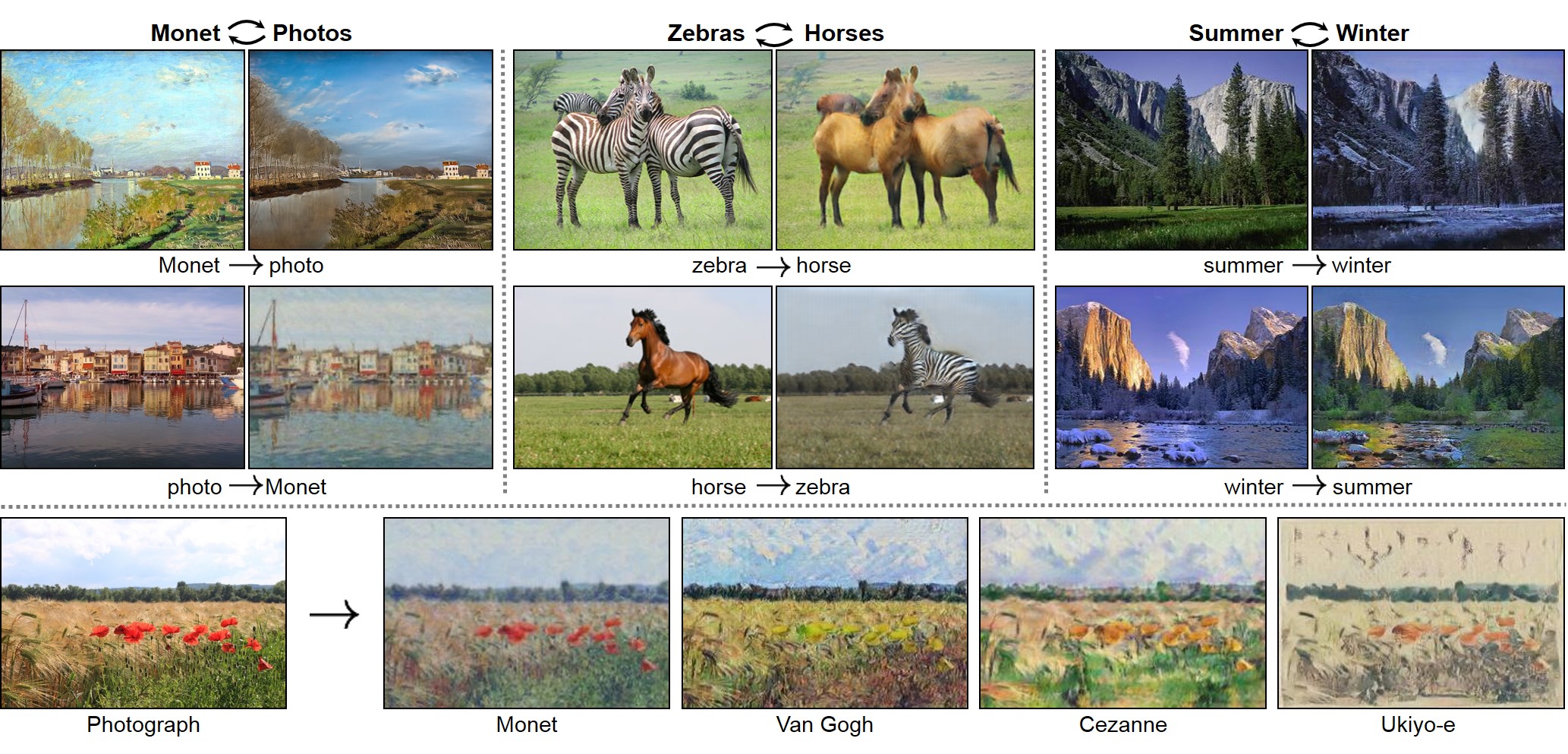
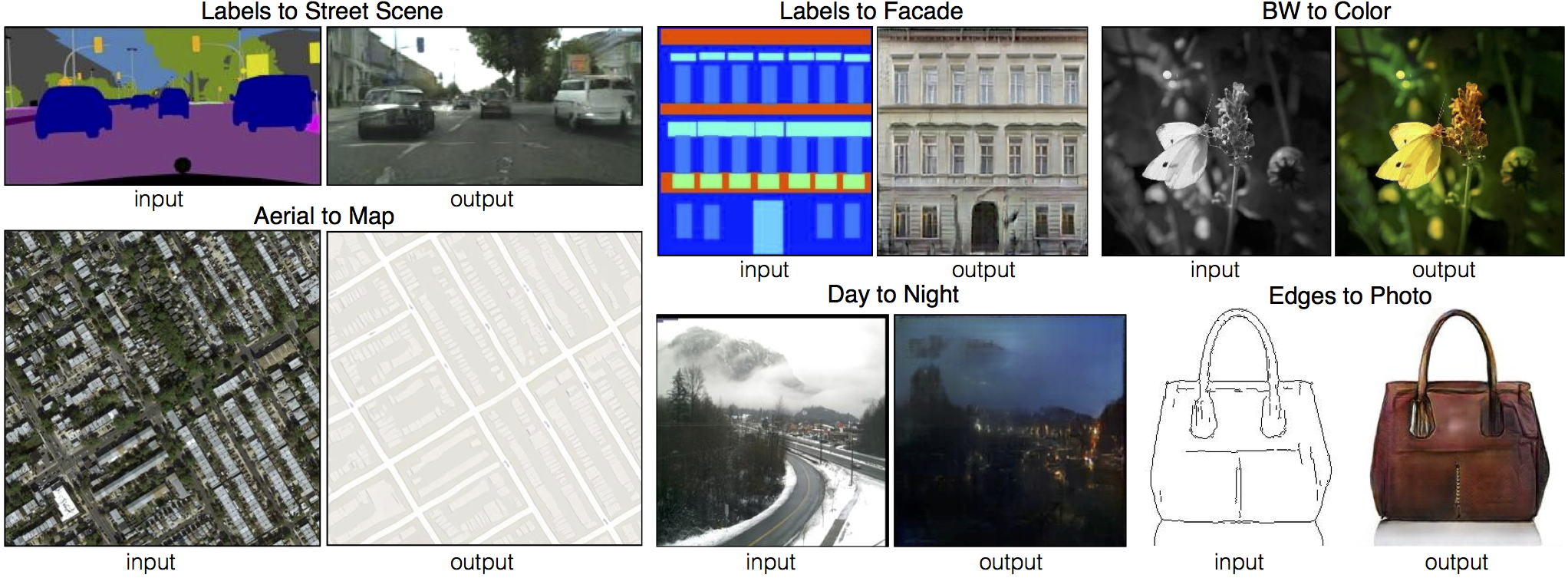
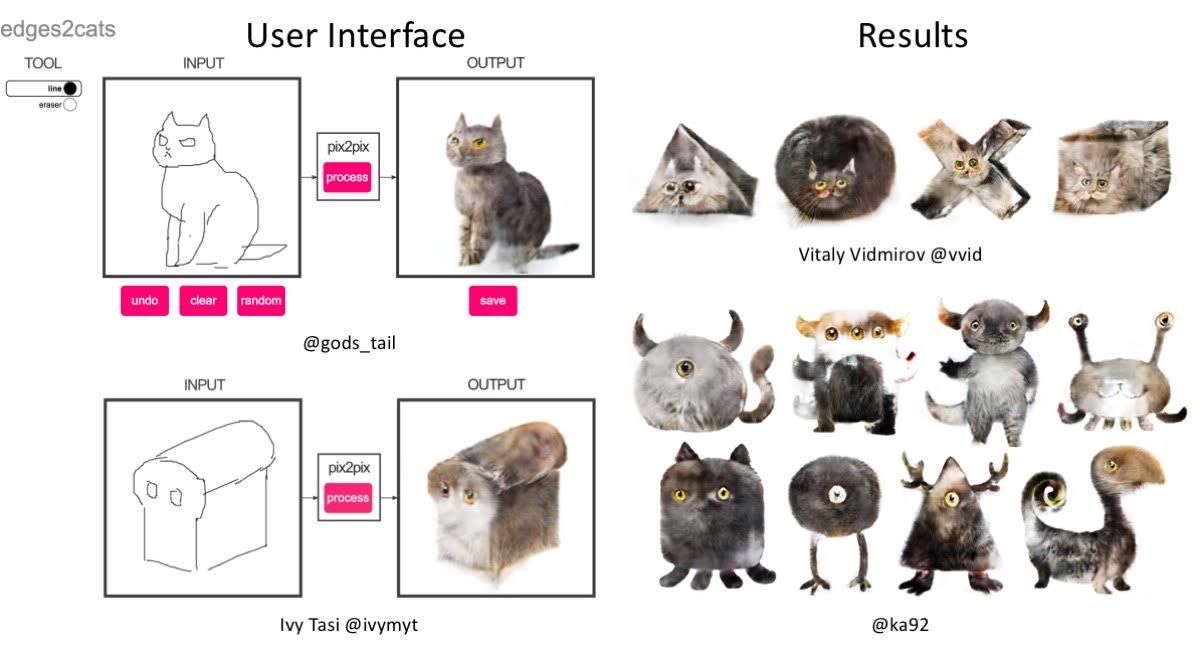
This is our PyTorch implementation for both unpaired and paired image-to-image translation. It is still under active development.
The code was written by Jun-Yan Zhu and Taesung Park.
This PyTorch implementation produces results comparable or better than our original Torch software. If you would like to reproduce the exact same results as in the papers, check out the original CycleGAN Torch and pix2pix Torch code
Note: The current software works well with PyTorch 0.1-0.3. PyTorch 0.4 support will be added by the end of May.
Written by Christopher Hesse
If you use this code for your research, please cite:
Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks
Jun-Yan Zhu*, Taesung Park*, Phillip Isola, Alexei A. Efros
In ICCV 2017. (* equal contributions)
Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks
Phillip Isola, Jun-Yan Zhu, Tinghui Zhou, Alexei A. Efros
In CVPR 2017.
[Tensorflow] (by Harry Yang), [Tensorflow] (by Archit Rathore), [Tensorflow] (by Van Huy), [Tensorflow] (by Xiaowei Hu), [Tensorflow-simple] (by Zhenliang He), [TensorLayer] (by luoxier), [Chainer] (by Yanghua Jin), [Minimal PyTorch] (by yunjey), [Mxnet] (by Ldpe2G), [lasagne/keras] (by tjwei)
[Tensorflow] (by Christopher Hesse), [Tensorflow] (by Eyyüb Sariu), [Tensorflow (face2face)] (by Dat Tran), [Tensorflow (film)] (by Arthur Juliani), [Tensorflow (zi2zi)] (by Yuchen Tian), [Chainer] (by mattya), [tf/torch/keras/lasagne] (by tjwei), [Pytorch] (by taey16)
- Linux or macOS
- Python 2 or 3
- CPU or NVIDIA GPU + CUDA CuDNN
- Install PyTorch and dependencies from http://pytorch.org
- Install Torch vision from the source.
git clone https://github.com/pytorch/vision
cd vision
python setup.py installpip install visdom
pip install dominate- Clone this repo:
git clone https://github.com/junyanz/pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix
cd pytorch-CycleGAN-and-pix2pix- Download a CycleGAN dataset (e.g. maps):
bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh maps- Train a model:
#!./scripts/train_cyclegan.sh
python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_gan --no_dropout- To view training results and loss plots, run
python -m visdom.serverand click the URL http://localhost:8097. To see more intermediate results, check out./checkpoints/maps_cyclegan/web/index.html - Test the model:
#!./scripts/test_cyclegan.sh
python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/maps --name maps_cyclegan --model cycle_gan --phase test --no_dropoutThe test results will be saved to a html file here: ./results/maps_cyclegan/latest_test/index.html.
- Download a pix2pix dataset (e.g.facades):
bash ./datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh facades- Train a model:
#!./scripts/train_pix2pix.sh
python train.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --lambda_A 100 --dataset_mode aligned --no_lsgan --norm batch --pool_size 0- To view training results and loss plots, run
python -m visdom.serverand click the URL http://localhost:8097. To see more intermediate results, check out./checkpoints/facades_pix2pix/web/index.html - Test the model (
bash ./scripts/test_pix2pix.sh):
#!./scripts/test_pix2pix.sh
python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades --name facades_pix2pix --model pix2pix --which_model_netG unet_256 --which_direction BtoA --dataset_mode aligned --norm batchThe test results will be saved to a html file here: ./results/facades_pix2pix/latest_val/index.html.
More example scripts can be found at scripts directory.
- You can download a pretrained model (e.g. horse2zebra) with the following script:
bash pretrained_models/download_cyclegan_model.sh horse2zebraThe pretrained model is saved at ./checkpoints/{name}_pretrained/latest_net_G.pth.
- To test the model, you also need to download the horse2zebra dataset:
bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh horse2zebra- Then generate the results using
python test.py --dataroot datasets/horse2zebra/testA --checkpoints_dir ./checkpoints/ --name horse2zebra_pretrained --no_dropout --model test --dataset_mode single --loadSize 256The results will be saved at ./results/. Use --results_dir {directory_path_to_save_result} to specify the results directory.
-
Note: The models trained using Torch and PyTorch produce slightly different results, although we were not able to decide which result is better. If you would like to reproduce the same results in our paper, we recommend using the pretrained models in the Torch codebase.
-
If you would like to apply a pre-trained model to a collection of input images (rather than image pairs), please use
--dataset_mode singleand--model testoptions. Here is a script to apply a model to Facade label maps (stored in the directoryfacades/testB).
#!./scripts/test_single.sh
python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades/testB/ --name {your_trained_model_name} --model test --dataset_mode singleYou might want to specify --which_model_netG to match the generator architecture of the trained model.
Download a pre-trained model with ./pretrained_models/download_pix2pix_model.sh.
- For example, if you would like to download label2photo model on the Facades dataset,
bash pretrained_models/download_pix2pix_model.sh facades_label2photo- Download the pix2pix facades datasets
bash ./datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh facades- Then generate the results using
python test.py --dataroot ./datasets/facades/ --which_direction BtoA --model pix2pix --name facades_label2photo_pretrained --dataset_mode aligned --which_model_netG unet_256 --norm batchNote that we specified --which_direction BtoA as Facades dataset's A to B direction is photos to labels.
- See a list of currently available models at
bash pretrained_models/download_pix2pix_model.sh
- Flags: see
options/train_options.pyandoptions/base_options.pyfor all the training flags; seeoptions/test_options.pyandoptions/base_options.pyfor all the test flags. - CPU/GPU (default
--gpu_ids 0): set--gpu_ids -1to use CPU mode; set--gpu_ids 0,1,2for multi-GPU mode. You need a large batch size (e.g.--batchSize 32) to benefit from multiple GPUs. - Visualization: during training, the current results can be viewed using two methods. First, if you set
--display_id> 0, the results and loss plot will appear on a local graphics web server launched by visdom. To do this, you should havevisdominstalled and a server running by the commandpython -m visdom.server. The default server URL ishttp://localhost:8097.display_idcorresponds to the window ID that is displayed on thevisdomserver. Thevisdomdisplay functionality is turned on by default. To avoid the extra overhead of communicating withvisdomset--display_id 0. Second, the intermediate results are saved to[opt.checkpoints_dir]/[opt.name]/web/as an HTML file. To avoid this, set--no_html. - Preprocessing: images can be resized and cropped in different ways using
--resize_or_cropoption. The default option'resize_and_crop'resizes the image to be of size(opt.loadSize, opt.loadSize)and does a random crop of size(opt.fineSize, opt.fineSize).'crop'skips the resizing step and only performs random cropping.'scale_width'resizes the image to have widthopt.fineSizewhile keeping the aspect ratio.'scale_width_and_crop'first resizes the image to have widthopt.loadSizeand then does random cropping of size(opt.fineSize, opt.fineSize). - Fine-tuning/Resume training: to fine-tune a pre-trained model, or resume the previous training, use the
--continue_trainflag. The program will then load the model based onwhich_epoch. By default, the program will initialize the epoch count as 1. Set--epoch_count <int>to specify a different starting epoch count. - For Conda users, we include a script
./scripts/conda_deps.shto install PyTorch and other libraries.
Download the CycleGAN datasets using the following script. Some of the datasets are collected by other researchers. Please cite their papers if you use the data.
bash ./datasets/download_cyclegan_dataset.sh dataset_namefacades: 400 images from the CMP Facades dataset. [Citation]cityscapes: 2975 images from the Cityscapes training set. [Citation]maps: 1096 training images scraped from Google Maps.horse2zebra: 939 horse images and 1177 zebra images downloaded from ImageNet using keywordswild horseandzebraapple2orange: 996 apple images and 1020 orange images downloaded from ImageNet using keywordsappleandnavel orange.summer2winter_yosemite: 1273 summer Yosemite images and 854 winter Yosemite images were downloaded using Flickr API. See more details in our paper.monet2photo,vangogh2photo,ukiyoe2photo,cezanne2photo: The art images were downloaded from Wikiart. The real photos are downloaded from Flickr using the combination of the tags landscape and landscapephotography. The training set size of each class is Monet:1074, Cezanne:584, Van Gogh:401, Ukiyo-e:1433, Photographs:6853.iphone2dslr_flower: both classes of images were downlaoded from Flickr. The training set size of each class is iPhone:1813, DSLR:3316. See more details in our paper.
To train a model on your own datasets, you need to create a data folder with two subdirectories trainA and trainB that contain images from domain A and B. You can test your model on your training set by setting --phase train in test.py. You can also create subdirectories testA and testB if you have test data.
You should not expect our method to work on just any random combination of input and output datasets (e.g. cats<->keyboards). From our experiments, we find it works better if two datasets share similar visual content. For example, landscape painting<->landscape photographs works much better than portrait painting <-> landscape photographs. zebras<->horses achieves compelling results while cats<->dogs completely fails.
Download the pix2pix datasets using the following script. Some of the datasets are collected by other researchers. Please cite their papers if you use the data.
bash ./datasets/download_pix2pix_dataset.sh dataset_namefacades: 400 images from CMP Facades dataset. [Citation]cityscapes: 2975 images from the Cityscapes training set. [Citation]maps: 1096 training images scraped from Google Mapsedges2shoes: 50k training images from UT Zappos50K dataset. Edges are computed by HED edge detector + post-processing. [Citation]edges2handbags: 137K Amazon Handbag images from iGAN project. Edges are computed by HED edge detector + post-processing. [Citation]
We provide a python script to generate pix2pix training data in the form of pairs of images {A,B}, where A and B are two different depictions of the same underlying scene. For example, these might be pairs {label map, photo} or {bw image, color image}. Then we can learn to translate A to B or B to A:
Create folder /path/to/data with subfolders A and B. A and B should each have their own subfolders train, val, test, etc. In /path/to/data/A/train, put training images in style A. In /path/to/data/B/train, put the corresponding images in style B. Repeat same for other data splits (val, test, etc).
Corresponding images in a pair {A,B} must be the same size and have the same filename, e.g., /path/to/data/A/train/1.jpg is considered to correspond to /path/to/data/B/train/1.jpg.
Once the data is formatted this way, call:
python datasets/combine_A_and_B.py --fold_A /path/to/data/A --fold_B /path/to/data/B --fold_AB /path/to/dataThis will combine each pair of images (A,B) into a single image file, ready for training.
If you use this code for your research, please cite our papers.
@inproceedings{CycleGAN2017,
title={Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networkss},
author={Zhu, Jun-Yan and Park, Taesung and Isola, Phillip and Efros, Alexei A},
booktitle={Computer Vision (ICCV), 2017 IEEE International Conference on},
year={2017}
}
@inproceedings{isola2017image,
title={Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks},
author={Isola, Phillip and Zhu, Jun-Yan and Zhou, Tinghui and Efros, Alexei A},
booktitle={Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2017 IEEE Conference on},
year={2017}
}
CycleGAN: Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks
pix2pix: Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial nets
iGAN: Interactive Image Generation via Generative Adversarial Networks
If you love cats, and love reading cool graphics, vision, and learning papers, please check out the Cat Paper Collection:
[Github] [Webpage]
Code is inspired by pytorch-DCGAN.