All Javascript and style packages are respectively managed by npm and bower.
npm install
bower install // bower install --allow-root
gulpOpen /src/scripts/route.coffee ,add following code to create a new state.
.state 'module1'
,
url: 'page1'
templateUrl: '/modules/page1/index.html'
controller: 'page1Ctrl'create your page(coffee,jade,less) in /src/modules/page1
page1
├── index.ctrl.coffee
├── index.jade
└── index.less
page1/index.ctrl.coffee:
angular.module 'Seed'
.classy.controller
name: 'page1Ctrl'
inject: [
'$scope'
'$rootScope'
'$state'
]
initScope: ->
hello: 'This is a new page.'
data: null
init: -> null
methods: nullpage1/index.jade:
.page1
{{hello}}page1/index.less:
.page1 {
text-align: center;
}Add page1's js file and css file to this app
src/modules/mod-index.jade:
script(src='./modules/page1/index.ctrl.js')
src/modules/mod-styles.less:
@import "./page1/index";
Use gulp to build app, then open http://localhost:9000/page1 in browser.
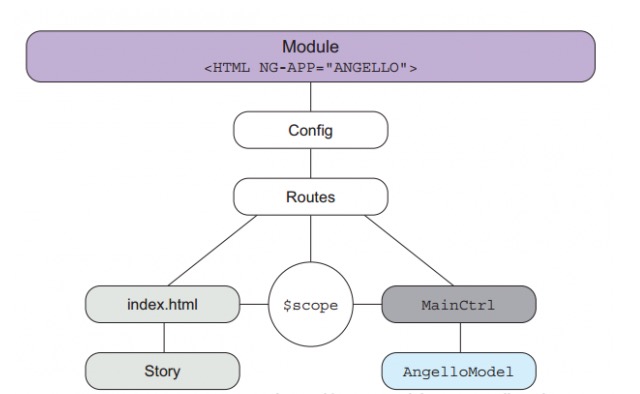
This front-end app is based on AngularJs. All features and functions of Angular are availble to use. See the Angular developer API reference
Coding in a simple and efficient way, CoffeeScript, Jade and LessCSS are employed in this framework as a improved version of Javascript, Html and CSS.
- CoffeeScript http://coffee-script.org/
- Jade http://jade-lang.com/
- LessCSS http://lesscss.org/
Here is an example:
1.Add these code in page1/index.jade:
.page1
p {{hello}}
label
| Name:
input(type='text',ng-model='user.name')
button(ng-click='btnFunc()') Button
p user.name = {{user.name}}2.Create btnFunc() for the Button in page1/index.ctrl.coffee:
angular.module 'Seed'
.classy.controller
name: 'page1Ctrl'
inject: [
'$scope'
'$rootScope'
'$state'
]
initScope: ->
hello: 'This is a new page.'
user:
name: null
data: null
init: -> null
methods:
btnFunc: () ->
@scope.user.name = 'button clicked.'Angular Classy are employed to make controllers more structured and prescriptive. See more details on Angular-classy.
- name : Controller unique name.
- inject : An array of all dependencies.
- initScope : All data present in the view layer [Not required]
- data : All data cached in controller
- init : An init method for your initialization code.
- methods : Controller methods are defined inside of the methods object.
1.Run backend app in /back-end/
python index.py test url http://localhost:5000/api/testGET?test=123 in browser and you will get
{"message": "success", "result": "123_GET_processed"}2.add testGET() and testPOST() functions in src/scripts/services/api/user.coffee
angular.module 'Seed'
.factory 'apiUserBase', [
'Restangular'
'CONFIG'
(
Restangular
CONFIG
) ->
baseURL = "#{CONFIG.BASEURL.API_SEED}"
Restangular.withConfig (RestangularConfigurer) ->
RestangularConfigurer.setBaseUrl baseURL
]
.factory 'apiUser', [
'apiUserBase'
'AUTH'
(
apiUserBase
AUTH
) ->
testGET: ->
meta = apiUserBase.one 'api'
.one 'testGET'
new Promise (resolve, reject) ->
meta.get()
.then (result) ->
resolve result
, (res) ->
reject res
testPOST: ->
meta = apiUserBase.one 'api'
.all 'testPOST'
new Promise (resolve, reject) ->
meta.post()
.then (result) ->
resolve result
, (res) ->
reject res
] - Restangular on GitHub (Official Documentation) - AngularJS service to handle Rest API Restful Resources properly and easily
- 《AngularJS权威教程_AriLerner著_涵盖1.2.x_人民邮电出版社》 page 142 "15.13 使用 Restangular"
- testGET() and testPOST() return
new Promise(...). - Promises are a concurrency primitive with a proven track record and language integration in most modern programming languages.
Add API service file to this app
src/scripts/services/mod-index.jade:
script(src="./scripts/services/api/user.js")
src/modules/page1/index.ctrl.coffee:
angular.module 'Seed'
.classy.controller
name: 'page1Ctrl'
inject: [
'$scope'
'$rootScope'
'$state'
'apiUser'
]
initScope: ->
hello: 'This is a new page.'
user:
name: null
data:
apiUser: 'apiUser'
init: -> null
methods:
btnFunc: () ->
@$scope.user.name = 'button clicked.'
callGET: (arg) ->
Promise.bind @
.then ->
@apiUser.testGET arg
.then (out)->
@$scope.user.name = out.result
.catch (err) ->
console.log err
callPOST: (arg) ->
Promise.bind @
.then ->
@apiUser.testPOST arg
.then (out)->
@$scope.user.name = out.result
.catch (err) ->
console.log errapiUser: 'apiUser'indataequalsthis.apiUser = this.$scope.apiUserPromise.bind @is the most efficient way of utilizing this with promises.