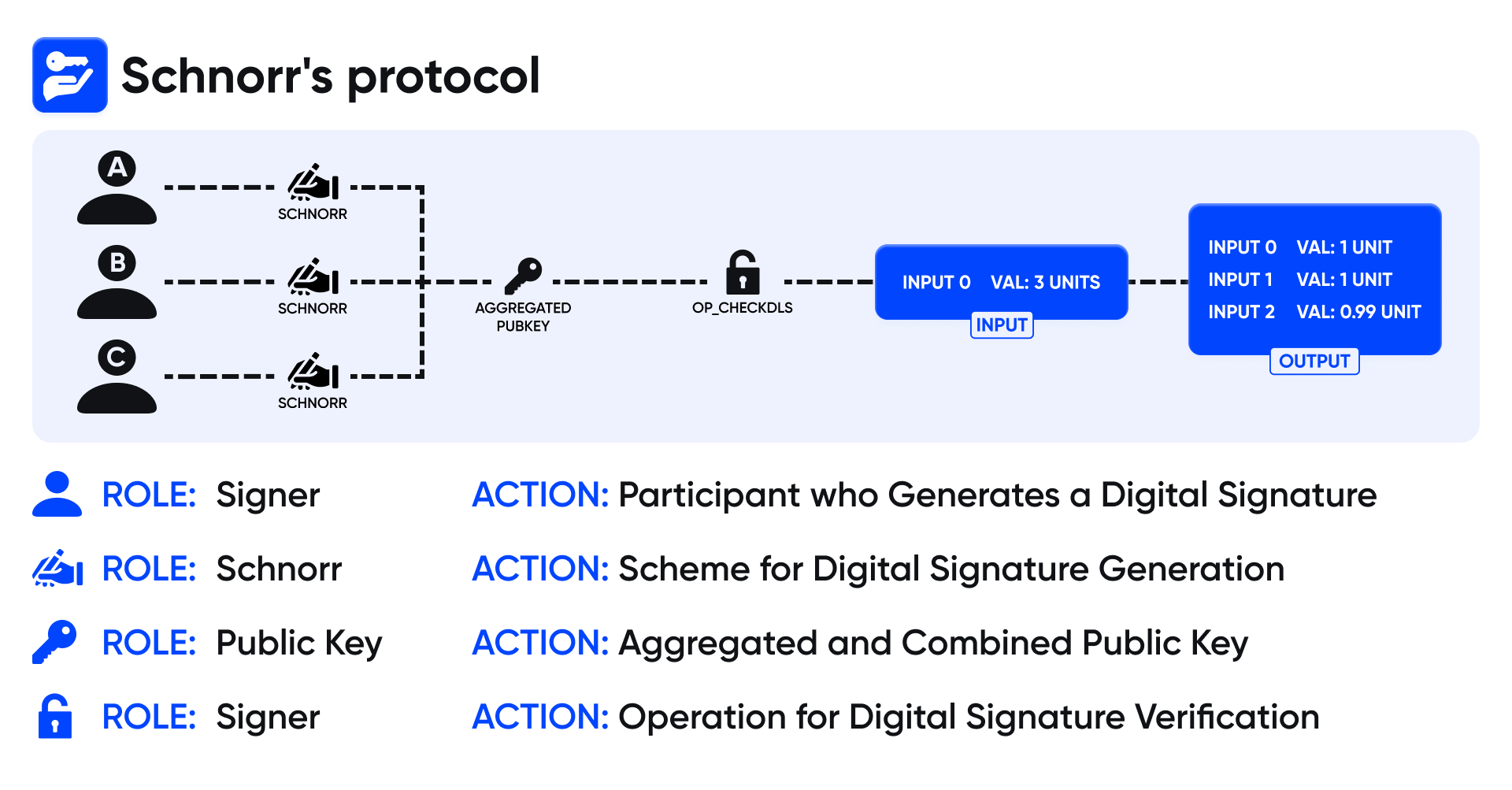
This repository hosts a refined implementation of Schnorr's Protocol, innovatively incorporating a state seed for enhanced security measures. While the underlying proofs may appear intricate, I aim to elucidate their functionality to the best of my ability. However, for a deeper understanding, I encourage referencing the seminal research papers underpinning this implementation, as they offer comprehensive insights.
For further exploration:
Additionally, this repository delves into the concepts of "Zero-Knowledge" Proofs (ZKPs) and Hash-based Message Authentication Codes (HMACs). ZKPs are cryptographic protocols that allow one party (the prover) to prove to another party (the verifier) that a given statement is true, without revealing any additional information beyond the validity of the statement itself. This property is particularly valuable for preserving privacy while establishing trust.
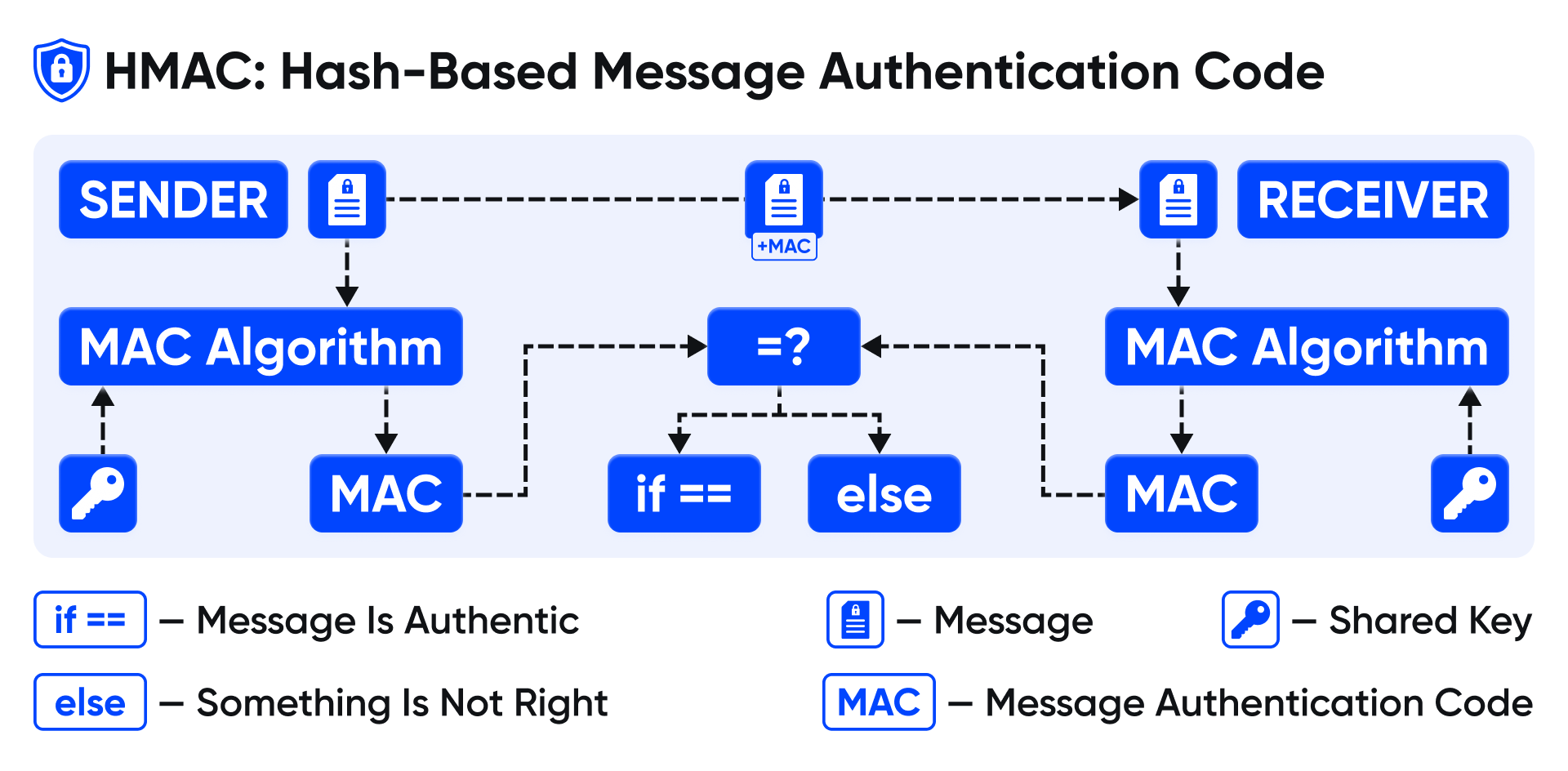
On the other hand, HMACs are a type of cryptographic hash function used for message authentication. They involve a cryptographic hash function (such as SHA-256) and a secret cryptographic key. HMACs provide a way to verify both the data integrity and the authenticity of a message, ensuring that it has not been altered or tampered with during transmission and that it indeed originates from the purported sender.
In today's rapidly evolving IT and application development landscape, "Zero-Knowledge" Proofs (ZKPs) emerge as a pivotal paradigm for authentication security. Their capacity to affirm the validity of a claim, such as proving possession of a secret password — without revealing any sensitive information about the claim itself, such as passwords or hashes, revolutionizes the assurance of secure AAA operations (authentication, authorization, and accounting).
zk-Call & Labs represents an implementation of a Non-Interactive "Zero-Knowledge" Proof (NIZKP) protocol tailored specifically for validating text-based secrets. This framework proves invaluable for safeguarding passwords and other authentication mechanisms, ensuring robust security measures without compromising privacy. Additionally, the integration of HMAC (Hash-Based Message Authentication Code) further fortifies the authentication process, enhancing data integrity and thwarting potential security breaches.
The authentication protocol employed in this system operates based on two fundamental concepts:
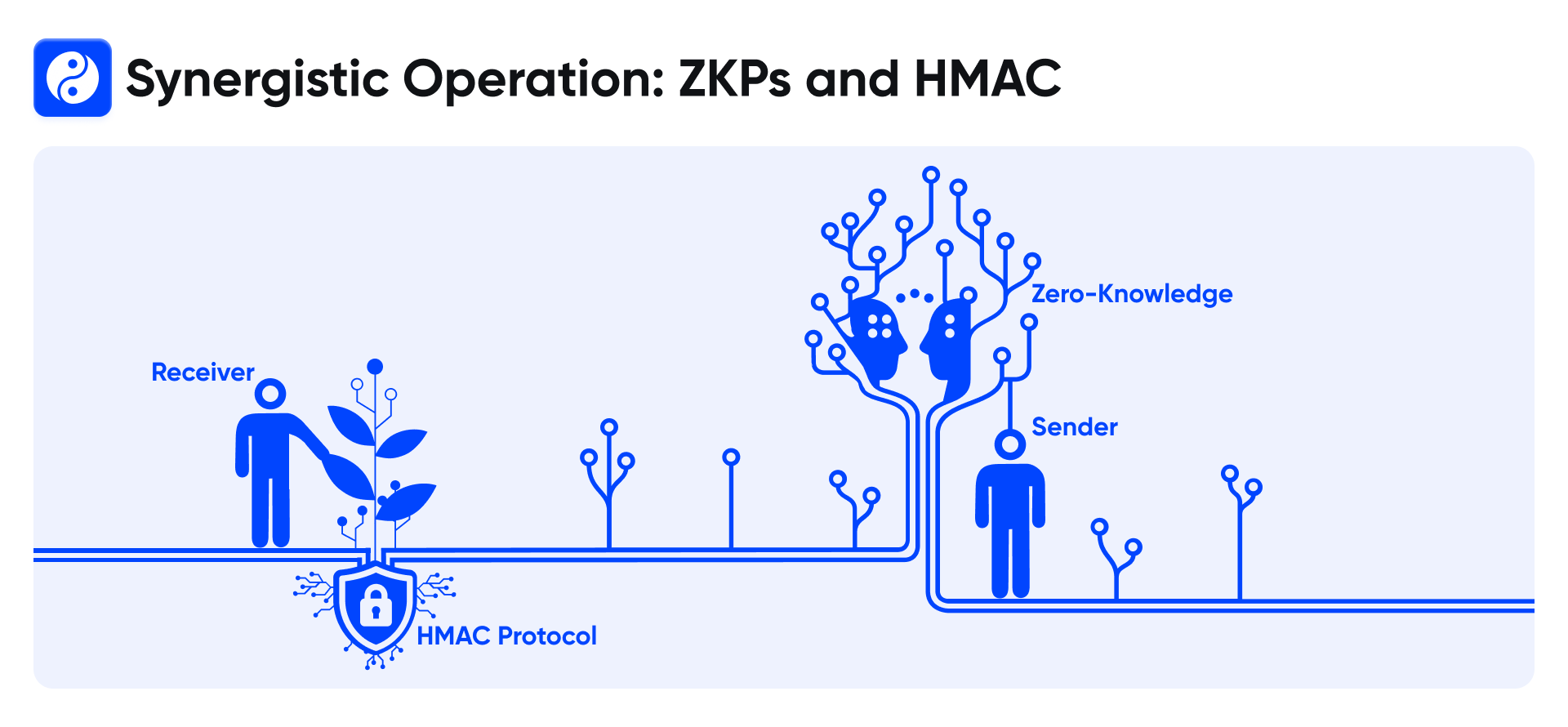
"Zero-Knowledge" Proofs (ZKPs) and Hash-Based Message Authentication Code (HMAC). Let's delve into each of these components and understand how they synergize to ensure secure authentication in messaging applications.
ZKPs form the bedrock of privacy-preserving authentication mechanisms. These proofs allow one party (the prover) to demonstrate the validity of a claim to another party (the verifier) without revealing any additional information beyond the claim's validity. In essence, ZKPs enable authentication without the need for the prover to disclose sensitive data, such as passwords or cryptographic keys.
In the context of messaging applications, ZKPs play a pivotal role in verifying a user's identity without the need to transmit explicit credentials over the network. Instead, users can generate cryptographic proofs attesting to their identity or possession of certain credentials without exposing those credentials themselves. This ensures that sensitive information remains confidential during the authentication process, bolstering security and privacy.
HMAC provides a robust mechanism for verifying the integrity and authenticity of messages exchanged between parties. It involves the use of a cryptographic hash function in conjunction with a secret key to generate a unique code (the HMAC) for each message. This code serves as a digital signature, allowing the recipient to verify that the message has not been tampered with or altered during transmission.
In messaging applications, HMAC can be employed to authenticate message senders and ensure the integrity of communication channels. By appending an HMAC to each message using a shared secret key, both the sender and recipient can validate the message's authenticity upon receipt. Any unauthorized modifications to the message would result in a mismatch between the computed HMAC and the received HMAC, thereby alerting the recipient to potential tampering.
When combined, "Zero-Knowledge" Proofs and HMAC create a formidable framework for secure authentication in messaging applications. ZKPs facilitate identity verification without divulging sensitive information, while HMAC ensures the integrity and authenticity of messages exchanged between parties. Together, these mechanisms uphold the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of communication channels, safeguarding users' privacy and security in the digital realm.
The "Zero-Knowledge" JavaScript API is meant to be simple and intuitive:
The Core Components are key for establishing a secure and efficient framework for cryptographic protocols; streamlining the creation and validation of "Zero-Knowledge" Proofs (ZKPs). They enhance anonymous, data-safe proof validations.
The parameters used to initialize the "Zero-Knowledge" crypto system.
class ZeroKnowledgeParams(NamedTuple):
"""
Parameters used to construct a Zero-Knowledge Proof state, utilizing an elliptic curve and a random salt
"""
algorithm: str # Hashing algorithm name
curve: str # Standard Elliptic Curve name to use
s: int # Random salt for the state
A cryptographic "Zero-Knowledge" signature that can be used to verify future messages.
class ZeroKnowledgeSignature(NamedTuple):
"""
Cryptographic public signature designed to verify future messages
"""
params: ZeroKnowledgeParams # Reference ZeroKnowledge Parameters
signature: int # The public key derived from your original secret
A cryptographic proof that can be verified against a signature.
class ZeroKnowledgeProof(NamedTuple):
"""
Non-deterministic cryptographic Zero-Knowledge Proof designed to confirm that the
private key creating the proof matches the key used to generate the signature
"""
params: ZeroKnowledgeParams # Reference ZeroKnowledge Parameters
c: int # The hash of the signed data and random point, R
m: int # The offset from the secret `r` (`R=r*g`) from c * Hash(secret)
Wrapper that contains a proof and the necessary data to validate the proof against a signature.
class ZeroKnowledgeData(NamedTuple):
"""
Wrapper designed to hold data along with its corresponding signed proof
"""
data: Union[str, bytes, int]
proof: ZeroKnowledgeProof
The ZeroKnowledge class is the central component of ZeroKnowledge and its state (defined by ZeroKnowledgeParams) should be inherently known to both the Client (Prover) and Server (Verifier).
| Method | Params | Role | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
create_signature |
secret: Union[str, bytes] |
Prover | Create a cryptographic signature derived from the value secret to be generated during initial registration and stored for subsequent challenge proofs. |
sign |
secret: Union[str, bytes] data: Union[str, bytes, int] |
Prover | Create a ZeroKnowledgeData object using the secret and any additional data.
|
verify |
challenge: Union[ZeroKnowledgeData, ZeroKnowledgeProof] signature: ZeroKnowledgeSignature data: Optional[Union[str, bytes, int]] |
Verifier | Verify the user-provided challenge against the stored signature and randomly generated token to verify the validity of the challenge. |
TODO: Include Example Usage
import {HMACClient} from './src/HMAC/core/base.mjs';
import {SeedGenerator} from './src/SeedGeneration/core/base.mjs';
// DEBUG constant used for enabling/disabling debugging messages
const DEBUG = true;
// Function to print messages with specific formatting if DEBUG is enabled
function printMsg(who, message) {
if (DEBUG) {
console.log(`[${who}] ${message}\n`);
}
}
// The main function of the script
function main() {
// Generating a client seed using a SeedGenerator instance
const client_seed = new SeedGenerator("job").generate();
// Creating an HMAC client instance for the client using sha256 algorithm and the generated seed
const client_hmac = new HMACClient("sha256", client_seed, 1);
// Creating an HMAC server instance for the server using sha256 algorithm and the same generated seed
const serverhmac = new HMACClient("sha256", client_seed, 1);
// Checking if the encrypted message from client and server matches
if (client_hmac.encrypt_message('') === serverhmac.encrypt_message('')) {
// Defining a message to be sent from client to server
const client_message = 'hello';
// Encrypting the client message in chunks using the client HMAC instance
const client_encrypted_message_for_server = client_hmac.encrypt_message_by_chunks(client_message)
// Printing a message indicating that client has sent an encrypted message
printMsg('client', 'sent has encrypted message')
// Decrypting the message received from client by the server using server HMAC instance
const server_decrypted_message = serverhmac.decrypt_message_by_chunks(client_encrypted_message_for_server)
// Printing a message indicating that server has decrypted the message
printMsg('server', 'server has decrypt message')
// Encrypting the decrypted message by the server
const server_response = serverhmac.encrypt_message(server_decrypted_message)
// Printing a message indicating that server has encrypted the message
printMsg('server', 'server has encrypted message')
// Checking if the encrypted message from client matches the server's response
if (client_hmac.encrypt_message(client_message) === server_response) {
// Printing a message indicating that server has successfully read the message from client
printMsg('client', 'server has read message')
}
}
}
// Calling the main function to start the script execution
main()
// Importing necessary modules
import { ZeroKnowledge } from "./src/ZeroKnowledge/core/base.mjs"; // Importing ZeroKnowledge class
import { ZeroKnowledgeData } from "./src/ZeroKnowledge/models/base.mjs"; // Importing ZeroKnowledgeData class
// DEBUG constant used for enabling/disabling debugging messages
const DEBUG = true;
// Function to print messages with specific formatting if DEBUG is enabled
function printMsg(who, message) {
if (DEBUG) {
console.log(`[${who}] ${message}\n`); // Print formatted message
}
}
// The main function of the script
function main() {
// Generating a client seed using a SeedGenerator instance
const server_password = "SecretServerPassword"; // Define server password
// Creating ZeroKnowledge instances for server and client
const server_object = ZeroKnowledge.new("secp256k1", "sha3_256"); // Initialize server ZeroKnowledge instance
const client_object = ZeroKnowledge.new("secp256k1", "sha3_256"); // Initialize client ZeroKnowledge instance
// Creating signatures for server and client
const server_signature = server_object.create_signature(server_password); // Generate server signature
printMsg("Server", `Server signature: ${server_signature}`); // Print server signature
const idenity = 'John'; // Define client identity
const client_sig = client_object.create_signature(idenity); // Generate client signature
printMsg("Client", `Client signature: ${client_sig}`); // Print client signature
// Signing and generating token for server and client
const server_token = server_object.sign(server_password, client_object.token()); // Sign and generate token for server
printMsg("Server", `Server token: ${server_token}`); // Print server token
const client_proof = client_object.sign(idenity, server_token.data); // Sign token data for client
printMsg("Client", `Client proof: ${client_proof}`); // Print client proof
// Creating ZeroKnowledgeData instance for token verification
const token_veif = new ZeroKnowledgeData(client_proof.data, client_proof.proof);
// Verifying the token against server signature
const server_verif = server_object.verify(token_veif, server_signature); // Verify token against server signature
printMsg("Server", `Server verification: ${server_verif}`); // Print server verification
}
// Calling the main function to start the script execution
main();
// Importing necessary modules
import {ZeroKnowledge} from "./src/ZeroKnowledge/core/base.mjs"; // Importing ZeroKnowledge class
import {ZeroKnowledgeData} from "./src/ZeroKnowledge/models/base.mjs";
import {SeedGenerator} from "./src/SeedGeneration/core/base.mjs";
import {HMACClient} from "./src/HMAC/core/base.mjs"; // Importing ZeroKnowledgeData class
// DEBUG constant used for enabling/disabling debugging messages
const DEBUG = true;
// Function to print messages with specific formatting if DEBUG is enabled
function printMsg(who, message) {
if (DEBUG) {
console.log(`[${who}] ${message}\n`); // Print formatted message
}
}
// The main function of the script
function main() {
// Generating a client seed using a SeedGenerator instance
const server_password = "SecretServerPassword"; // Define server password
// Creating ZeroKnowledge instances for server and client
const server_object = ZeroKnowledge.new("secp256k1", "sha3_256"); // Initialize server ZeroKnowledge instance
const client_object = ZeroKnowledge.new("secp256k1", "sha3_256"); // Initialize client ZeroKnowledge instance
// Creating signatures for server and client
const server_signature = server_object.create_signature(server_password); // Generate server signature
printMsg("Server", `Server signature: ${server_signature}`); // Print server signature
const idenity = 'John'; // Define client identity
const client_sig = client_object.create_signature(idenity); // Generate client signature
printMsg("Client", `Client signature: ${client_sig}`); // Print client signature
// Signing and generating token for server and client
const server_token = server_object.sign(server_password, client_object.token()); // Sign and generate token for server
printMsg("Server", `Server token: ${server_token}`); // Print server token
const client_proof = client_object.sign(idenity, server_token.data); // Sign token data for client
printMsg("Client", `Client proof: ${client_proof}`); // Print client proof
// Creating ZeroKnowledgeData instance for token verification
const token_veif = new ZeroKnowledgeData(client_proof.data, client_proof.proof);
// Verifying the token against server signature
const server_verif = server_object.verify(token_veif, server_signature); // Verify token against server signature
printMsg("Server", `Server verification: ${server_verif}`); // Print server verification
if (server_verif) {
// Generating a client seed using a SeedGenerator instance
const client_seed = new SeedGenerator("job").generate();
// Creating an HMAC client instance for the client using sha256 algorithm and the generated seed
const client_hmac = new HMACClient("sha256", client_seed, 1);
// Creating an HMAC server instance for the server using sha256 algorithm and the same generated seed
const serverhmac = new HMACClient("sha256", client_seed, 1);
// Checking if the encrypted message from client and server matches
if (client_hmac.encrypt_message('') === serverhmac.encrypt_message('')) {
// Defining a message to be sent from client to server
const client_message = 'hello';
// Encrypting the client message in chunks using the client HMAC instance
const client_encrypted_message_for_server = client_hmac.encrypt_message_by_chunks(client_message)
// Printing a message indicating that client has sent an encrypted message
printMsg('client', 'sent has encrypted message')
// Decrypting the message received from client by the server using server HMAC instance
const server_decrypted_message = serverhmac.decrypt_message_by_chunks(client_encrypted_message_for_server)
// Printing a message indicating that server has decrypted the message
printMsg('server', 'server has decrypt message')
// Encrypting the decrypted message by the server
const server_response = serverhmac.encrypt_message(server_decrypted_message)
// Printing a message indicating that server has encrypted the message
printMsg('server', 'server has encrypted message')
// Checking if the encrypted message from client matches the server's response
if (client_hmac.encrypt_message(client_message) === server_response) {
// Printing a message indicating that server has successfully read the message from client
printMsg('client', 'server has read message')
}
}
}
}
// Calling the main function to start the script execution
main();
![zk-Call Preview [JS]](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/zk-Call/zkp-hmac-communication-js/main/assets/zk-Call%20Preview%20%5BJS%5D.png)





.png)
.png)