为了学习以及分享个人学习心得,会在该仓库中添加一些的readme说明以及代码注释进行模块讲解和代码分析(可以看下提交记录),以及实际训练和测试过程。个人拓展说明放在原作者README.md最后个人学习和实践记录 。
For a good and more up-to-date implementation for faster/mask RCNN with multi-gpu support, please see the example in TensorPack here.
A Tensorflow implementation of faster RCNN detection framework by Xinlei Chen (xinleic@cs.cmu.edu). This repository is based on the python Caffe implementation of faster RCNN available here.
Note: Several minor modifications are made when reimplementing the framework, which give potential improvements. For details about the modifications and ablative analysis, please refer to the technical report An Implementation of Faster RCNN with Study for Region Sampling. If you are seeking to reproduce the results in the original paper, please use the official code or maybe the semi-official code. For details about the faster RCNN architecture please refer to the paper Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks.
The current code supports VGG16, Resnet V1 and Mobilenet V1 models. We mainly tested it on plain VGG16 and Resnet101 (thank you @philokey!) architecture. As the baseline, we report numbers using a single model on a single convolution layer, so no multi-scale, no multi-stage bounding box regression, no skip-connection, no extra input is used. The only data augmentation technique is left-right flipping during training following the original Faster RCNN. All models are released.
With VGG16 (conv5_3):
- Train on VOC 2007 trainval and test on VOC 2007 test, 70.8.
- Train on VOC 2007+2012 trainval and test on VOC 2007 test (R-FCN schedule), 75.7.
- Train on COCO 2014 trainval35k and test on minival (Iterations: 900k/1190k), 30.2.
With Resnet101 (last conv4):
- Train on VOC 2007 trainval and test on VOC 2007 test, 75.7.
- Train on VOC 2007+2012 trainval and test on VOC 2007 test (R-FCN schedule), 79.8.
- Train on COCO 2014 trainval35k and test on minival (900k/1190k), 35.4.
More Results:
- Train Mobilenet (1.0, 224) on COCO 2014 trainval35k and test on minival (900k/1190k), 21.8.
- Train Resnet50 on COCO 2014 trainval35k and test on minival (900k/1190k), 32.4.
- Train Resnet152 on COCO 2014 trainval35k and test on minival (900k/1190k), 36.1.
Approximate baseline setup from FPN (this repository does not contain training code for FPN yet):
- Train Resnet50 on COCO 2014 trainval35k and test on minival (900k/1190k), 34.2.
- Train Resnet101 on COCO 2014 trainval35k and test on minival (900k/1190k), 37.4.
- Train Resnet152 on COCO 2014 trainval35k and test on minival (900k/1190k), 38.2.
Note:
- Due to the randomness in GPU training with Tensorflow especially for VOC, the best numbers are reported (with 2-3 attempts) here. According to my experience, for COCO you can almost always get a very close number (within ~0.2%) despite the randomness.
- The numbers are obtained with the default testing scheme which selects region proposals using non-maximal suppression (TEST.MODE nms), the alternative testing scheme (TEST.MODE top) will likely result in slightly better performance (see report, for COCO it boosts 0.X AP).
- Since we keep the small proposals (< 16 pixels width/height), our performance is especially good for small objects.
- We do not set a threshold (instead of 0.05) for a detection to be included in the final result, which increases recall.
- Weight decay is set to 1e-4.
- For other minor modifications, please check the report. Notable ones include using
crop_and_resize, and excluding ground truth boxes in RoIs during training. - For COCO, we find the performance improving with more iterations, and potentially better performance can be achieved with even more iterations.
- For Resnets, we fix the first block (total 4) when fine-tuning the network, and only use
crop_and_resizeto resize the RoIs (7x7) without max-pool (which I find useless especially for COCO). The final feature maps are average-pooled for classification and regression. All batch normalization parameters are fixed. Learning rate for biases is not doubled. - For Mobilenets, we fix the first five layers when fine-tuning the network. All batch normalization parameters are fixed. Weight decay for Mobilenet layers is set to 4e-5.
- For approximate FPN baseline setup we simply resize the image with 800 pixels, add 32^2 anchors, and take 1000 proposals during testing.
- Check out here/here/here for the latest models, including longer COCO VGG16 models and Resnet ones.
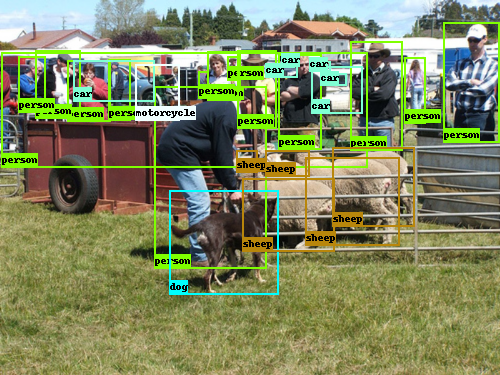 |
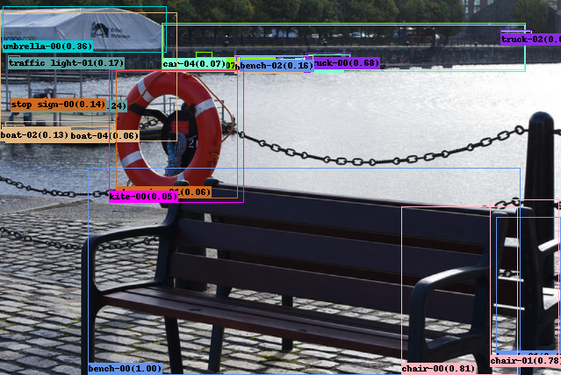 |
|---|---|
| Displayed Ground Truth on Tensorboard | Displayed Predictions on Tensorboard |
Additional features not mentioned in the report are added to make research life easier:
- Support for train-and-validation. During training, the validation data will also be tested from time to time to monitor the process and check potential overfitting. Ideally training and validation should be separate, where the model is loaded every time to test on validation. However I have implemented it in a joint way to save time and GPU memory. Though in the default setup the testing data is used for validation, no special attempts is made to overfit on testing set.
- Support for resuming training. I tried to store as much information as possible when snapshoting, with the purpose to resume training from the latest snapshot properly. The meta information includes current image index, permutation of images, and random state of numpy. However, when you resume training the random seed for tensorflow will be reset (not sure how to save the random state of tensorflow now), so it will result in a difference. Note that, the current implementation still cannot force the model to behave deterministically even with the random seeds set. Suggestion/solution is welcome and much appreciated.
- Support for visualization. The current implementation will summarize ground truth boxes, statistics of losses, activations and variables during training, and dump it to a separate folder for tensorboard visualization. The computing graph is also saved for debugging.
- A basic Tensorflow installation. The code follows r1.2 format. If you are using r1.0, please check out the r1.0 branch to fix the slim Resnet block issue. If you are using an older version (r0.1-r0.12), please check out the r0.12 branch. While it is not required, for experimenting the original RoI pooling (which requires modification of the C++ code in tensorflow), you can check out my tensorflow fork and look for
tf.image.roi_pooling. - Python packages you might not have:
cython,opencv-python,easydict(similar to py-faster-rcnn). Foreasydictmake sure you have the right version. I use 1.6. - Docker users: Since the recent upgrade, the docker image on docker hub (https://hub.docker.com/r/mbuckler/tf-faster-rcnn-deps/) is no longer valid. However, you can still build your own image by using dockerfile located at
dockerfolder (cuda 8 version, as it is required by Tensorflow r1.0.) And make sure following Tensorflow installation to install and use nvidia-docker[https://github.com/NVIDIA/nvidia-docker]. Last, after launching the container, you have to build the Cython modules within the running container.
- Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/endernewton/tf-faster-rcnn.git- Update your -arch in setup script to match your GPU
cd tf-faster-rcnn/lib
# Change the GPU architecture (-arch) if necessary
vim setup.py| GPU model | Architecture |
|---|---|
| TitanX (Maxwell/Pascal) | sm_52 |
| GTX 960M | sm_50 |
| GTX 1080 (Ti) | sm_61 |
| Grid K520 (AWS g2.2xlarge) | sm_30 |
| Tesla K80 (AWS p2.xlarge) | sm_37 |
Note: You are welcome to contribute the settings on your end if you have made the code work properly on other GPUs. Also even if you are only using CPU tensorflow, GPU based code (for NMS) will be used by default, so please set USE_GPU_NMS False to get the correct output.
- Build the Cython modules
make clean
make
cd ..- Install the Python COCO API. The code requires the API to access COCO dataset.
cd data
git clone https://github.com/pdollar/coco.git
cd coco/PythonAPI
make
cd ../../..Please follow the instructions of py-faster-rcnn here to setup VOC and COCO datasets (Part of COCO is done). The steps involve downloading data and optionally creating soft links in the data folder. Since faster RCNN does not rely on pre-computed proposals, it is safe to ignore the steps that setup proposals.
If you find it useful, the data/cache folder created on my side is also shared here.
- Download pre-trained model
# Resnet101 for voc pre-trained on 07+12 set
./data/scripts/fetch_faster_rcnn_models.shNote: if you cannot download the models through the link, or you want to try more models, you can check out the following solutions and optionally update the downloading script:
- Create a folder and a soft link to use the pre-trained model
NET=res101
TRAIN_IMDB=voc_2007_trainval+voc_2012_trainval
mkdir -p output/${NET}/${TRAIN_IMDB}
cd output/${NET}/${TRAIN_IMDB}
ln -s ../../../data/voc_2007_trainval+voc_2012_trainval ./default
cd ../../..- Demo for testing on custom images
# at repository root
GPU_ID=0
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=${GPU_ID} ./tools/demo.pyNote: Resnet101 testing probably requires several gigabytes of memory, so if you encounter memory capacity issues, please install it with CPU support only. Refer to Issue 25.
- Test with pre-trained Resnet101 models
GPU_ID=0
./experiments/scripts/test_faster_rcnn.sh $GPU_ID pascal_voc_0712 res101Note: If you cannot get the reported numbers (79.8 on my side), then probably the NMS function is compiled improperly, refer to Issue 5.
-
Download pre-trained models and weights. The current code support VGG16 and Resnet V1 models. Pre-trained models are provided by slim, you can get the pre-trained models here and set them in the
data/imagenet_weightsfolder. For example for VGG16 model, you can set up like:mkdir -p data/imagenet_weights cd data/imagenet_weights wget -v http://download.tensorflow.org/models/vgg_16_2016_08_28.tar.gz tar -xzvf vgg_16_2016_08_28.tar.gz mv vgg_16.ckpt vgg16.ckpt cd ../..
For Resnet101, you can set up like:
mkdir -p data/imagenet_weights cd data/imagenet_weights wget -v http://download.tensorflow.org/models/resnet_v1_101_2016_08_28.tar.gz tar -xzvf resnet_v1_101_2016_08_28.tar.gz mv resnet_v1_101.ckpt res101.ckpt cd ../..
-
Train (and test, evaluation)
./experiments/scripts/train_faster_rcnn.sh [GPU_ID] [DATASET] [NET]
# GPU_ID is the GPU you want to test on
# NET in {vgg16, res50, res101, res152} is the network arch to use
# DATASET {pascal_voc, pascal_voc_0712, coco} is defined in train_faster_rcnn.sh
# Examples:
./experiments/scripts/train_faster_rcnn.sh 0 pascal_voc vgg16
./experiments/scripts/train_faster_rcnn.sh 1 coco res101Note: Please double check you have deleted soft link to the pre-trained models before training. If you find NaNs during training, please refer to Issue 86. Also if you want to have multi-gpu support, check out Issue 121.
- Visualization with Tensorboard
tensorboard --logdir=tensorboard/vgg16/voc_2007_trainval/ --port=7001 &
tensorboard --logdir=tensorboard/vgg16/coco_2014_train+coco_2014_valminusminival/ --port=7002 &- Test and evaluate
./experiments/scripts/test_faster_rcnn.sh [GPU_ID] [DATASET] [NET]
# GPU_ID is the GPU you want to test on
# NET in {vgg16, res50, res101, res152} is the network arch to use
# DATASET {pascal_voc, pascal_voc_0712, coco} is defined in test_faster_rcnn.sh
# Examples:
./experiments/scripts/test_faster_rcnn.sh 0 pascal_voc vgg16
./experiments/scripts/test_faster_rcnn.sh 1 coco res101- You can use
tools/reval.shfor re-evaluation
By default, trained networks are saved under:
output/[NET]/[DATASET]/default/
Test outputs are saved under:
output/[NET]/[DATASET]/default/[SNAPSHOT]/
Tensorboard information for train and validation is saved under:
tensorboard/[NET]/[DATASET]/default/
tensorboard/[NET]/[DATASET]/default_val/
The default number of training iterations is kept the same to the original faster RCNN for VOC 2007, however I find it is beneficial to train longer (see report for COCO), probably due to the fact that the image batch size is one. For VOC 07+12 we switch to a 80k/110k schedule following R-FCN. Also note that due to the nondeterministic nature of the current implementation, the performance can vary a bit, but in general it should be within ~1% of the reported numbers for VOC, and ~0.2% of the reported numbers for COCO. Suggestions/Contributions are welcome.
If you find this implementation or the analysis conducted in our report helpful, please consider citing:
@article{chen17implementation,
Author = {Xinlei Chen and Abhinav Gupta},
Title = {An Implementation of Faster RCNN with Study for Region Sampling},
Journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:1702.02138},
Year = {2017}
}
Or for a formal paper, Spatial Memory Network:
@article{chen2017spatial,
title={Spatial Memory for Context Reasoning in Object Detection},
author={Chen, Xinlei and Gupta, Abhinav},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.04224},
year={2017}
}
For convenience, here is the faster RCNN citation:
@inproceedings{renNIPS15fasterrcnn,
Author = {Shaoqing Ren and Kaiming He and Ross Girshick and Jian Sun},
Title = {Faster {R-CNN}: Towards Real-Time Object Detection
with Region Proposal Networks},
Booktitle = {Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems ({NIPS})},
Year = {2015}
}
r-cnn介绍
spp介绍
fast r-cnn介绍
faster r-cnn介绍
目标检测评估指标P-R曲线
ubuntu18.04+GeForce GTX 1070+anaconda2(python2.7)+cuda10.0
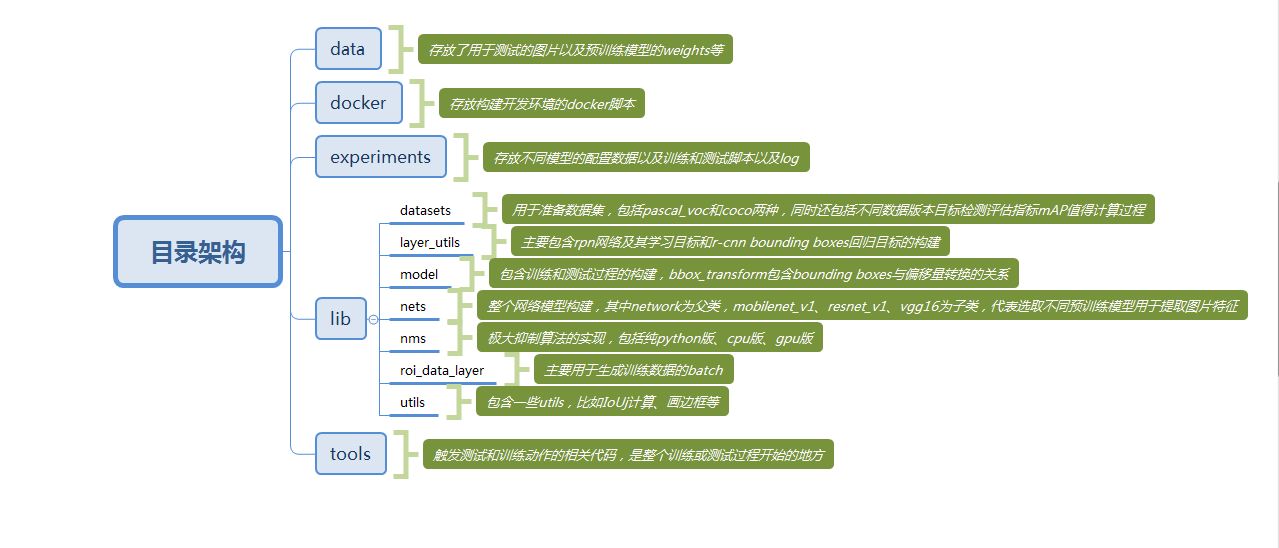
使用pycharm,为了查看代码和运行方便,我把原作者的代码架构改成了pycharm工程,直接使用pycharm打开根目录即可。
- 参考原作者的步骤,测试demo程序
- 编译lib目录中的cython库,具体说明见nms讲解。
- 安装coco python api
cd data git clone https://github.com/pdollar/coco.git cd coco/PythonAPI make all make install # 我本地把coco python api 安装了一下,为了方便pycharm工程导入这些api。 cd ../../..
- 下载已经训练好的模型,在如下链接https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B1_fAEgxdnvJSmF3YUlZcHFqWTQ 中找到voc_0712_80k-110k.tgz,下载到本地。
- 将模型参数saver放到特定目录,创建符号链接:
NET=res101 TRAIN_IMDB=voc_2007_trainval+voc_2012_trainval mkdir -p output/${NET}/${TRAIN_IMDB} cd output/${NET}/${TRAIN_IMDB} ln -s ../../../data/voc_2007_trainval+voc_2012_trainval ./default cd ../../..
- 运行demo.py
GPU_ID=0 export PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:./ CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=${GPU_ID} ./tools/demo.py --net=res101 --dataset=pascal_voc_0712
- 参考原作者的步骤,测试已训练好的faster-rcnn模型
- 下载VOC2007训练和测试数据集
进官网中看下数据集介绍:
http://host.robots.ox.ac.uk/pascal/VOC/voc2007/index.html
下载训练和测试数据集:
http://host.robots.ox.ac.uk/pascal/VOC/voc2007/VOCtrainval_06-Nov-2007.tar
http://host.robots.ox.ac.uk/pascal/VOC/voc2007/VOCtest_06-Nov-2007.tar - 下载好后,两个VOC2007数据集目录合并,放到data/VOCdevkit2007目录。
- 回到代码根目录,mkdir -p data/VOCdevkit2007/results/VOC2007/Main/
- 运行测试脚本
GPU_ID=0 export PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:./ ./experiments/scripts/test_faster_rcnn.sh $GPU_ID pascal_voc_0712 res101
- 实际运行的代码是test_net.py,并且指定使用VOC2007的测试集来测试已经训练好的res101-faster-rcnn模型,运行完结果如下:
AP for aeroplane = 0.8303 AP for bicycle = 0.8697 AP for bird = 0.8133 AP for boat = 0.7405 AP for bottle = 0.6851 AP for bus = 0.8764 AP for car = 0.8801 AP for cat = 0.8831 AP for chair = 0.6247 AP for cow = 0.8679 AP for diningtable = 0.7061 AP for dog = 0.8855 AP for horse = 0.8731 AP for motorbike = 0.8299 AP for person = 0.8270 AP for pottedplant = 0.5314 AP for sheep = 0.8109 AP for sofa = 0.7767 AP for train = 0.8369 AP for tvmonitor = 0.7936 Mean AP = 0.7971
- 下载VOC2007训练和测试数据集
- 参考原作者的步骤,训练和测试faster-rcnn模型
- 使用vgg16模型来训练faster-rcnn
- 下载vgg16预训练模型
mkdir -p data/imagenet_weights cd data/imagenet_weights wget -v http://download.tensorflow.org/models/vgg_16_2016_08_28.tar.gz tar -xzvf vgg_16_2016_08_28.tar.gz mv vgg_16.ckpt vgg16.ckpt cd ../..
- 执行训练脚本
./experiments/scripts/train_faster_rcnn.sh [GPU_ID] [DATASET] [NET] # GPU_ID is the GPU you want to test on # DATASET {pascal_voc, pascal_voc_0712, coco} is defined in train_faster_rcnn.sh # NET in {vgg16, res50, res101, res152} is the network arch to use export PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:./ ./experiments/scripts/train_faster_rcnn.sh 0 pascal_voc vgg16
- 实际执行trainval_net.py和test_net.py程序,并且指定使用VOC2007数据集来训练和测试vgg16-faster-rcnn模型,运行完结果如下:
AP for aeroplane = 0.6968 AP for bicycle = 0.7873 AP for bird = 0.7050 AP for boat = 0.6009 AP for bottle = 0.5785 AP for bus = 0.7850 AP for car = 0.8302 AP for cat = 0.8435 AP for chair = 0.5122 AP for cow = 0.7476 AP for diningtable = 0.6596 AP for dog = 0.8117 AP for horse = 0.8370 AP for motorbike = 0.7428 AP for person = 0.7827 AP for pottedplant = 0.4434 AP for sheep = 0.7119 AP for sofa = 0.6474 AP for train = 0.7489 AP for tvmonitor = 0.7233 Mean AP = 0.7098 - 利用训练好的vgg16-faster-rcnn模型来检测demo中的物体
GPU_ID=0 export PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:./ CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=${GPU_ID} ./tools/demo.py --net=vgg16 --dataset=pascal_voc
- 使用resnet101模型来训练faster-rcnn
- 下载resnet101预训练模型
mkdir -p data/imagenet_weights cd data/imagenet_weights wget -v http://download.tensorflow.org/models/resnet_v1_101_2016_08_28.tar.gz tar -xzvf resnet_v1_101_2016_08_28.tar.gz mv resnet_v1_101.ckpt resnet101.ckpt cd ../..
- 执行训练脚本
./experiments/scripts/train_faster_rcnn.sh [GPU_ID] [DATASET] [NET] # GPU_ID is the GPU you want to test on # DATASET {pascal_voc, pascal_voc_0712, coco} is defined in train_faster_rcnn.sh # NET in {vgg16, res50, res101, res152} is the network arch to use export PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:./ ./experiments/scripts/train_faster_rcnn.sh 0 pascal_voc res101
- 实际执行trainval_net.py和test_net.py程序,并且指定使用VOC2007数据集来训练和测试resnet101-faster-rcnn模型,运行完结果如下:
AP for aeroplane = 0.7400 AP for bicycle = 0.8104 AP for bird = 0.7549 AP for boat = 0.6382 AP for bottle = 0.6278 AP for bus = 0.7929 AP for car = 0.8138 AP for cat = 0.8655 AP for chair = 0.5928 AP for cow = 0.8243 AP for diningtable = 0.7003 AP for dog = 0.8609 AP for horse = 0.8631 AP for motorbike = 0.7766 AP for person = 0.7926 AP for pottedplant = 0.4562 AP for sheep = 0.7539 AP for sofa = 0.7535 AP for train = 0.7839 AP for tvmonitor = 0.7521 Mean AP = 0.7477 - 利用训练好的resnet101-faster-rcnn模型来检测demo中的物体
这里注意需要修改一下demo.py中的第40行 NETS = {'vgg16': ('vgg16_faster_rcnn_iter_70000.ckpt',),'res101': ('res101_faster_rcnn_iter_110000.ckpt',)} 改为 NETS = {'vgg16': ('vgg16_faster_rcnn_iter_70000.ckpt',),'res101': ('res101_faster_rcnn_iter_70000.ckpt',)}GPU_ID=0 export PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:./ CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=${GPU_ID} ./tools/demo.py --net=res101 --dataset=pascal_voc
- 使用vgg16模型来训练faster-rcnn