This package performs KDE operations on multidimensional data to: 1) calculate estimated PDFs (probability distribution functions), and 2) resample new data from those PDFs.
pip install kalepygit clone https://github.com/lzkelley/kalepy.git
pip install -e kalepy/In this case the package can easily be updated by changing into the source directory, pulling, and rebuilding:
cd kalepy
git pull
pip install -e .
# Optional: run unit tests (using the `nosetests` package)
nosetestsimport numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
import kalepy as kale
from kalepy.plot import nbshowGenerate some random data, and its corresponding distribution function
NUM = int(1e4)
np.random.seed(12345)
_d1 = np.random.normal(4.0, 1.0, NUM)
_d2 = np.random.lognormal(0, 0.5, size=NUM)
data = np.concatenate([_d1, _d2])
xx = np.linspace(0.0, 7.0, 100)[1:]
yy = 0.5*np.exp(-(xx - 4.0)**2/2) / np.sqrt(2*np.pi)
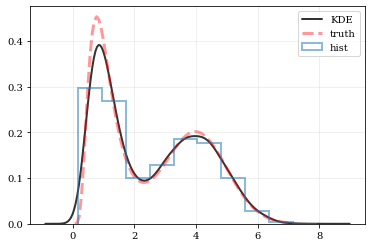
yy += 0.5 * np.exp(-np.log(xx)**2/(2*0.5**2)) / (0.5*xx*np.sqrt(2*np.pi))# Reconstruct the probability-density based on the given data points.
# If `points` aren't provided then `kalepy` automatically generates them
points, density = kale.density(data, probability=True)
# Plot the PDF
plt.plot(points, density, 'k-', lw=2.0, alpha=0.8, label='KDE')
# Plot the "true" PDF
plt.plot(xx, yy, 'r--', alpha=0.4, lw=3.0, label='truth')
# Plot the standard, histogram density estimate
plt.hist(data, density=True, histtype='step', lw=2.0, alpha=0.5, label='hist')
plt.legend()
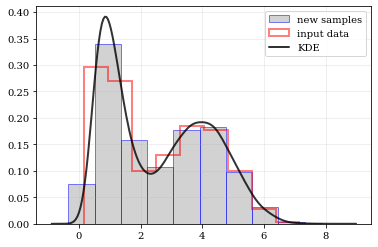
nbshow()Draw a new sample of data-points from the KDE PDF
# Draw new samples from the KDE reconstructed PDF
samples = kale.resample(data)
# Plot new samples
plt.hist(samples, density=True, alpha=0.5, label='new samples', color='0.65', edgecolor='b')
# Plot the KDE reconstructed PDF
plt.plot(points, density, 'k-', lw=2.0, alpha=0.8, label='KDE')
# Plot the "true" PDF
plt.plot(xx, yy, 'r--', alpha=0.4, lw=3.0, label='truth')
plt.legend()
nbshow()# Load some random-ish data
data = kale.utils._random_data_3d_01()
# Construct a KDE
kde = kale.KDE(data)
import kalepy.plot
# Build a corner plot using the `kalepy` plotting submodule
corner = kale.plot.Corner(kde, figsize=[10, 10])
# Data points: red scatter and histograms
corner.plot_data(color='red', scatter=dict(s=10, alpha=0.15))
# KDE reconstructed density-distribution: blue contours and curves
corner.plot_kde(color='blue')
plt.show()/Users/lzkelley/Programs/kalepy/kalepy/utils.py:1082: RuntimeWarning: covariance is not positive-semidefinite.
data = np.random.multivariate_normal(np.zeros_like(sigma), cov, num).T
What if the distributions you're trying to capture have edges in them, like in a uniform distribution between two bounds? Here, the KDE chooses 'reflection' locations based on the extrema of the given data.
# Uniform data (edges at -1 and +1)
np.random.seed(54321)
data = np.random.uniform(-1.0, 1.0, int(1e3))
# Histogram the data, use fixed bin-positions
edges = np.linspace(-1, 1, 12)
plt.hist(data, bins=edges, density=True, alpha=0.5, label='data', color='0.65', edgecolor='k')
# Standard KDE will undershoot just-inside the edges and overshoot outside edges
points, pdf_basic = kale.density(data, probability=True)
plt.plot(points, pdf_basic, 'r--', lw=4.0, alpha=0.5, label='Basic KDE')
# Reflecting KDE keeps probability within given bounds
points, pdf_basic = kale.density(data, reflect=True, probability=True)
plt.plot(points, pdf_basic, 'b-', lw=3.0, alpha=0.75, label='Reflecting KDE')
plt.legend()
nbshow()Explicit reflection locations can also be provided (in any number of dimensions).
# Construct random data, add an artificial 'edge'
np.random.seed(5142)
edge = 1.0
data = np.random.lognormal(sigma=0.5, size=int(3e3))
data = data[data >= edge]
# Histogram the data, use fixed bin-positions
edges = np.linspace(edge, 4, 20)
plt.hist(data, bins=edges, density=True, alpha=0.5, label='data', color='0.65', edgecolor='k')
# Standard KDE with over & under estimates
points, pdf_basic = kale.density(data, probability=True)
plt.plot(points, pdf_basic, 'r--', lw=4.0, alpha=0.5, label='Basic KDE')
# Reflecting KDE setting the lower-boundary to the known value
# There is no upper-boundary when `None` is given.
points, pdf_basic = kale.density(data, reflect=[edge, None], probability=True)
plt.plot(points, pdf_basic, 'b-', lw=3.0, alpha=0.5, label='Reflecting KDE')
plt.gca().set_xlim(edge - 0.5, 3)
plt.legend()
nbshow()