- Show how adding renewable generation in the right places in the network can reduce the need for network expansion
- Compare optimisation outcome of generation-only expansion vs. transmission-only expansion, and everything in between
- Computed in
build_renewable_profiles- Installable potentials based on land use, nature reserves and bathymetry (river depths?) data
- Weather potentials calculated by
atlite- Uses cutouts defined in
renewable.solar.cutout(europe-2013-sarahfor solar)
- Uses cutouts defined in
- By default, the cutouts for 2013 are retrieved from Zenodo in
retrieve_cutouts - I recreated ERA5 cutouts with atlite by defining a new cutout called
europe-2022-era5- The ERA5 website says data is available with a ~5-day delay from realtime
- As of 2022-09-29 13:19, the most recent data available is from 2022-09-22
- Usually, solar irradiation data is refined with Sarah data, but as of 2022-09-28, that's only available till the end of 2017, so I only use ERA5 data
- The cutout date range is defined separately from the snapshots range
- The request spanning multiple months looks like this:
request = { 'product_type': 'reanalysis', 'format': 'netcdf', 'variable': ['runoff'], 'area': [72.0, -12.0, 33.0, 34.8], 'grid': [0.3, 0.3], 'year': '2022', 'month': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9], 'day': [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31 ], 'time': [ '00:00', '01:00', '02:00', '03:00', '04:00', '05:00', '06:00', '07:00', '08:00', '09:00', '10:00', '11:00', '12:00', '13:00', '14:00', '15:00', '16:00', '17:00', '18:00', '19:00', '20:00', '21:00', '22:00', '23:00' ] }
- I.e. there's not really a way to request data for a part of the final month
- For building the hydro profile, it seems that storage level calculation presumes at least a week of data
ValueError: Moving window (=168) must between 1 and 48, inclusive, functionresult.rollinginatlite/convert.py - When setting a week, I get a new error:
File "/Users/zoltan/mambaforge/envs/pypsa-eur/lib/python3.9/site-packages/atlite/convert.py", line 746, in runoff assert len(years), "Need at least a full year of data (more is better)"- This seems to happen due the
normalize_using_yearly=eia_statsparameter, because those stats include only data up to 2020: https://www.eia.gov/international/data/world/electricity/electricity-generation?pd=2&p=000000000000000000000000000000g&u=1&f=A&v=mapbubble&a=-&i=none&vo=value&t=R&g=000000000000002&l=73-1028i008017kg6368g80a4k000e0ag00gg0004g8g0ho00g000400008&s=315532800000&e=1577836800000&ev=false&
- This seems to happen due the
- This is currently loaded from OPSD in the
retrieve_load_datain the Snakefile, which only has data until 2020-09-30 (as of 2022-09-28)- As a quickfix, I replaced the 2020-09-21 date with 2022-09-21 in
data/load_raw.csv
- As a quickfix, I replaced the 2020-09-21 date with 2022-09-21 in
Renewables expansion_limit should probably be run along with listing
at least solar and onwind in electricity.extendable_carriers.
Grid expansion factor (scenario.ll) |
v1.01 |
v1.1 |
v1.0 |
Renewables expansion_limit |
false |
1.0 |
1.1 |
Extendable renewables (extendable_carriers) |
[] |
[] |
[solar, onwind] |
Deleted base.nc? |
Yes | No | No |
| successful grid expansion iterations | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| final iteration outcome | Numerical trouble | Infeasible or unbounded | Infeasible or unbounded |
| num LP iterations in final iteration | 573 | 0 | 0 |
| output file generated? | No | Yes | Yes |
- Use
datashaderfor dense data on a map (example) config.default.yamldefinesagg_p_nom_limits: data/agg_p_nom_minmax.csv- How are already installed renewables presented?
- They weren't, but I added them by listing wind and solar in
renewable_capacities_from_OPSD
- They weren't, but I added them by listing wind and solar in
- Nice way to highlight lines: link
- Running
ilopfonlv1.01succeeds on the first few iterations, but fails on later iterations with Gurobi reporting "Numerical trouble encountered". Reducing the number of iterations may help, but it's weird - CBC doesn't run in parallel unless compiled so. I tried to fix that using https://sysid.github.io/cbc/ but it still
seems to not use all cores :(
- Actually, the default simplex algorithm is inherently sequential. Gurobi runs it in parallel with several cores of the barrier algorith (whose factorization stage can be parallelised)
- Removing GB from the countries list also removes Ireland :/
- As of 2022-06-27, the most recent available load data on
open-power-system-datais from 2020-09-30, even though the snapshot is from 2020-10-06.- In the CSV, the relevant column says
DE_load_actual_entsoe_transparency, so there may be fresher data available on the ENTSO-E transparency page
- In the CSV, the relevant column says
solve_operations_network.pysays it "Solves linear optimal dispatch in hourly resolution using the capacities of previous capacity expansion in rule :mod:solve_network."- From
pypsaOptimal Power Flow documentation: The linear OPF module can optimise the dispatch of generation and storage and the capacities of generation, storage and transmission infrastructure. lopfis used if (transmission) lines are not to be extended.ilopfis used with iterative transmission line expansion.- The rule
solve_all_networksruns the rulesolve_networkfor allscenarios in the configuration file. - Defining the same carrier type in both
extendable_carriers/Generatorandconventional_carrersresults in errors likeAssertionError: In Generator cluster p_nom_extendable the values of attribute p_nom_extendable do not agree: Generator C3113 False 2 OCGT True
- Paper by Tom Brown's gang from June 2021 shows how to cluster smart
- To plot a DAG, run
# The `tail -n +4` bit skips the Gurobi logging
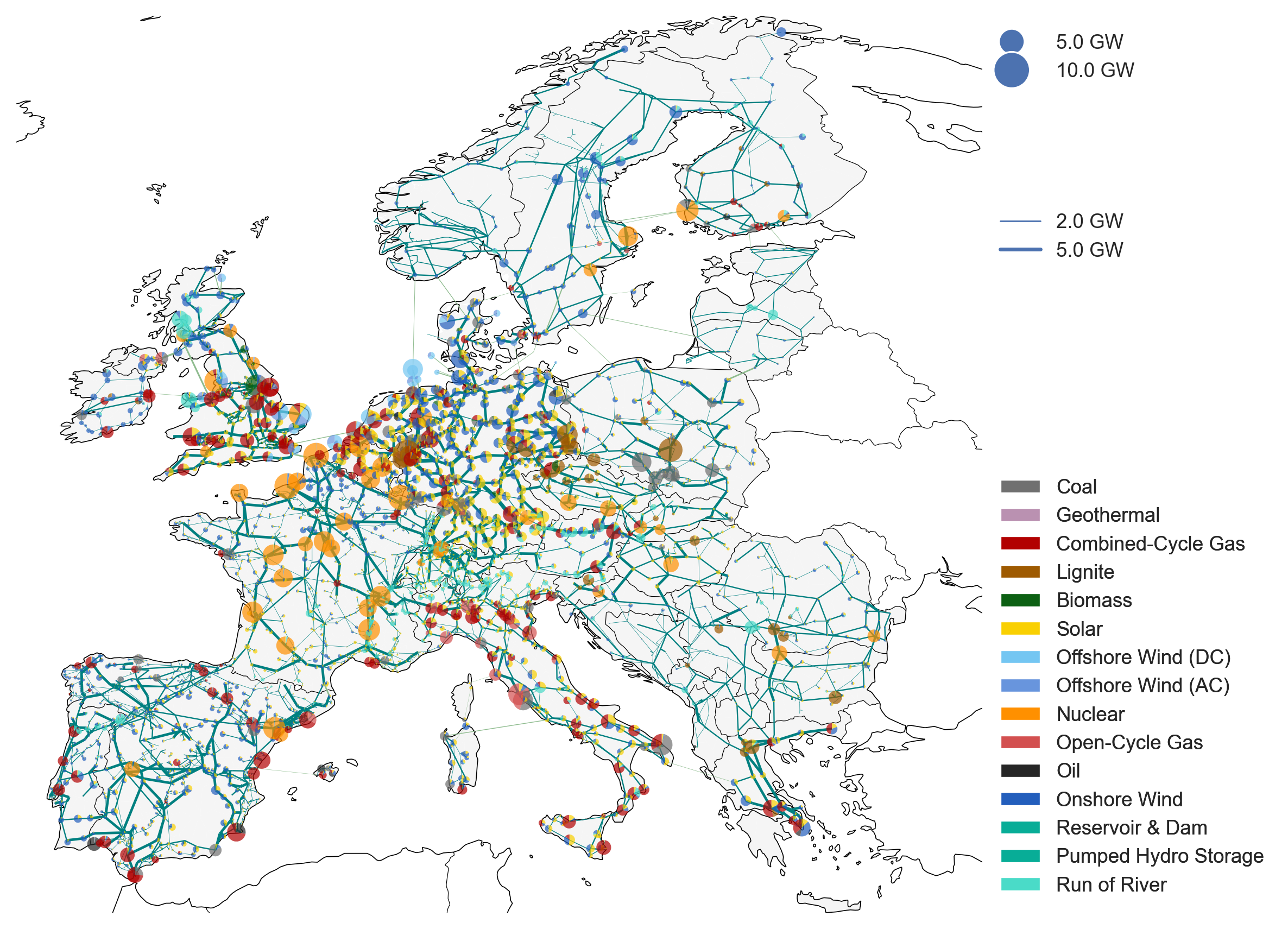
snakemake -n --rulegraph solve_all_networks | tail -n +4 | dot -Tsvg > dags/solve_all_networks.svgPyPSA-Eur is an open model dataset of the European power system at the transmission network level that covers the full ENTSO-E area. The model is suitable both for operational studies and generation and transmission expansion planning studies. The continental scope and highly resolved spatial scale enables a proper description of the long-range smoothing effects for renewable power generation and their varying resource availability.
The model is described in the documentation and in the paper PyPSA-Eur: An Open Optimisation Model of the European Transmission System, 2018, arXiv:1806.01613.
WARNING: Please read the limitations section of the documentation and paper carefully before using the model. We do not recommend to use the full resolution network model for simulations. At high granularity the assignment of loads and generators to the nearest network node may not be a correct assumption, depending on the topology of the underlying distribution grid, and local grid bottlenecks may cause unrealistic load-shedding or generator curtailment. We recommend to cluster the network to a couple of hundred nodes to remove these local inconsistencies. See the discussion in Section 3.4 "Model validation" of the paper.
The model building routines are defined through a snakemake workflow. The model is designed to be imported into the open toolbox PyPSA for operational studies as well as generation and transmission expansion planning studies.
The dataset consists of:
- A grid model based on a modified GridKit extraction of the ENTSO-E Transmission System Map. The grid model contains 6763 lines (alternating current lines at and above 220kV voltage level and all high voltage direct current lines) and 3642 substations.
- The open power plant database powerplantmatching.
- Electrical demand time series from the OPSD project.
- Renewable time series based on ERA5 and SARAH, assembled using the atlite tool.
- Geographical potentials for wind and solar generators based on land use (CORINE) and excluding nature reserves (Natura2000) are computed with the atlite library.
Already-built versions of the model can be found in the accompanying Zenodo repository.
A version of the model that adds building heating, transport and industry sectors to the model, as well as gas networks, can be found in the PyPSA-Eur-Sec repository.