lane on the freeway based on color and gradient thresholding (denoted in green shade)
- Current curvature of the lane based on real-time lane fitting and moving average smooth
- Current distance from the center of the car to the center of the lane
Video Demo: https://youtu.be/cfjSrEUsKJk
- Thresholds are hard coded arbitrary, which can be improved by assigning dynamic values by learning the image/video via machine learning algorithms
- The pipeline does not work well for more complicated images with varying weather/road/lighting conditions. Adding smoothing and image processing steps may be helpful.
- More real-time information may be added for analysis/diagnosis purpose.
- http://docs.opencv.org/2.4/modules/calib3d/doc/camera_calibration_and_3d_reconstruction.html
- https://medium.com/@vivek.yadav/robust-lane-finding-using-advanced-computer-vision-techniques-mid-project-update-540387e95ed3#.xczay6o2c
- https://github.com/kunfengchen/carnd-p4
- https://github.com/Dalaska/CarND-P4-Advance-Lane-Lines
- http://www.intmath.com/applications-differentiation/8-radius-curvature.php

