FIES is a QEMU fault injection extension.
The following picture shows the main points, where FIES takes action during an QEMU binary translation:
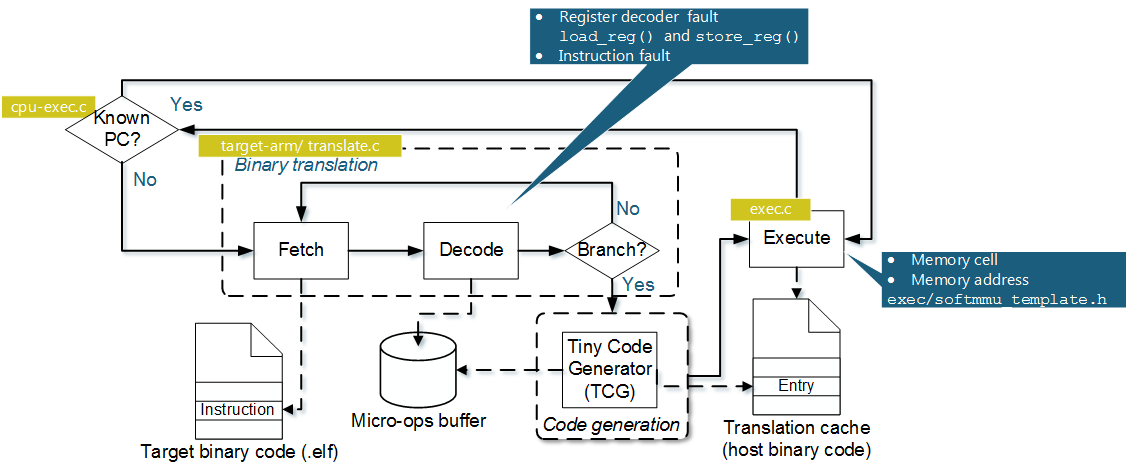
The working principle of FIES is described in the following publications:
- A. Höller, G. Schönfelder, N. Kajtazovic, T. Rauter, and C. Kreiner, “FIES: A Fault Injection Framework for the Evaluation of Self-Tests for COTS-Based Safety-Critical Systems,” in 15th IEEE International Microprocessor Test and Verification Workshop (MTV), 2014, vol. 2015-April, pp. 105–110.
- A. Höller, G. Macher, T. Rauter, J. Iber, and C. Kreiner, “A Virtual Fault Injection Framework for Reliability-Aware Software Development,” in IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks Workshops (DSN-W), 2015, pp. 69 – 74.
- A. Höller, A. Krieg, T. Rauter, J. Iber, and C. Kreiner, “QEMU-Based Fault Injection for a System-Level Analysis of Software Countermeasures Against Fault Attacks,” in 18th Euromicro Conference on Digital System Design (DSD), 2015, pp. 530 – 533.
-
Install required libraries: libffi, libiconv, gettext, python, pkg-config, glib, sdl, zlib, pixman, libfdt, libxml2 For detailed information about QEMU-required packages see http://wiki.qemu.org/Hosts/Linux . Additionally FIES requires
libxml2. -
Configure and build FIES
CF=$(xml2-config --cflags)
LF=$(xml2-config --libs)
PP=$(which python2)
./configure --target-list=arm-softmmu --extra-cflags="$CF" --extra-ldflags="$LF" --python="$PP" --enable-sdl
cd pixman
./configure
cd ..
makeFor illustration we created a simple hello-world app and exemplary fault libraries in the folder fies_sandbox
Currently, FIES supports only ARM architectures. Thus, to compile an application that should be simulated with FIES compile it for ARM.
GCC example:
arm-none-eabi-gcc -marm *.c --specs=nosys.specsClang example:
clang -target arm -marm *.c If you use Code Sourcery use the following settings (C/C++ Build > Tool Settings)
- Board: QEMU ARM Simulator (VFP)
- Profile: Simulator
- Hosting: Hosted
Start the application the same way as you start a normal QEMU emulation (see http://wiki.qemu.org/download/qemu-doc.html#pcsys_005fquickstart)
Hint: to pass arguments use the -append flag
arm-softmmu/qemu-system-arm -semihosting -kernel <binary>Use the -profiling flag to record register and memory usage
Options:
mprofile memory usagerprofile register usage
Results are stored in profiling_meory.txt or/and profiling_registers.txt
Example:
arm-softmmu/qemu-system-arm -semihosting -kernel <binary> -profiling rmFaults that should be injected are described in an XML file.
XML fault lib example:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<injection>
<fault>
<id>1</id>
<component>RAM</component>
<target>MEMORY CELL</target>
<mode>SF</mode>
<trigger>ACCESS</trigger>
<type>PERMANENT</type>
<params>
<address>0x07FFFFDC</address>
<mask>0xFF</mask>
<set_bit>0xFF</set_bit>
</params>
</fault>
</injection>XML Fields:
<fault>: Defines start and end of fault description. Multiple faults are injected concurrently if multiple fault descriptions are provided.<id>: Defines fault ID<component>:CPU,RAM, orREGISTER<target>:- for
CPUfaults:INSTRUCTION DECODER,INSTRUCTION EXECUTION, orCONDITION FLAGS - for
REGISTERfaults:ADDRESS DECODER,REGISTER CELL - for
RAMfaults:ADDRESS DECODER,MEMORY CELL
- for
<mode>: Defines the fault mode- Condition flags:
VF,ZF,CF,NF,QF - General fault modes:
NEW VALUE,SF,BIT-FLIP - Operation-dependent static faults:
TF0,TF1,WDF0,WDF1,IRF0,IRF1,DRDF0,DRDF1,RDF0,RDF1 - Operation-dependent dynamic faults:
RDF00,RDF01,RDF10,RDF11,IRF00,IRF01,IRF10,IRF11,DRDF00,DRDF01,DRDF10,DRDF11 - Coupling faults:
CFST00,CFST01,CFST10,CFST11,CFTR00,CFTR01,CFTR10,CFTR11,CFWD00,CFWD01,CFWD10,CFWD11,CFRD00,CFRD01,CFRD10,CFRD11,CFIR00,CFIR01,CFIR10,CFIR11,CFDR00,CFDR01,CFDR10,CFDR11,CFDS0W00,CFDS0W01,CFDS0W10,CFDS0W11,CFDSW00,CFDS1W01,CFDS1W10,CFDS1W11,CFDS0R00,CFDS0R01,CFDS0R10,CFDS1R11
- Condition flags:
<trigger>:ACCESS,TIME,PC<type>:TRANSIENT,PERMANENT,INTERMITTEND<duration>: duration for intemittend and transient faults in ms (e.g.10MS)<interval>: interval for intermittent faults in ms (e.g.10MS)<params>: parameter descriptions to specify fault mode<address>: register or memory address<mask>: mask for the position where fault should be active (e.g. to inject fault in last bit0x1), or new value definition inNEW VALUEmode<cf_address>: coupling addrsss for coupling faults<instruction>: instruction number that should be replaced forCPU INSTRUCTION DECODERfaults<set_bit>: mask to select if bits defined in<mask>should be set (e.g.0x1for SAF-1) or resetted (e.g.0x0for SAF-0). Aggressor-bit mask for intercoupling faults.
Use the -fi flag to give the fault library and start FIES with fault injection
arm-softmmu/qemu-system-arm -semihosting -kernel <binary> -fi <fault-lib.xml>See fies.log for error messages