The application offers a Quick Look Extension for macOS 10.15 Catalina and later for previewing source files. Inside it uses Highlight to render source code with syntax highlighting.
Syntax Highlightis distributed in the hope that it will be useful but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY.
- Installation
- Enable the Quick Look extension
- File format management
- Application settings
- Command line interface
- Add support to a custom format
- FAQ
- Known bugs
- Note for developers
- Credits
You can install the application in various ways. When the main application is launched it automatically checks for updates.
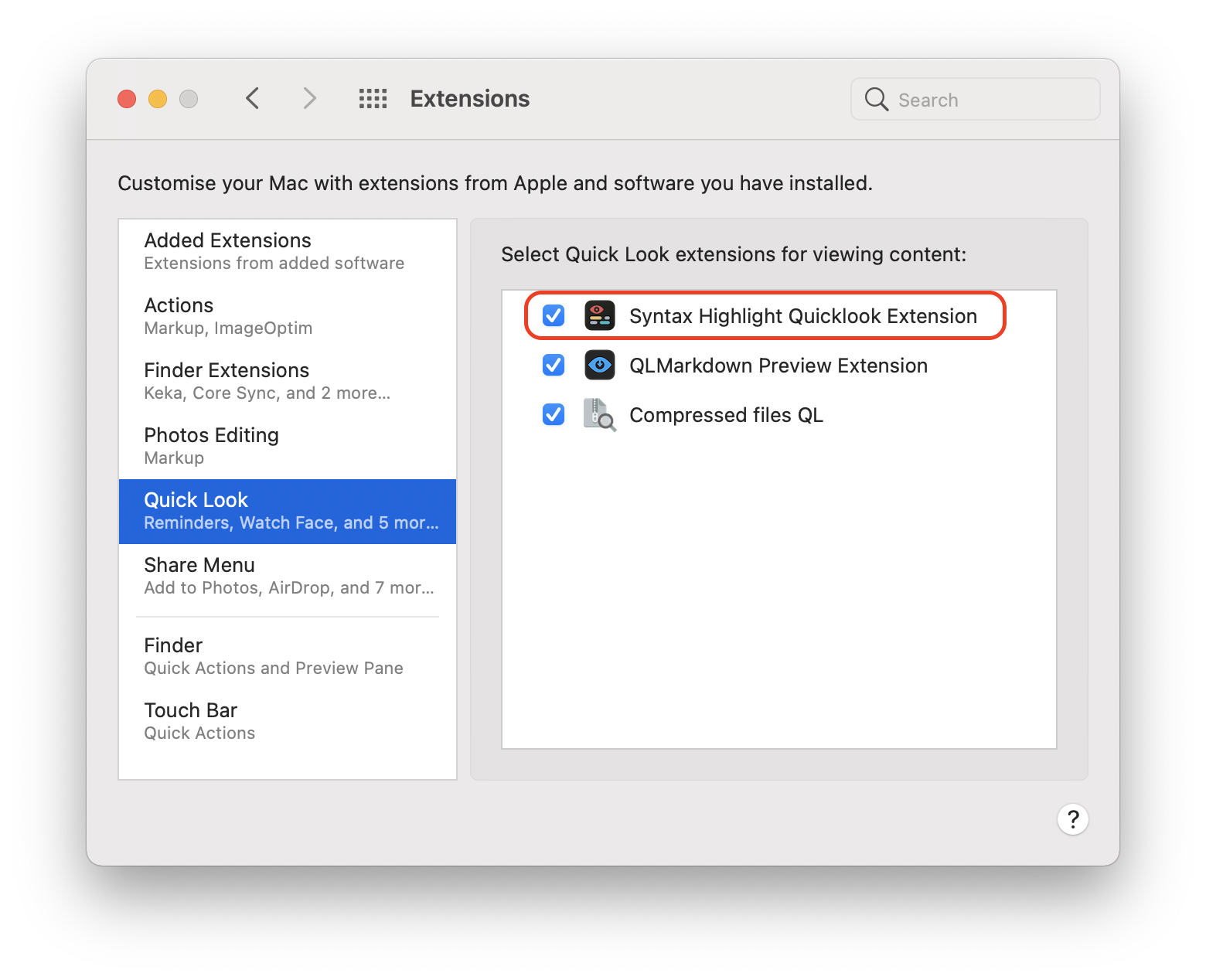
After installation, the application must be launched at least once to allow the system to detect the Quick Look extension. See below for instructions on how to enable the Quick Look extension.
Head over to the releases page to view the latest version. Move Syntax Highlight.app into the Applications folder.
Syntax Highlight can also be installed via Homebrew Cask. If you have not installed Homebrew, follow the simple instructions here. After that, install the current version of Syntax Highlight with the following command:
brew install --cask --no-quarantine syntax-highlightThe precompiled app is not notarized or signed, so the first time you run the app the system may show a warning about the impossibility to check for malicious software.
To fix, you can launch the app with right-click (or Control-click) on the app icon and choose the open action.
You can also execute this command from the terminal:
xattr -r -d com.apple.quarantine "FULL PATH OF Syntax Highlight.app (you can drag the file to get the pull path)"Alternatively, after trying to launch the app for the first time, you can open the System Preferences > Security & Privacy > General (tab) and click the Open Anyway button.
This will resolve the error of an unsigned application when launching the app.
The release application is compiled as a universal binary (Intel and Apple silicon processor).
After cloning remember to fetch submodules:
git submodule initgit submodule updateTo use the Quick Look preview you must launch the Application at least once. In this way the Quick Look Extension will be discovered by the system and will be available in the System preferences > Extensions > Quick Look.
When opening the app for the first time, you may see a pop-up warning about unable to check malicious software.
To fix follow these steps:
- Switch to Finder and navigate to the application.
- Right-click (or Control-click)
Syntax Highlight.appand choose theOpenitem from the contextual menu. - A modal popup appears stating:
"Syntax Highlight.app" can’t be opened because Apple cannot check it for malicious software.
- Click
Opento confirm.
This warning is because the app is neither codesigned nor notarized.
For more info see the note for the precompiled release.
The Quick Look Extension uses the Uniform Type Identifier (UTI) to handle the supported formats (and not simply the file name extension). Inside the definition on an UTI there are the list of extensions and mime type associated with it.
Some file types are directly associated to a UTI by the system. Other formats are registered by the owner application. In this way some extensions can be associated to multiple UTIs based on the applications currently installed. For this reason, this application supports many UTIs even if they are apparently redundant.
MacOS 10.15 Catalina does not allow to manage some file formats including (but not limited to): .xml, .plist, .html, .ts, .dart, .txt, common images (.jpg, .gif, .png), …
On macOS 11 Big Sur, the system allows you to manage these previously unauthorized extensions: .plist.
On macOS 12 Monterey, the system allows you to manage these previously unauthorized extensions: .xml.
Most programming languages are supported. The application can also handle some plain files without extension.
- Ada (
.ada) - Adobe Acrobat Sequence files (
.sequ) asXML - Adobe Flash ActionScript source files (
.as) - Adobe JSX script files (
.jsx) - Apple workflow (
.wflow) asplist (XML) - AppleScript (
.scpt,.applescript,.ascr) automatically decompiled withosadecompile - Apple shell script files (
.command) - Assembler source files (
.asm,.s79) - Astro files (
.astro) as JSX. - Autolit files (
.au3,.a3x) - Azkaban flow files (
.flow) asYAML - ATL files (
.atl) - (G)AWK files (
.awk) - Bash Script files (
.bash) - Bezel (
.bezel) as plain text - BibTex (
.bib) - C shell script files (
.csh) - C source files (
.c,.h) - C# source files (
.cs) - C++ source files (
.cpp,.cp,.c++,.cc,.cxx,.hpp,.hh,.hxx,.ipp) - ClojureScript (
.cli,.cljs,.cljc,.edn) - CMake files (
.cmake) - CocoaPod files (
.podspec) asRuby - CoffeeScript source files (
.coffee) - ColdFusion files (
.cfc,.cfm,.cfml) - Configuration files (
.conf) - Configuration profiles (
.mobileconfig) asXML - Crystal language (
.cr) - CSON source files (
.cson) - CSS files (
.css) - D (
.d) - Dart source files (
.dart).dartis reserved by macOS and cannot be handled. - Diff files (
.diff,.patch) - Dockerfile (
.dockerfile) - Document Type Definition (
.dtd) - DOS batch files (
.bat,.cmd) - Dylang (
.dylan) - ECore files (
.ecore) - Eiffel project files (
.ecf) asXML - Eiffel source files (
.e,.ex,.exs) - Erlang source files (
.erl,.hri) - F# source files (
.fsx,.fs) - fish source files (
.fish) - Fortran source files (
.f,.for,.f90,.f95) - GCC linked files (
.ld,.map,.d) - Gdscript (Godot engine) (
.gd). - Golang source files (
.go) - Google Earth KML Document files (
.kml) asXML - Gradle source files (
.gradle) - Graphics Language Transmission Format (
.gltf) asJSON - Groovy source files (
.groovy) - Haskell source files (
.hs,.lhs) - HTML Abstraction Markup Language (
.haml) - IDL source files (
.pro) - INF files (
.inf) - INI configuration files (
.ini,.cfg) - Inno source files (
.iss) - INO source files (
.ino) - IntelliJ IDEA module (
.iml) - Interface Builder Storyboard (
.storybard) asXML - Interface Builder XIB (
.xib) asXML - Java Compiled Class (
.class) requirejavapto decompile - Java Properties files (
.properties) asINI - Java Server Page files (
.jsp) - Java source code (
.java,.jav) - Java Web Start (
.jnlp) - JavaFX ML (
.fxml) - JavaScript files (
.js,.jscript,.javascript,.mjs,.jsm) - JSON files (
.json,.jsonc) ** On macOS 13 Ventura with Apple Silicon the.jsonextension is reserved by the system and cannot be handled.** - JSON Line files (
.jsonl) asJSON - Julia source files (
.jl) - Kermeta source files (
.kmt) - Korn Shell script files (
.ksh) - Kotlin source files (
.kt,.kts) - LESS stylesheet (
.less) - Lilypond files (
.ly)x1 - Lisp source files (
.lisp,.lsp,.asd,.el) - Logos source files (
.xm) - Lua source files (
.lua) - Makefile files (
.mk,.mak) - Markdown files (
.md,.rmd): please use QLMarkdown which allows you to choose whether to display formatted output or the highlighted source code. - Media Presentation Description (
.mpd) as XML. - MF source files (
.mf) - Microsoft Active Server Page files (
.asp,.aspx) - Microsoft PowerShell files (
.psm1,.psd1,.ps1) - NextFlow (
.nf) as Groovy (Java) - Nim source files (
.nim) - Node CommonJS module (
.cjs) - Objective-C source files (
.m) - Objective-C++ source files (
.mm) - OCaml source files (
.ml,.mll,.mly) - OpenSSH RSA public key (
.pub) as plain text - OPML (Outline Processor Markup Language) files (
.opml) asXML - Oracle PL/SQL files (
.fnc,.prc,.trg,.pks,.pkb,.pck,.tps,.tpb,.typ,.tab,.avt,.con,.sqs,.vw,.mvw,.trg) asSQL - Paradox files (
.sc) - Pascal source files (
.pas) - Patch files (
.patch,.diff) - PDE source files (
.pde,.ino) - Perl script files (
.pl,.pm,.t) - Planning Domain Description Language (
.pddl) asLisp - PHP source files (
.php,.php3,.php4,.ph3,.ph4,.phtml) - Properties files (
.properties) asINI - Property List files (
.plist) dynamically decompiled withplutilOn macOS 10.15 Catalina.plistis reserved by the system and cannot be handled. - Python source files (
.py) - R (
.r) - Racket (
.rkt) asLisp - RDF files (
.rdf) - README files (
.readme) as plain text - reStructuredText document (
.rst) - Rez files (
.r) - Ruby on Rails files (
.rhtml,.erb,.rjs) - Ruby Gems file (
.gemfile) - Ruby script (
.rb,.rbw) - Rust source files (
.rs) - SageMath files (
.sage) asPython - SAS files (
.sas) - SASS/SCSS files (
.scss) - Scala source files (
.sc,.sbt,.scala) - Scheme source files (
.scm) - Shell script files (
.bashrc,.zshrc,.sh) - Smali (
.smali) as plain text. - Solidity source files (
.sol) - SQL files (
.sql) - Standard ML source files (
.ml) - Stata files (
.do,.ado) as plain text - Steam app manifest files (
.acf) as plain text. - Svelte (
.svelte) asHTML - Swift source files (
.swift) - Symfony Twig files (
.twig) - TCL source files (
.tcl) - Tenex C Shell script files (
.tcsh) - Terraform files (
.tfvars,.tf,.hcl) asYAML - TeX and LaTeX files (
.tex,.sty,.cls,.latex,.ltx,.texi,.ctx,.sty) - Text files (
.txt,.text) - TOML files (
.toml) - TypeScript files (
.ts,.tsx,.cts,.mts).tsand.mtsare reserved by macOS and cannot be handled. - Visual Studio Code Workspace (
.code-workspace) _ asJSON_ - Verilog HDL files (
.v,.vl) - VHDL source files (
.vhd,.vhdl) - VIM script files (
.vim) - Visual Basic source files (
.vb,.bas,.basic,.vbs) - Vue source files (
.vue) - XAML source files (
.xaml) as XML - Xcode entitlement files (
.entitlements) (dynamically decompiled withplutil) as XML - Xcode localizable strings files (
.strings,.stringsdict) (dynamically decompiled withplutil) as XML - XHTML files (
.xhtml) - XML files (
.xml) Before macOS 12 Monterey.xmlis reserved by the system and cannot be handled. - XSD Schema files (
.xsd,.xquery,.xq,.xu) - XUL files (
.xul) - YAML files (
.yaml) - Z shell script files (
.zsh)
With the standalone application you can customize the rendering settings.
You can show advanced settings using the relative command on the view menu.
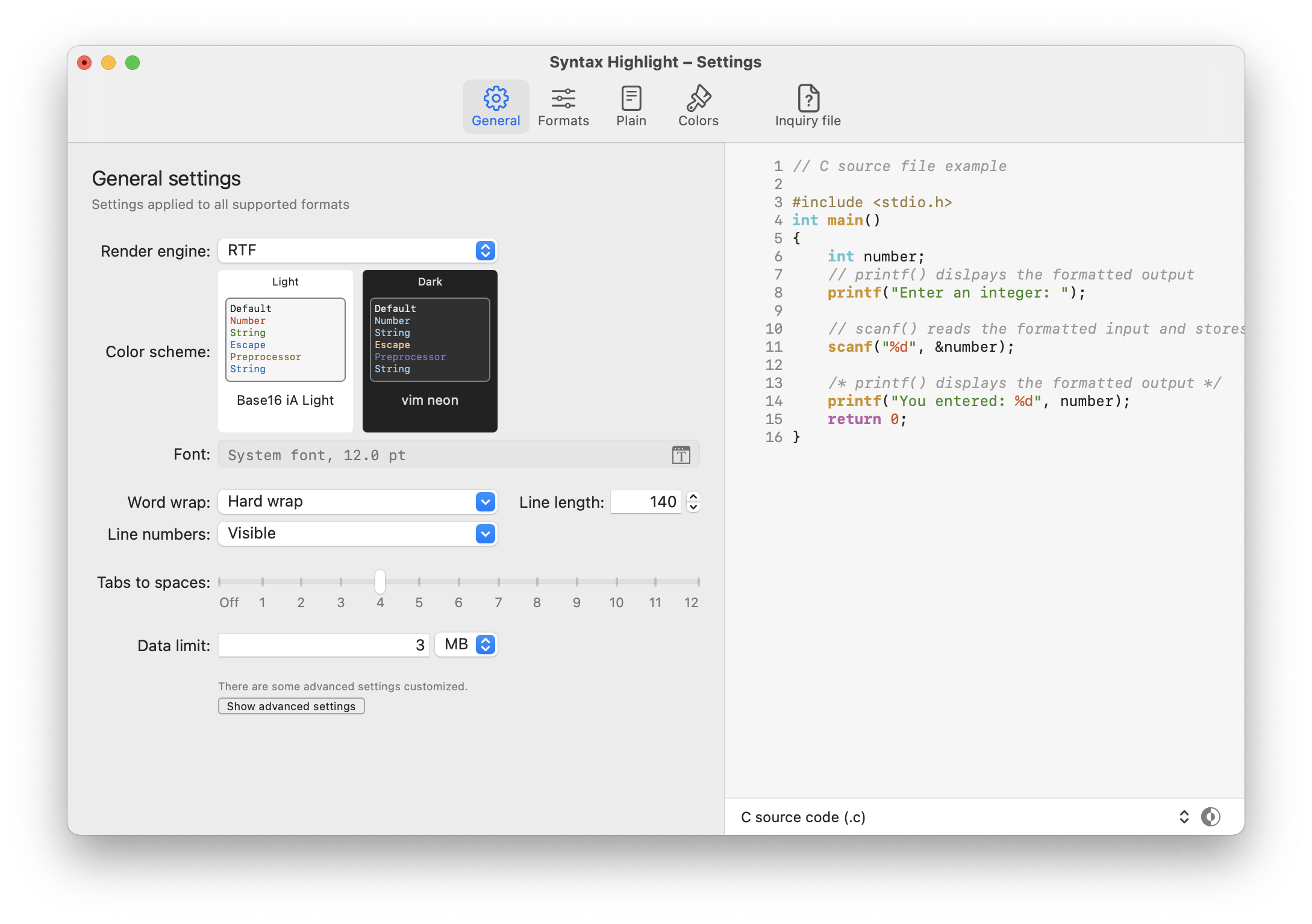
You can set the settings for all supported formats on the General tab.
| Settings | Description | Advanced |
|---|---|---|
| Render engine | Engine used to render the highlighted code. Before macOS 12 Monterey the recommended engine is RTF. Choose the HTML engine if you want to use a custom CSS to override the color scheme (or you have choose a theme with some extra CSS inside it). Advanced users must choose the HTML engine to handle the hover functionality of a Language Server. |
|
| Color scheme | Chose the color scheme for light and dark appearance. | |
| Font | You can chose a preferred font or use the standard monospaced font. | |
| Word wrap | Allow to handle word wrap for long lines. Hard wrap break the line after a fixed length (can cause some highlight glitch). Soft wraps allow to break the line at the preview windows width. When word wraps is disabled, you can only enable it for minified files that have only one line. One line file detection is done on the source file and not on the preprocessor output. Starting from macOS 12 Monterey the soft wrap is always enabled when using the RTF engine. |
|
| Line numbers | Allow to show the line numbers. | |
| Tabs to spaces | Allow to translate tabs to spaces. Set to zero to use tabs. | |
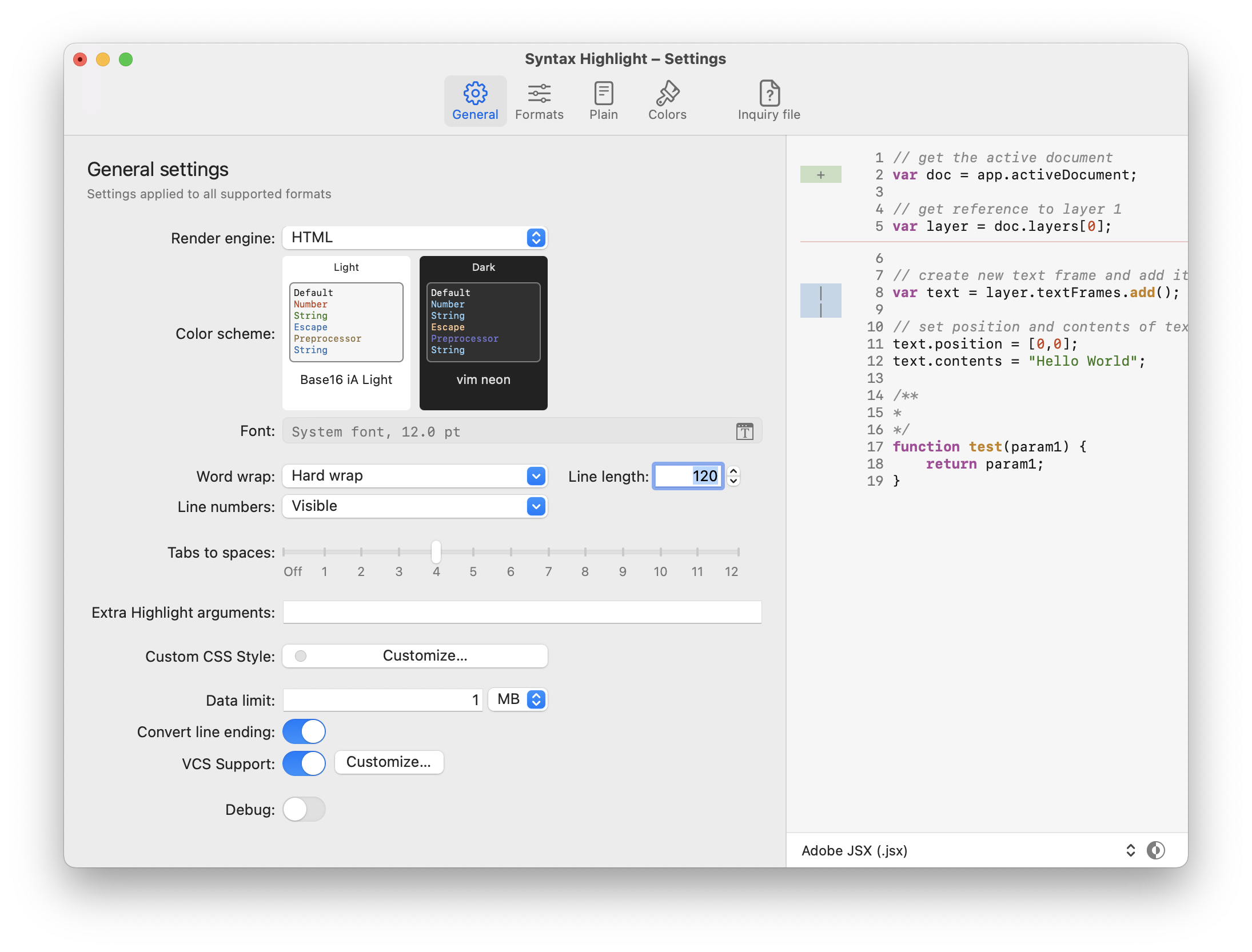
| Extra highlight arguments | Additional standard argument passed to highlight. Arguments that contains a white space must be protected inside quotes. See man highlight to a list of valid arguments and plugins. Eg: --doc-title='title with space' |
Yes |
| Custom CSS Style | If the render engine is set to HTML allow to define a custom CSS style to override/extend the color scheme. More info about highlight HTML output on this page. |
Yes |
| Interactive preview | DEPRECATED and available only before macOS 12 Monterey. If the render engine is set to HTML enable the javascript interpreter inside the preview window. Set only if you use some highlight plugins that output javascript code. This option disable the possibility to move the Quick Look preview with click and drag inside the window and opening the file with a double click. |
Yes |
| Data limit | Maximum amount of data to format, data beyond the limit is omitted. Specify 0 to not limit. This option is ignored when using a Language Server. | |
| Convert line ending | Allow to convert Windows (CRLF) and Mac Classic (CR) line ending to the Unix style (LN). This option is ignored when a preprocessor is set or when a Language Server is enabled. The line ending conversion is made my dos2unix. |
Yes |
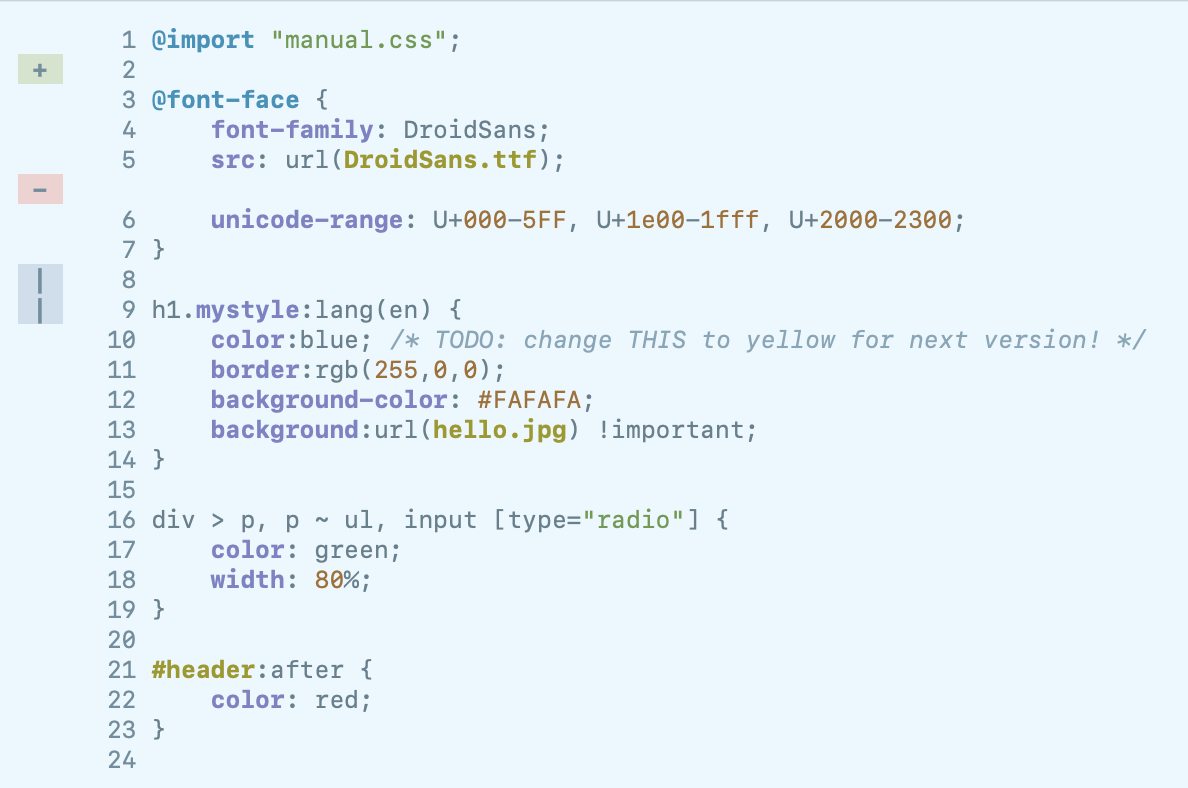
| VCS Support | If enabled, allow to highlight lines added/edited/removed from last commit. It can handle VCS based on git and mercurial. |
Yes |
| Custom Quick Look size | Allow you to choose a custom size for the content area of the Quick Look window. Use with caution on macOS before version 12 Monterey. | |
| Debug | If enabled, a colorize.log and colorize.rtf|html file will be created on your Desktop folder with the log of last rendering. |
Yes |
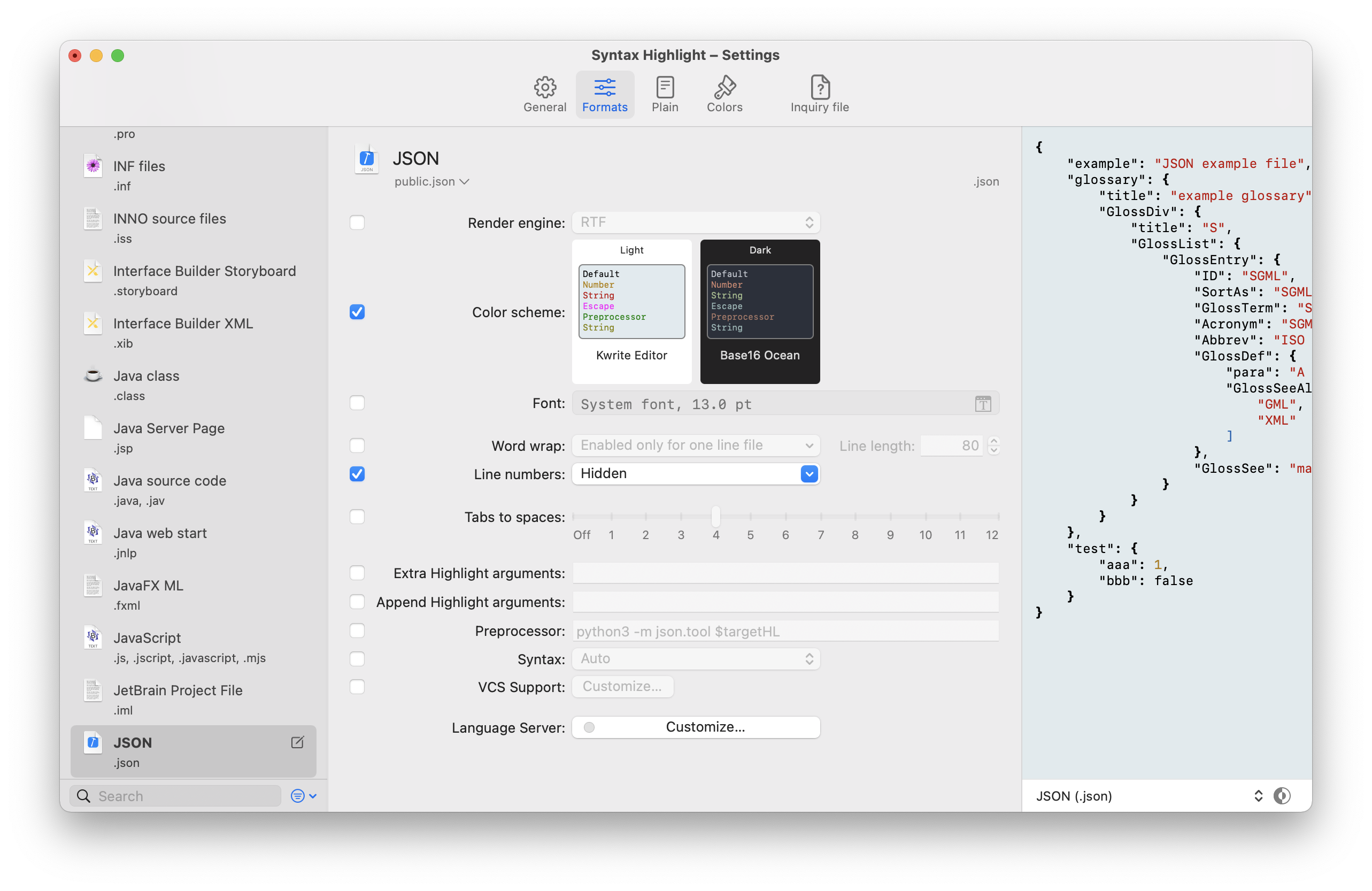
You can also override the global options for some formats on the Formats tab.
When customizing the settings for a specific format, these options will be available:
| Settings | Description | Advanced |
|---|---|---|
| Append highlight arguments | Arguments appended to the Extra highlight arguments. Arguments that contains a white space must be protected inside quotes. | Yes |
| Preprocessor | Set a program or a shell script to preprocess the source file before the formatting. The program must output to stdout the data to be passed to highlight. You must pass the name of the source file using the $targetHL placeholder. You can also use the placeholder $escaped_targetHL with the special chars escaped inside a double quotes. With the preprocessor you can handle file format not directly supported by highlight. This option is ignored when using a Language Server. The execution of the preprocessor is made inside the same env of the script that handle highlight. For example you can beautify a JSON file with this preprocessor: python3 -m json.tool $targetHL or python3 -m json.tool "$escaped_targetHL". When you use a preprocessor you will probably want to disable the support for version control. |
Yes |
| Syntax | Set which language must be used to recognize the source file. If not set will be used the file name extension. | Yes |
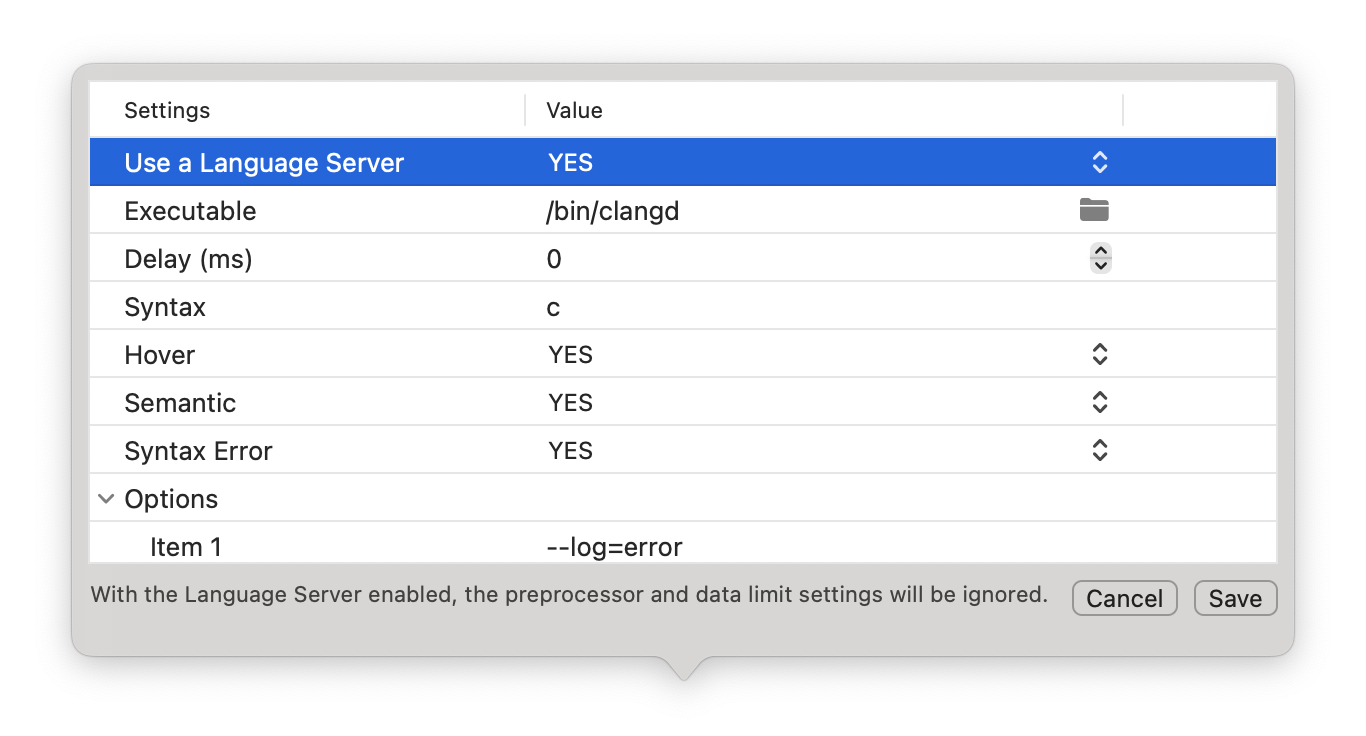
Advanced users can customize the single format to use an external Language Server:
| Settings | Description | Advanced |
|---|---|---|
| Executable | Full path of the Language Server executable. | Yes |
| Delay | Server initialization delay in ms. | Yes |
| Syntax | Syntax which is understood by the server. | Yes |
| Hover | Execute hover requests. Require the HTML render engine. |
Yes |
| Semantic | Retrieve semantic token types (the Language Server must implement the protocol 3.16). | Yes |
| Syntax Error | Retrieve syntax error information (assumes hover or semantic). | Yes |
| Options | Custom command line options to pass to the Language Server. | Yes |
When using an external Language Server the preprocessor and the data limit settings are ignored.
Some format have a preconfigured custom settings to handle the data (for example java compiled class file can be decompiled before render).
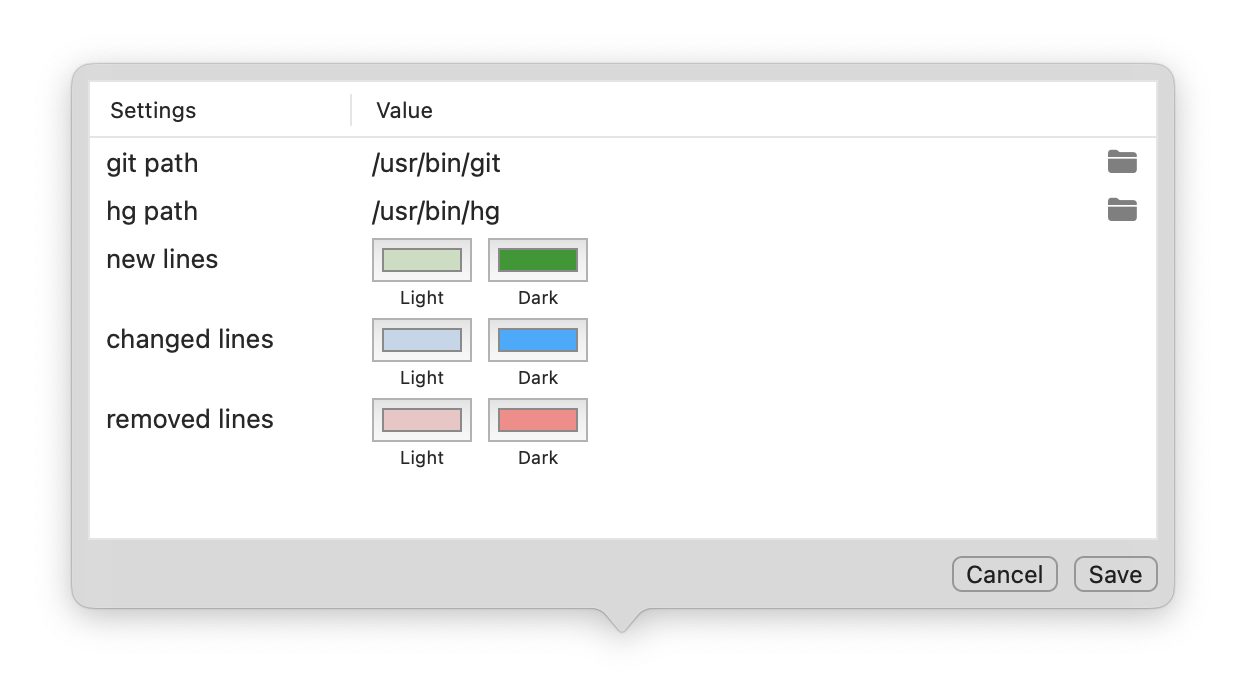
You can also enable the support of common VCS to highlight the added/edited/removed lines from last commit.
In the General settings you must enable the VCS support. Then you can customize the path of git and mercurial binary.
The you can choose the colors used to mark the changed lines. On every format you can also customize the colors.
On RTF mode, the VCS plugin can be disabled if the syntax language defines more keyword groups than those defined in the theme.
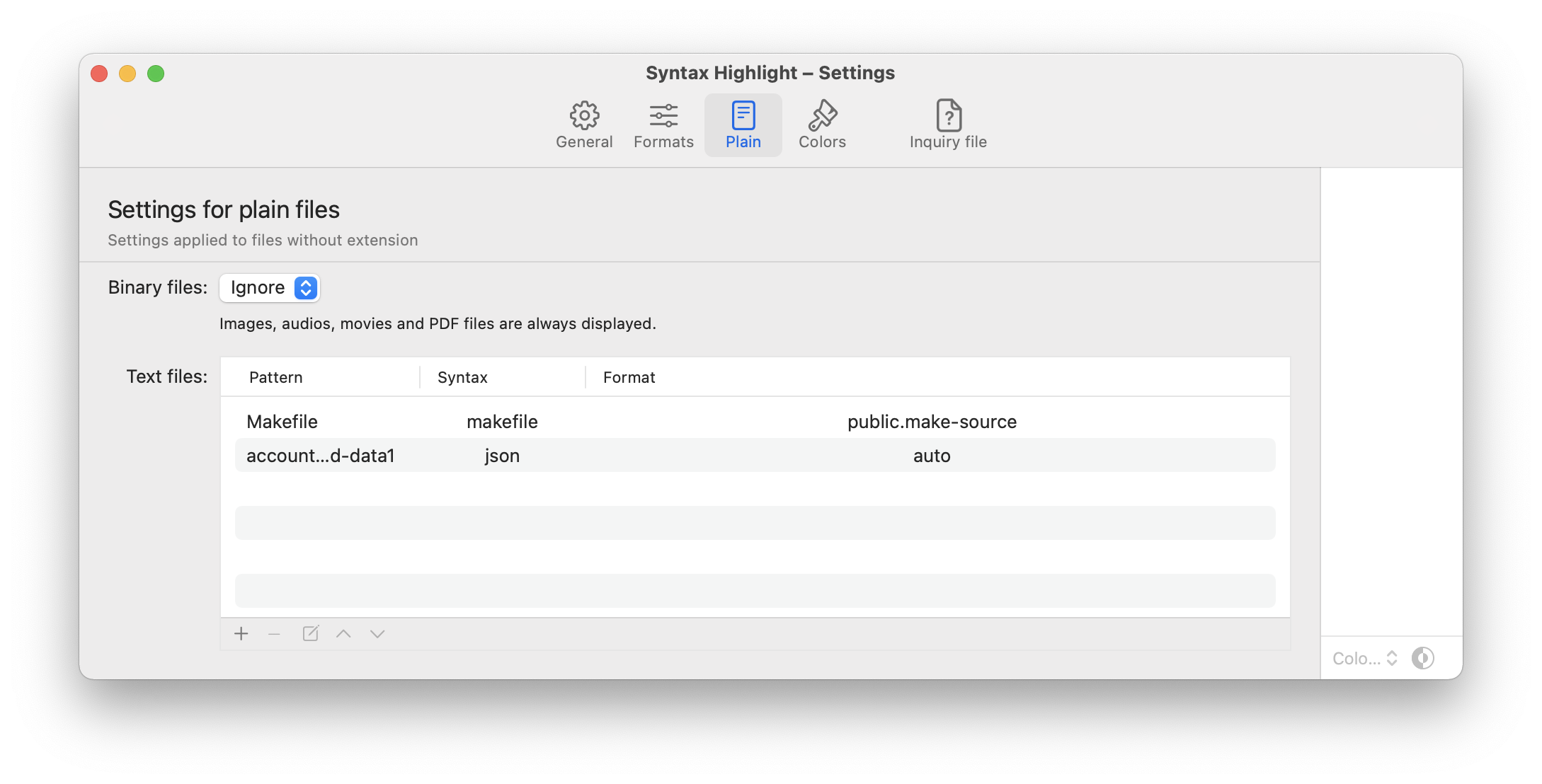
The Application can preview plain files without an extension whose format is unknown.
Only files recognized by the system with one of the following UTIs can be handled:
public.datapublic.itempublic.contentpublic.unix-executable
Files with an extension or associated to a dynamic UTI will not be handled. Files that have a only one dot as the first character in their name (like .gitignore, .env, ...) are considered to have no extension.
Unknown files are analyzed with the system utility /usr/bin/file for recognize mime type and encoding. No preprocessor is applied before analyzing the file.
Files recognized as images are handled by displaying the content within a web page (even if the rendering engine set in the settings is RTF). To be displayed correctly, the image format must be supported by WebKit.
On macOS 12 Monterey images and even, audio, movies and PDF files are displayed with the native Quick Look interface.
For other binary files it is possible to display a hex dump.
For text files, syntax highlighting is tried.
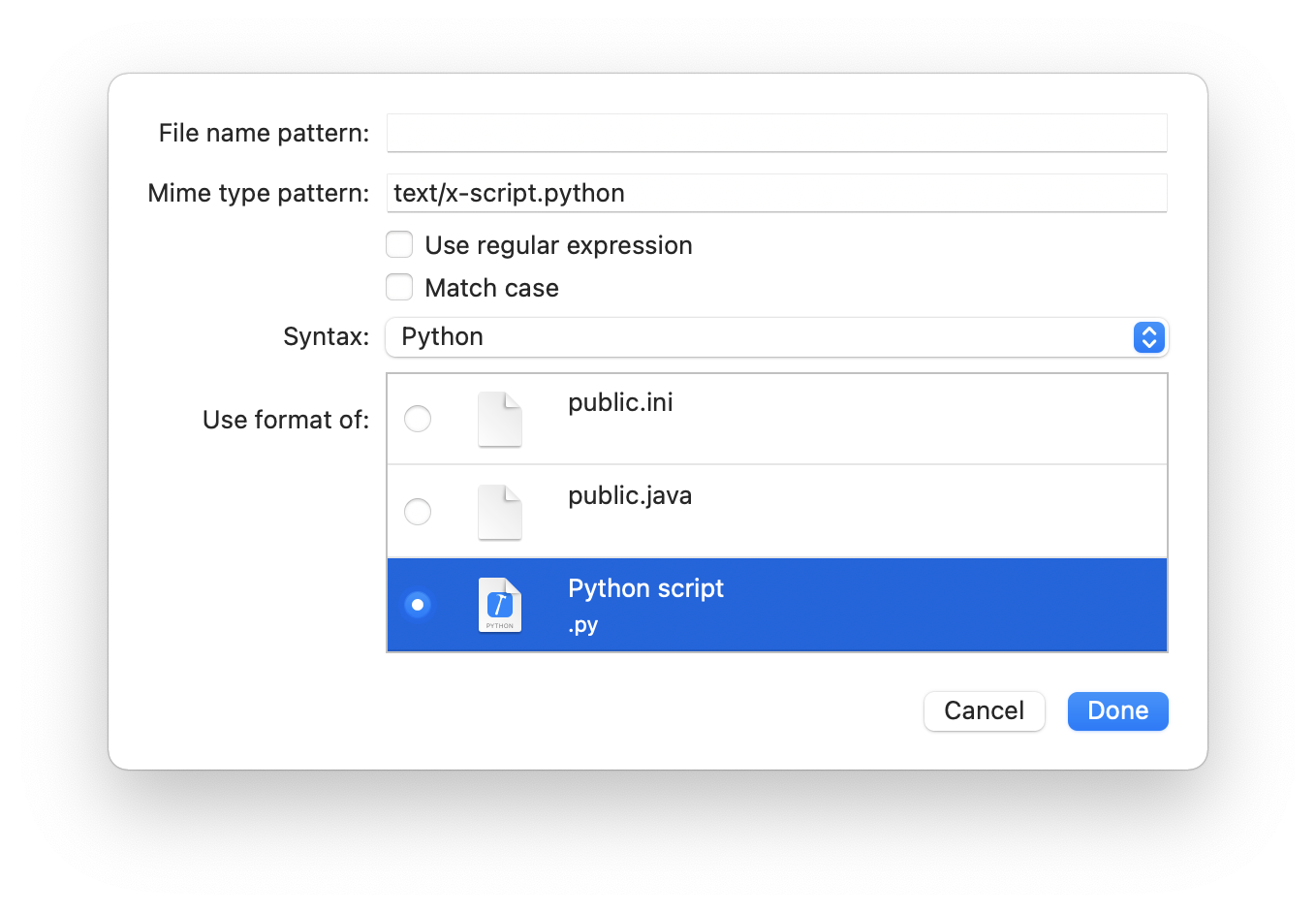
You can specify a criteria for the file name and the mime type to apply a syntax highlighting and/or a specific display format. The criteria are evaluated in the order in which they are set.
If no display format is set, the system will try to derive it starting from the mime type.
Note that some files with no extension can be recognized by macOS with a UTI if they have the com.apple.FinderInfo extended attributed set.
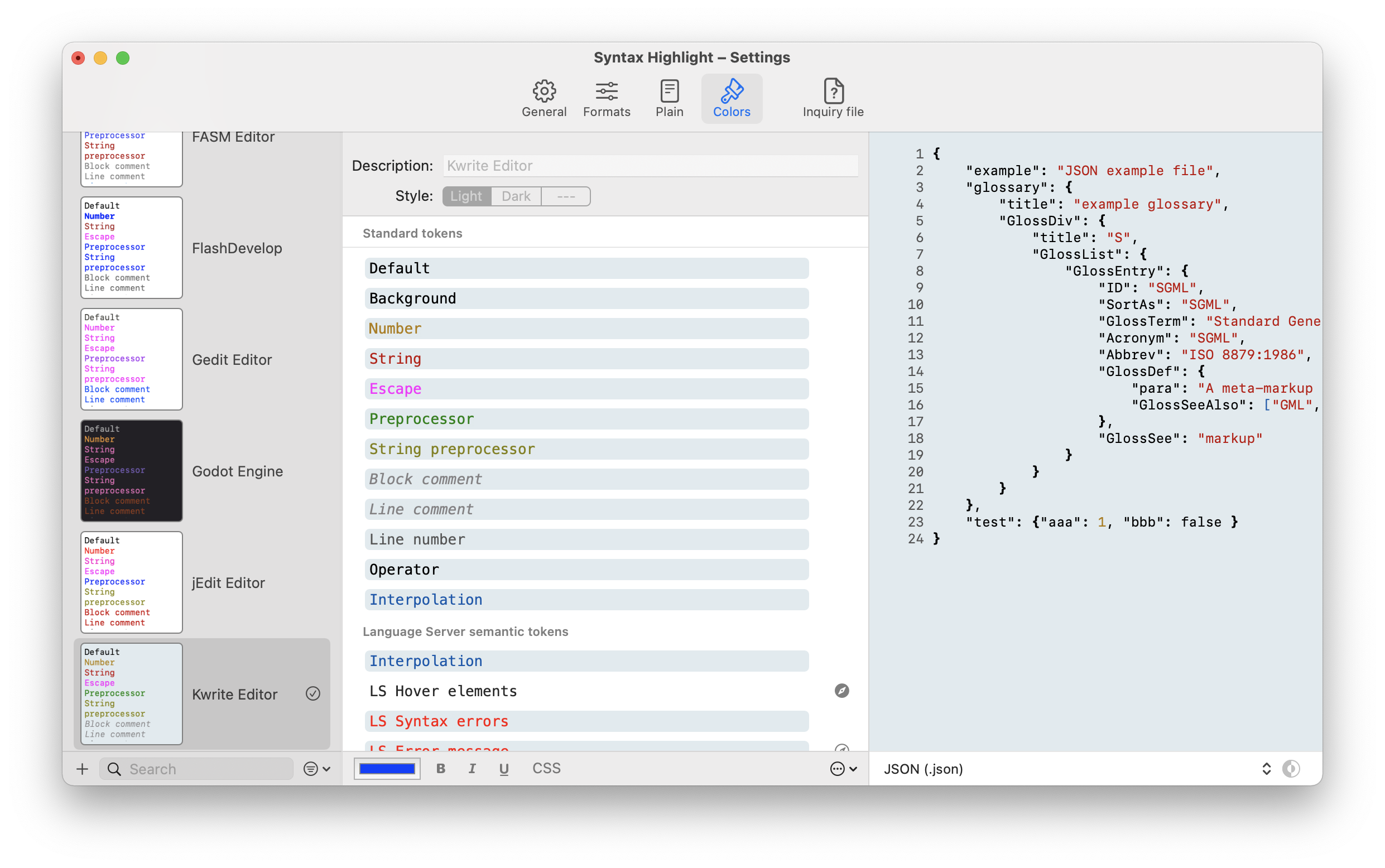
The Application has a GUI to customize the color schemes.
Standard schemas provided by highlight cannot be edited but can be duplicated and then customized.
For every tokens of a color scheme you can also set a custom inline CSS style. Some basic CSS style can be handled also by the RTF engine, but for a best view you must choose the HTML render engine. For this reason the preview of the Color Scheme always uses the HTML engine.
Please note that the inline CSS style is not put inside the HTML style attribute but embedded on the global <style> tag inside the class style definition of the token. So you can define a custom CSS style sheet that override the inline settings.
When inserting the style of a theme token it is possible to indicate whether this should override the default values for color and font style. If you want to use the custom theme with the RTF rendering engine it is required not to override the standard values.
Color schemes that uses inline CSS style are highlighted by an icon.
With the advanced settings enabled you can also customize the appearance of the Language Server Protocol tokens.
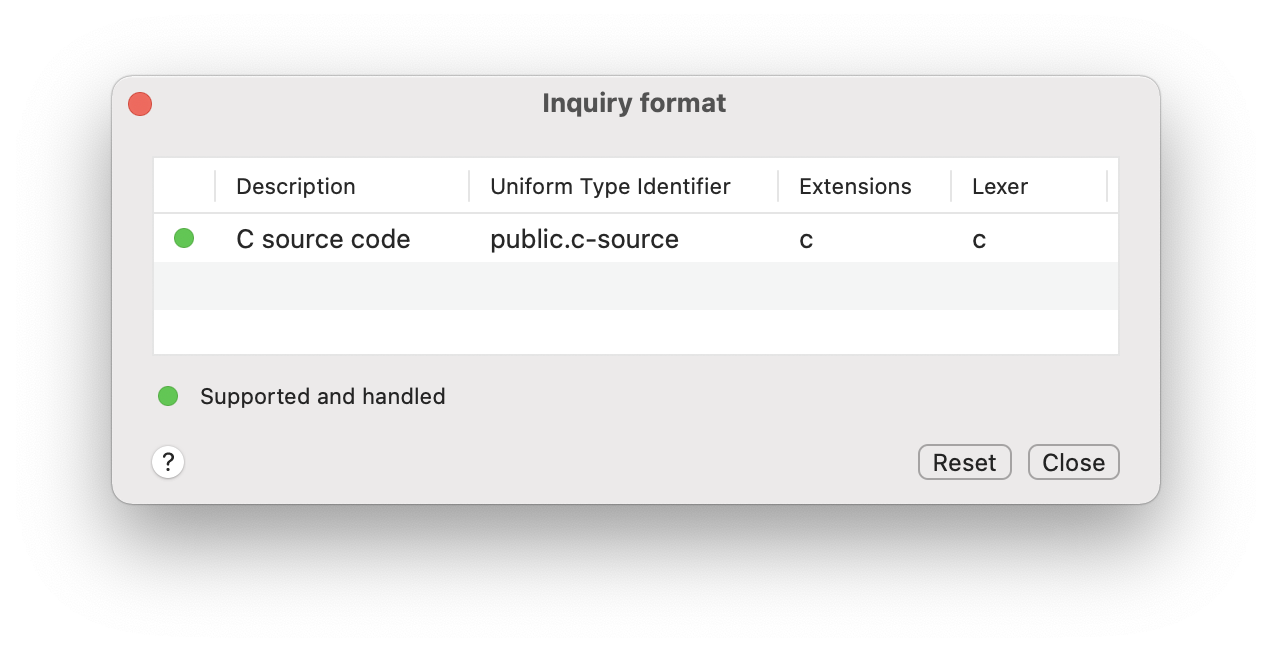
With the Inquiry window you can see if a specific file type is handled by the Quick Look Extension and also if it is supported by highlight.
Alternatively you can see the UTI of a file with this Terminal command:
mdls -name kMDItemContentType -name kMDItemContentTypeTree filename.extIt's likely that I didn't associate all the possible extensions managed by highlight.
If you found an unhandled format please send me the output of above command.
Only the formats supported by highlight can be managed by this application.
A syntax_highlight_cli command line interface (CLI) is available to perform batch conversion.
The tool is located inside the Syntax Highlight.app/Contents/Resources folder (and should not be moved outside).
From the Application menu you can create a symbolic link into /usr/local/bin folder.
/Application/Syntax\ Highlight.app/Contents/Resources/syntax_highlight_cli -hUsage: syntax_highlight_cli [-o <path>] <file> [..]
Arguments:
-h Show this help and exit.
-t Test without save/output the result.
-o <path> Save the output to <path>.
If <path> is a directory a new file is created with the name of the source.
Extension will be automatically added.
Destination file is always overwritten.
-v Verbose mode. Valid only with the -o option.
--log file Save the log to the specified file.
--appearance light|dark Force the requested appearance.
--theme-light name Theme for light appearance.
--theme-dark name Theme for dark appearance.
--theme name Theme for all appearance.
--format html|rtf
--syntax value
--preprocessor value Protect the preprocessor code inside quotes.
--font family Font name. Use '-' to choose the system monospace.
--font-size value Font size in points.
--wrap hard|soft|no Word wrap.
--wrap-one-line Force word wrap for only one line files.
--line-length value
--line-numbers on|zeros|off
--tab-spaces value Number of spaces for every tab. Set to zero to disable the tab conversion.
--extra arguments Extra arguments passed to highlight. Protect the arguments inside quotes.
--extra-appended arguments Extra arguments passed to highlight. Protect the arguments inside quotes.
--css file Extra css loaded from the specified file.
--max-data bytes Trim source file that exceeds the size.
--convert-eol on|off Convert end of line.
--vcs on|off Enable support for version control.
--vcs-git path Path of git binary.
--vcs-hg path Path of mercurial binary.
--vcs-color-add Color (in #rrggbb) for added lines.
--vcs-color-del Color (in #rrggbb) for removed lines.
--vcs-color-edit Color (in #rrggbb) for changed lines.
--lsp on|off Enable Language server protocol.
--lsp-exe file Path of the LSP executable.
--lsp-delay ms
--lsp-syntax value Recognize data processed by LSP with the provided syntax.
--lsp-hover on|off
--lsp-semantic on|off
--lsp-errors on|off
--lsp-option arg Extra argument passed to the LSP program. Protect the value inside quotes.
You can repeat --lsp-option multiple times.
--debug on|off
To handle multiple files at time you must pass the -o argument with a destination folder.
Unspecified rendering options will use the settings defined in the main application.
The CLI interface uses the same settings as the Quick Look extension, but you can override it if you wish.
The highlighted data is printed to the stdout or writed to file if you use the -o option.
The command line tool require macOS 10.15.4 or later.
** You cannot manually add support for a new file format.** This operation must be done during compilation time. Any attempt to manipulate the application causes the code signature to be violated, making it unusable!
See also the FAQ.
The problem may be due to several causes:
- The application is not registered under system extensions.
- Another application is handling the preview instead of Syntax Highlight.
- Some application has registered the format with unrecognized UTI.
- You are trying to view unsupported formats.
- You are trying to view a format reserved by the system.
If the problem affects all file formats it must related to points 1. and 2., so try one or more of these action:
- Try the
RTFrender engine, especially for macOS versions earlier than 12 Monterey.- Drag the application on the trash and back to the Applications folder and then relaunch.
- Check in the
System Preferences > Extensions > Quick Lookif the Syntax Highlight extension is present and checked.- In the
System Preferences > Extensions > Quick Look, drag the Syntax Highlight extension on the top.- In the
System Preferences > Extensions > Quick Lookdisable other extensions one at a time until you find the one that conflicts.If the problem affects only a specific format it is possible that this was registered by some application with a non-standard UTI. Check the UTI with the Inquiry window and send me the value. The support for each format must be defined at compile time.
Also remember that some common files cannot be handled by third party extension because are reserved by the system (for example,
.ts,.html, …).
No, Apple does not allow this functionality.
This is a deliberate choice. Most users want to see the formatted output and not the source code of their markdown files. If you need to view the markdown files (also with the possibility of choosing whether to show the formatting or the source code) I have developed QLMarkdown.
It depends… first the format must be handled by
highlight. Check in the Inquiry window if the file is supported. If is supported please send me the UTI associated to the file. You can also view the UTI with this terminal command:
mdls -name kMDItemContentType -name kMDItemContentTypeTree filename.extSome common files cannot be handled by third party extension because are reserved by the system (for example,
.ts,.html, …).You can customize the behavior for files with no extension yourself. See Plain files settings.
This Application only generate the Quick Look Preview and does not provide a thumbnail service for the Finder icon.
When the Debug option is enabled (on the advanced settings) on your Desktop folder will be created two files for the last preview action:
- colorize.log with the log of the highlight process.
- colorize.hml|rtf the output of the last rendering process.
On Big Sur you cannot scroll the preview inside a Quick Look window dragging the scrollbars with the mouse. This is a Big Sur bug. You can scroll only with a mouse/trackpad gesture.Fixed on maxOS 12 Monterey.- On macOS earlier than 12 Monterey, soft word wrap with RTF engine reacts when the window is enlarged but not when it is reduced.
- Icons of the custom file format are disabled on Catalina (cause an application freeze).
- In
RTFmode the colors may be slightly lighter than what is set (probably due to the different handling of color profile). - Typescript
.tsformat cannot be handled because is reserved by macOS and associated to the mpeg video stream format. - If a Quick Look window is opened when the system switch the theme appearance, the contents will not be refreshed to the new style.
Starting from macOS 10.15.0 Catalina the qlgenerator APIs are deprecated.
This project consists of these components:
- A Standalone Application to set the preferences.
- A Quick Look Extension to preview the source files.
- An XPC service that generate the preview and pass the formatted data to the application or the Quick Look Preview.
MacOS 10.15 Catalina require sandboxed extension that prevent the execution of external processes (like shell script). To work around this problem, it is possible to use an XPC service that may have different security policies than the application / extension that invokes it. In this case the XPC service is not sandboxed.
The XPC service is executed automatically when requested by the application or the Quick Look Extension. After closing the Quick Look preview the process is automatically closed after some seconds releasing the resources.
The Application and the Quick Look Extension can preview files showing the formatted code as HTML, inside a WKWebView, or as RTF inside a NSTextView. Especially in Big Sur, the use of WebKit within the Quick Look Preview has numerous bugs, so before macOS 12 Monterey, the suggested rendering engine is RTF. From macOS 12 Monterey, the plugin adopt the new data based Quick Look API.
The settings are stored in ~/Library/Preferences/org.sbarex.SourceCodeSyntaxHighlight.plist.
Custom themes and styles are saved in ~/Library/Application Support/Syntax Highlight.
The application embed the Highlight engine that is build inside the Xcode project.
- https://gist.github.com/jtbandes/19646e7457208ae9b1ad
- https://alastairs-place.net/blog/2012/06/06/utis-are-better-than-you-think-and-heres-why/
- whomwah/qlstephen#87
- https://www.cocoanetics.com/2012/09/fun-with-uti/
- whomwah/qlstephen#87 (comment) :
Ok, so according to the source I references above, I would do the following:
1. Generate the dyn content, in this case I guess its `?0=6:1=sql`. Though I am not sure if the `6` is correct or if it should be `7`. Where numbers are substituted as follows:0: UTTypeConformsTo 1: public.filename-extension 2: com.apple.ostype 3: public.mime-type 4: com.apple.nspboard-type 5: public.url-scheme 6: public.data 7: public.text 8: public.plain-text 9: public.utf16-plain-text A: com.apple.traditional-mac-plain-text B: public.image C: public.video D: public.audio E: public.directory F: public.folder2. Next you put this string into a custom base32 converter. E.g. [this website](https://cryptii.com/pipes/base32) Input: `?0=6:1=sql` Variant: `Custom` Alphabet: `abcdefghkmnpqrstuvwxyz0123456789` Padding: – Delete if there is any – 3. The output should be `h62d4rv4ge81g6pq`. If you have any trailing `=` delete it, thats the padding. 4. Prepend `dyn.a` and that is your final string. 5. What you should insert in the Info.plist is `dyn.ah62d4rv4ge81g6pq`<key>LSItemContentTypes</key> <array> <string>public.data</string> <string>public.content</string> <string>public.unix-executable</string> <string>dyn.ah62d4rv4ge81g6pq</string> </array>
List all registered UTIs:
/System/Library/Frameworks/CoreServices.framework/Versions/A/Frameworks/LaunchServices.framework/Versions/A/Support/lsregister -dump
- handle extension from command line (https://stackoverflow.com/questions/66546696/how-to-enable-and-debug-a-macos-file-provider-extension , https://stackoverflow.com/questions/34898903/what-do-the-prefixes-in-the-output-of-macos-pluginkit-mean/36839118#36839118 , https://kevin.deldycke.com/2019/07/macos-commands/ ):
List all registered Quick Look plugins:
pluginkit -mAvvv -p com.apple.quicklook.preview İnfo about a plugin:
pluginkit -m -v -i org.sbarex.SourceCodeSyntaxHighlight.QuickLookExtension --rawDeveloped by sbarex with ❤️.
Highlight is developed by Andre Simon.
Dos2unix is developed by Erwin Waterlander.
This application was inspired by anthonygelibert/QLColorCode and NSGod/qlstephen.