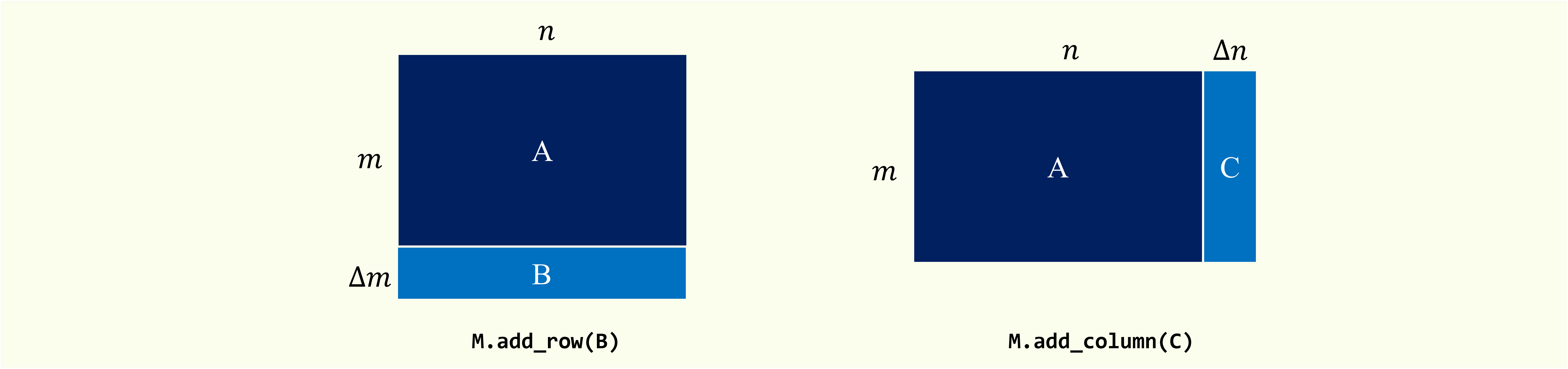IncSVD is a python package capable of dynamically maintaining the incremental Truncated Singular Value Decomposition (Truncated SVD) of evolving matrices.
This is the code implementation of the paper "Fast Updating Truncated SVD for Representation Learning with Sparse Matrices" (ICLR'24).
It is recommended to use python 3.8 or higher and install IncSVD with the following command.
pip install IncSVDInitialize the IncSVD using an data_init given the rank (dimension) k for which the truncated SVD needs to be computed. Here is an example to initialize a
class EvolvingMatrix(data, k, sparse = True, method = "RPI")
- data: data matrix
Data matrix used to initialize truncated SVD.
The format of this initial matrix can be
np.ndarrayorscipy.sparse. - k: int Truncated dimension in the maintained SVD. It should be a positive integer not greater than the length of the sides of the original matrix.
- sparse: bool, default=True Set true implies the update process will employ the proposed acceleration methods [1]. Set false implies using the original methods (ZhaSimon's [2], Vecharynski's [3], Yamazaki's [4]).
- method: {'ZhaSimon', 'GKL', 'RPI'}, default='RPI'
Method for SVD update.
It can be chosen from
['ZhaSimon', 'GKL', 'RPI'].
import scipy.sparse
import IncSVD.EvolvingMatrix as EM
m, n, k = 1000, 1000, 64
# data_init = scipy.sparse.rand(m, n, density=0.005).tocsr()
M = EM.EvolvingMatrix(data_init, k, sparse=True, method="ZhaSimon")Tip
We recommend using GKL or RPI when the rank of each update matrix (e.g. adding many rows at once) is large.
Expand the original matrix in row or column dimensions and update the corresponding SVD results.
add_row(update_matrix, l=None, t=None)
- update_matrix: data matrix
Data matrix to be appended.
This matrix should have the same number of columns as the original matrix. If type
sparseis True, this matrix should be inscipy.sparse._csr.csr_matrix. - l: {int, None}
Approximate dimension for the update matrix.
When using GKL or RPI, two methods that require an approximation space, it is necessary to set
l. The update matrix of rankswill be approximated with a smaller space of ranklfor further speedup. Set toNonewhen GKL and RPI is not applied. - t: {int, None}
The number of iterations to perform in the random power iteration.
It needs to be set when using the RPI. This approximation is more accurate when
tis larger, while the computational overhead is larger. Set toNonewhen RPI is not applied.
add_column(update_matrix, l=None, t=None)
- update_matrix: data matrix
Data matrix to be appended.
This matrix should have the same number of rows as the original matrix. If type
sparseis True, this matrix should be inscipy.sparse._csc.csc_matrix. - l: {int, None}
Approximate dimension for the update matrix.
Set to
Nonewhen GKL and RPI is not applied. - t: {int, None}
The number of iterations to perform in the random power iteration.
Set to
Nonewhen RPI is not applied.
''' Add rows '''
# data_append_row = scipy.sparse.rand(m, 10, density=0.005).tocsr() * 10
M.add_row(data_append_row)
''' Add columns '''
# data_append_col = scipy.sparse.rand(n, 10, density=0.005).tocsc() * 10
M.add_column(data_append_col)Note
If type sparse is True.
- [Add row] The input
data_append_rowis required to have the same number of columns as the original matrix columns and be inscipy.sparse._csr.csr_matrixtype. - [Add column] The input
data_append_colis required to have the same number of rows as the original matrix rows and be inscipy.sparse._csc.csc_matrixtype.
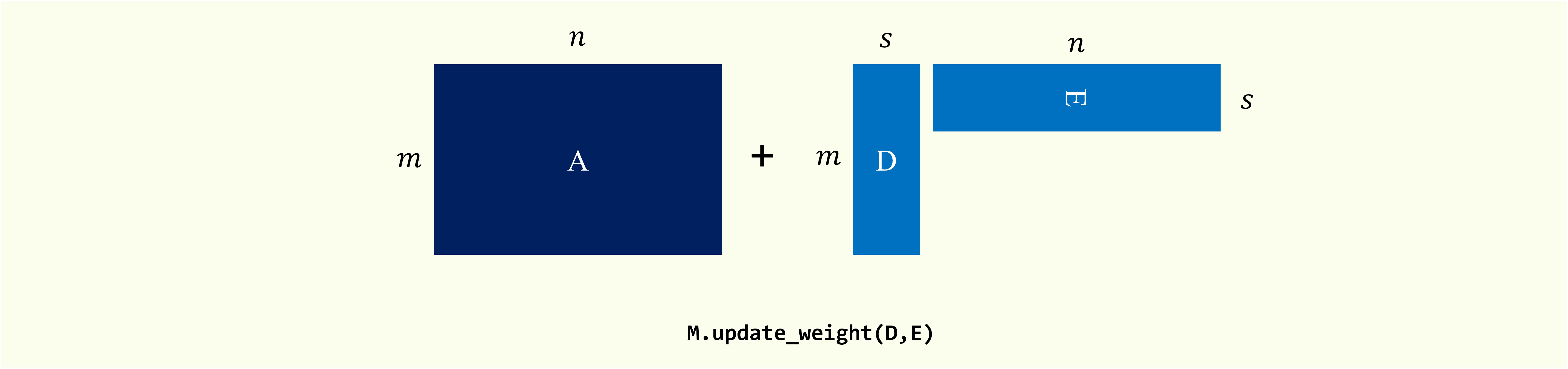
Perform low-rank update
- update_matrix_B: data matrix
Data matrix to be appended.
This matrix should have the same number of columns as the original matrix. If type
sparseis True, this matrix should be inscipy.sparse._csc.csc_matrix. - update_matrix_C: data matrix
Data matrix to be appended.
This matrix should have the same number of columns as the original matrix. If type
sparseis True, this matrix should be inscipy.sparse._csc.csc_matrix. - l: {int, None}
Approximate dimension for the update matrix.
Set to
Nonewhen GKL and RPI is not applied. - t: {int, None}
The number of iterations to perform in the random power iteration.
Set to
Nonewhen RPI is not applied.
''' Low-rank update '''
# data_dm = scipy.sparse.rand(m, 10, density=0.005).tocsc() * 10
# data_em = scipy.sparse.rand(n, 10, density=0.005).tocsc() * 10
M.update_weight(data_dm, data_em)Note
If type sparse is True, the input data_dm and data_em is required to be in scipy.sparse._csc.csc_matrix type.
Queries the current SVD result.
''' Get the result. '''
Uk, Sigmak, Vk = M.Uk, M.Sigmak, M.Vk
''' Get a row of singular vectors. '''
# i = 0
Uk0, Vk0 = M.Uki(i), M.Vki(i)
''' A low-rank approximation of data matrix can be obtained from. '''
Ak = Uk @ np.diag(Sigmak) @ Vk.TIf you have any questions about this code repository, feel free to raise an issue or email denghaoran@zju.edu.cn.
If you find our work useful, please consider citing the following paper:
@inproceedings{deng2024incsvd,
title={Fast Updating Truncated {SVD} for Representation Learning with Sparse Matrices},
author={Haoran Deng and Yang Yang and Jiahe Li and Cheng Chen and Weihao Jiang and Shiliang Pu},
booktitle={The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations},
year={2024},
url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=CX2RgsS29V}
}