Author: Zhixiang Min (Work done during an internship at Zillow Group)
Contacts: zmin1@stevens.edu, najik@zillowgroup.com
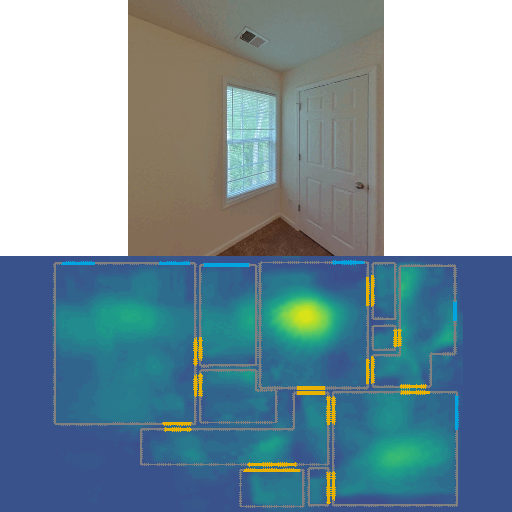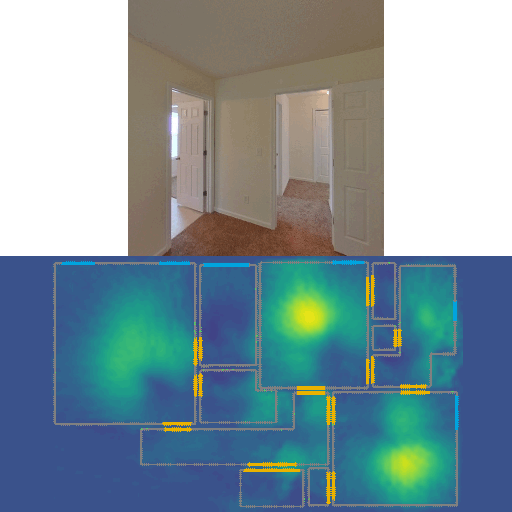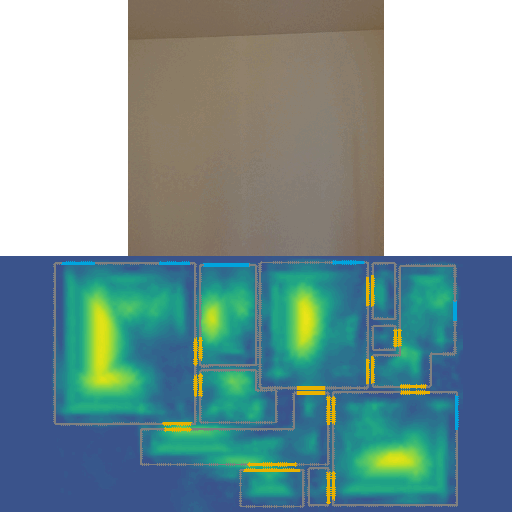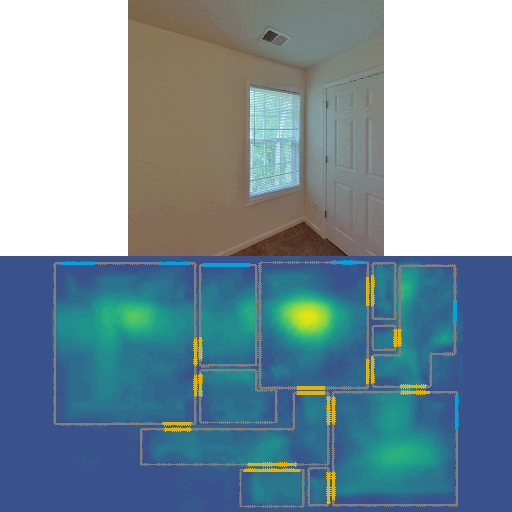
This repo contains code for our CVPR 2022 Oral paper LASER: LAtent SpacE Rendering for 2D Visual Localization. LASER introduces the concept of latent space rendering, where 2D pose hypotheses on the floor map are directly rendered into a geometrically-structured latent space by aggregating viewing ray features. Through a tightly coupled rendering codebook scheme, the viewing ray features are dynamically determined at rendering-time based on their geometries (i.e. length, incident-angle), endowing our representation with view-dependent fine-grain variability. Our codebook scheme effectively disentangles feature encoding from rendering, allowing the latent space rendering to run at speeds above 10KHz. LASER is an accurate single-image 2D Monte-Carlo localization model that supports images of arbitrary FoVs. Our method achieves 97% recall with a median error of 5cm 0.47deg with single 360° panorama query on ZInD dataset, while it only takes 1 sec to sample a house-scale map at a fine resolution.
LASER: LAtent SpacE Rendering for 2D Visual Localization Z. Min, N. Khosravan, Z. Bessinger, M. Narayana, S.B. Kang, E. Dunn, and I. Boyadzhiev CVPR 2022 (Oral) [paper]
@misc{https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.2204.00157,
doi = {10.48550/ARXIV.2204.00157},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.00157},
author = {Min, Zhixiang and Khosravan, Naji and Bessinger, Zachary and Narayana, Manjunath and Kang, Sing Bing and Dunn, Enrique and Boyadzhiev, Ivaylo},
keywords = {Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV), FOS: Computer and information sciences, FOS: Computer and information sciences},
title = {LASER: LAtent SpacE Rendering for 2D Visual Localization},
publisher = {arXiv},
year = {2022},
copyright = {Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International}
}- PyTorch 1.7.1
- (Other small requirements see
requirements.txt, or install usingpip install -r requirements.txt)
- Train with panorama
python train.py --gpu 0 --log_dir [.] --its 300000 --dataset zind --dataset_path [.]
- Train with 90 fov perspective images
python train.py --gpu 0 --log_dir [.] --fov 90 --its 300000 --dataset zind --dataset_path [.]
- Train with mixed (45-135) fov perspective images
python train.py --gpu 0 --log_dir [.] --fov2 45,135 --its 900000 --dataset zind --dataset_path [.]
python eval.py --save --log_dir [.] --dataset zind --dataset_path [.]
- If model is trained with mixed FoV, need specify a fov
--fov [.]for testing - Remove
--saveto visualize the results on fly - To use the pre-trained models, simply download models.zip, extract the zip and copy the desired model to the the desired log_dir, and point the script to it similar to the example above.
python scripts/generate_html.py --result_dir [.]
result_diris the folder created byeval.py.
- Analyze raw data
python scripts/analyze_data.py --log_dir [.]
- Plot data table
python scripts/plot_data.py --log_dir [.]
This work is released under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License (see LICENSE file for more details).