Dense visual descriptor learning for wide-baseline matching, using the idea of "descriptor space". The project organization was inspired by maskrcnn-benchmark.
Visual descriptor is an important topic in computer vision. For establishing robust correspondences between images, the extracted descriptors should be invariant to changes like illumination, viewpoint and scale, etc. However, deep neural networks are intrinsically not invariant to scale and viewpoint changes, and forcing these invariance can be hard. Further, as we revealed, this can even be harmful to training.
In this work, we do not train the network directly to enforce scale invariance. Instead, we build a "descriptor-space", which is descriptors extracted from different layers of a network. These descriptors are then used for matching.
This project uses Python3 and Pytorch. First, you will need to install package dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt
We use hard negative mining from UCN. This is written in cuda code, so you have to first bulid this. Run the following:
cd lib/utils/hard_mining
python setup.py build_ext --inplace
There might be some warnings.
For this work, we use MSCOCO2017 for training and HPatches full sequences for evaluation. The dataset should be downloaded under data and named MSCOCO2017 and HPATCHES respectively. The directory structure should look like:
├── data
│ ├── HPATCHES
│ │ ├── i_ajuntament
│ │ ├── i_autannes
│ │ ├── ...
│ │ ├── v_abstract
│ │ ├── v_adam
│ │ ├── ...
│ └── MSCOCO2017
│ ├── annotations
│ │ ├── stuff_train2017_pixelmaps
│ │ └── stuff_val2017_pixelmaps
│ ├── test2017
│ ├── train2017
│ └── val2017
During training, random homographies are sampled and applied to COCO images, and so each training example contain a pair of images and a homography H.
For evaluation, we tested on hpatches viewpoint and illumination dataset. We sample random keypoints use PCK (percentage of correct keypoints) with a threshold of 5 as metrics.
The baseline network called MSNetV0 uses Resnet18. We simply extract descriptors at C3 layer. To train this network, run
python run.py --config ./configs/msnet_v0.yaml
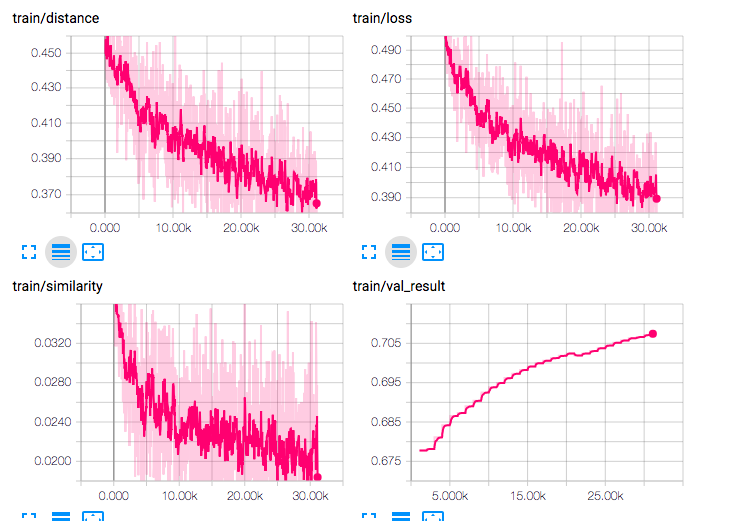
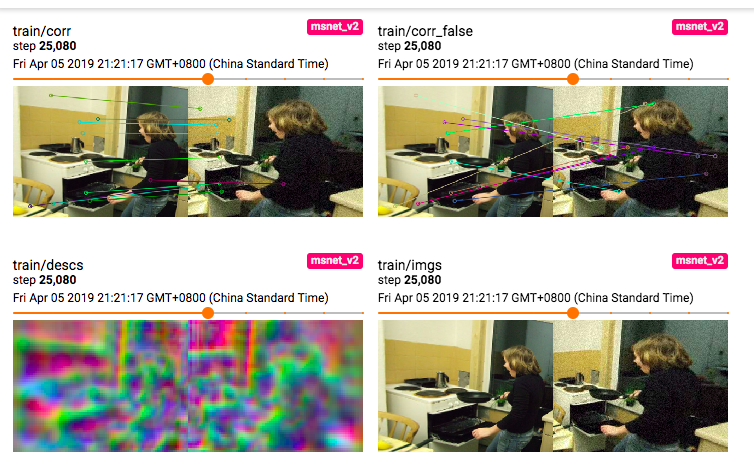
It is possible to visualize the losses, validation results, and descriptor visualization using tensorboardX. At project root, run
tensorboard --logdir==logs --port==6006
and visualize the results at port 6006 of your host, in the browser. Some example visualizations:
The checkpoints will be automatically saved under data/model/msnet_v0 directory. You are free to stop training and resume later. The checkpoints will be automatically loaded. For testing, last checkpoint will also be loaded.
We provide code for comparing three basic descriptors:
MSNetV0, our baseline networkSuperPointDAISY
To test these on hpatches viewpoint dataset, run the following respectively:
python run.py --config ./configs/msnet_v0.yaml --test
python run.py --config ./configs/superpoing.yaml --test
python run.py --config ./configs/daisy.yaml --test
Note for superpoint, you will first have to download the pretrained model weight from here to data/model.
Available test sets are HPATCHES, HPATCHES_VIEWPOINT, and HPATCHES_ILLUM. To test on a specific dataset, like HPATCHES_ILLUM, run
python run.py --config ./configs/msnet_v0.yaml --test DATASET.TEST HPATCHES_ILLUM
Here we provide some testing results with MSNetV0, Superpoint, DAISY, and two of our new networks based on descriptor space called MSNetV1 and MSNetV2, on hpatches, hpatches viewpoint and hpatches illumination dataset.
| All | Viewpoint | Illumination | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DAISY | 0.592 | 0.535 | 0.647 |
| SuperPoint | 0.646 | 0.592 | 0.702 |
| MSNetV0 | 0.626 | 0.619 | 0.644 |
| MSNetV1 | 0.742 | 0.732 | 0.752 |
| MSNetV2 | 0.690 | 0.719 | 0.657 |