这个项目主要是用vue+vuex实现一个单页面应用,纯粹是熟悉vue全家桶相关开发模式,用于练手非常合适。
着手开发完了之后可以学的东西:
- 熟悉vue单文件组件开发方式
- 熟悉如何写一个vue插件
- 熟悉如何使用vue-router以及挂载路由钩子函数
- 熟悉vuex是如何运作的,模块化维护应用状态数据
- 体验typescript的开发方式
如果想学vue的不妨进来看看。
- vue
- vuex
- vue-router
- typescript
开始之前,还是有必要去vue官网学习一下vue,至少得有个大致的了解,后面在用到vue-router和vuex时,再去对应的仓库看文档就可以了。
创建项目可以用vue-cli,具体看这里
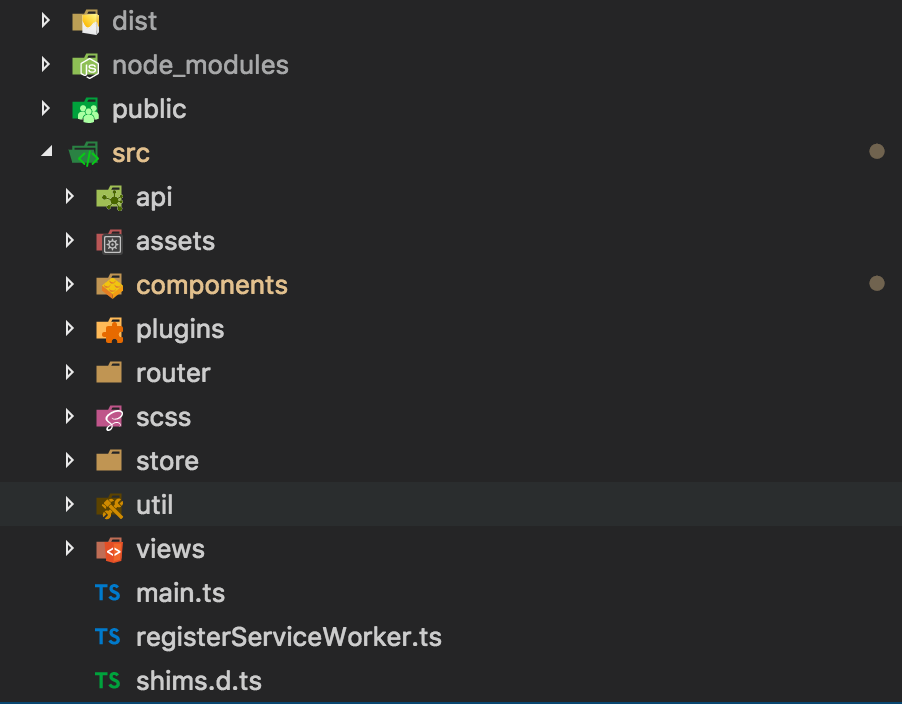
项目结构一般来说非常重要,定义好的目录结构,非常利于后续的项目维护,以及别人阅读理解。下面就是这个项目的结构,应该看一下就知道是干什么的,大致说一下。
项目结构分为静态资源目录,api接口请求目录,组件目录,插件目录,路由配置目录,公共样式目录,状态维护目录,工具类目录,页面视图目录。
vue开发一般都是单页面组件的方式,即一个以vue为后缀的文件就是一个组件,组件里包含了template模版,script脚本,style样式,组件内的逻辑可以完全封装在里面,对外可以提供接受的Props数据,可以对外发射一个事件emit,或者将外部组件组合到自己内部的slot里面。
<template>
<div class="topNav">
<ul class="list">
<li class="item left">
<app-icon :link="left" @click.native.stop="clickLeft" />
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { Component, Prop, Emit , Vue } from 'vue-property-decorator';
import AppIcon from './AppIcon.vue';
import {PREFIX} from '@/store/modules/user/CONSTANTS';
@Component({
components: {
AppIcon,
},
})
export default class TopNav extends Vue {
@Prop({required: true})
private left!: string;
private get avatar() {
return this.$store.state[PREFIX].avatar;
}
private clickLeft() {
this.$emit('left');
}
}
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
@import '../scss/theme.scss';
.topNav {
background: $topBarBgColor;
position: fixed;
}
</style>由于在客户端渲染的单页面应用,需要在客户端配置路由,实现页面间的切换。开发vue时官方推荐使用vue-router,在配置这个项目时,由于考虑登录态的维护,所以对路由配置加了meta数据,并增加了路由跳转钩子函数,进行鉴权控制受登录态的页面。
import Vue from 'vue';
import Router from 'vue-router';
import Sign from '@/views/Sign.vue';
import Me from '@/views/Me.vue';
import { hasLogin } from '@/util/session';
Vue.use(Router);
const router = new Router({
mode: 'history',
routes: [
{
path: '/',
name: 'sign',
component: Sign,
},
{
path: '/me',
name: 'me',
component: Me,
meta: { requiredAuth: true },
},
],
});
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
if (to.matched.some((record) => record.meta.requiredAuth)) {
// this route requires auth, check if logged in
// if not, redirect to login page.
if (!hasLogin()) {
next({
path: '/',
query: { redirect: to.fullPath },
});
} else {
next();
}
} else {
next(); // 确保一定要调用 next()
}
});
export default router;对于那种需要全组件共享,或者全局注入的方法等可以使用vue插件。其实,vue-router和vuex实际就是vue的插件,在入口处,调Vue.use(Router); 就可以了,比如 Vue.use(Router);
一个插件,可以是一个函数,或者一个包含install方法的对象,在调用Vue.use时,会调用install方法。
在插件里,我们可以
- 添加全局方法或者属性,
- 添加全局资源
- 通过全局 mixin 方法添加一些组件选项
- 添加 Vue 实例方法
import Vue, { VueConstructor, PluginObject } from 'vue';
import Loading from './Loading.vue';
type ShowFunc = () => () => void;
const plugin: PluginObject<{}> = {
install(Vue: VueConstructor, options = {}) {
const CONSTRUCTOR = Vue.extend(Loading);
let cache: Vue & { show: ShowFunc } | null = null;
function loading(): () => void {
const loadingComponent = cache || (cache = new CONSTRUCTOR());
if (!loadingComponent.$el) {
const vm = loadingComponent.$mount();
(document.querySelector('body') as HTMLElement).appendChild(vm.$el);
}
return loadingComponent.show();
}
Vue.prototype.$loading = loading;
},
};
export default plugin;单页面应用的状态管理使用vuex,上面提到了,它就是一个vue的插件,会在组件实例上注入$store对象,这个对象就是new Vuex.Store(),相比redux ,我觉得vuex简单很多。使用需要注意一下几点就可以了,
- 改变state,始终是通过commit一个mutation方式进行,mutation函数里必须是同步改变state,不能异步改变state。对应redux中,就是reducer函数的功能了。
- 对于异步改变state,可以通过dispatch一个action,action里面异步获取数据之后在commit一个对应的mutation。这个在redux里,是通过中间件处理异步action的。
- 对于state的过滤筛选,可以定义getter,getter是缓存依赖的。
- 对于大型复杂的state,可以采用模块化的方式管理各个模块的state,这个跟redux的**是一样的。
本次项目也是用模块化的管理状态的方式,把整个应用的状态以业务划分为子状态,最后在modules中合并
modules: {
user,
list,
filter,
},对于单个模块的state,按照上面的注意点即可以。
// user模块的state
import { ActionTree, MutationTree, ActionContext } from 'vuex';
import { login, loginOut, LoginInfo } from '@/api/login';
import { getUserInfo, getUserActions } from '@/api/user';
import { User } from './user';
import { RootState } from '../../rootstate';
const namespaced = true;
/* initial state */
const state = () => ({
id: null,
username: null,
email: null,
avatar: null,
likes_count: null,
goings_count: null,
past_count: null,
});
/* user actions */
const actions: ActionTree<User, RootState> = {
login({ commit, state }: ActionContext<User, RootState>, payload: LoginInfo) {
return login(payload).then(
({ token, user }: { token: string; user: User }) => {
commit('saveToken', token, { root: true });
commit('saveUser', user);
},
);
},
getUserInfo({ commit, state }: ActionContext<User, RootState>) {
return getUserInfo().then((user: User) => {
commit('saveUser', user);
});
},
};
/* user mutations */
const mutations: MutationTree<User> = {
saveUser(state, user) {
state.id = user.id;
state.username = user.username;
state.email = user.email;
state.avatar = user.avatar;
state.likes_count = user.likes_count;
state.goings_count = user.goings_count;
state.past_count = user.past_count;
},
};
export default {
state,
actions,
mutations,
namespaced,
};