FoolHD: Fooling speaker identification by Highly imperceptible adversarial Disturbances
Ali Shahin Shamsabadi1*, Francisco Sepúlveda Teixeira2*, Alberto Abad2, Bhiksha Raj3, Andrea Cavallaro1, Isabel Trancoso2
1CIS, Queen Mary University of London, UK.
2INESC-ID/IST, University of Lisbon, Portugal.
3Carnegie Mellon University, USA.
*Authors contributed equally.
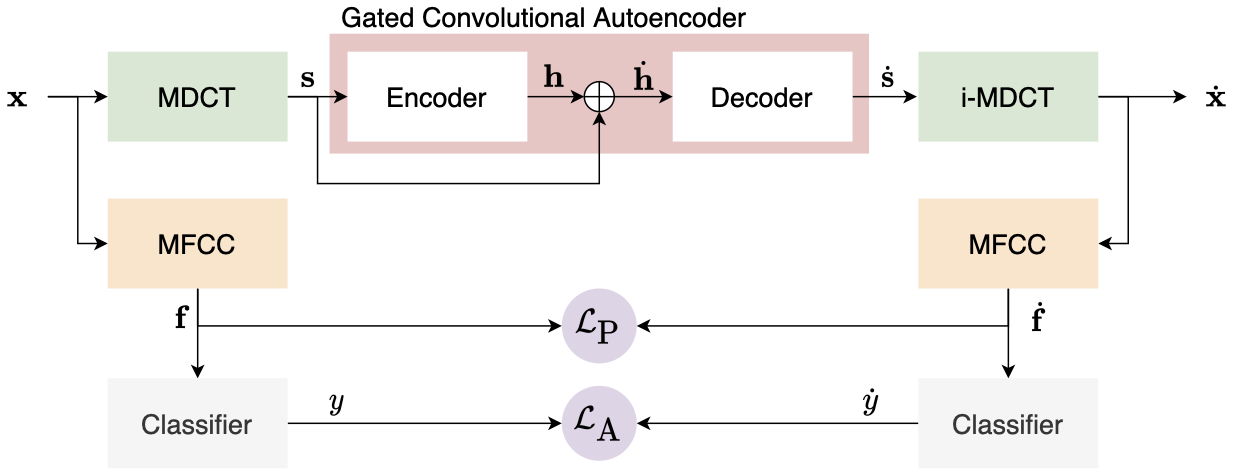
Speaker identification models are vulnerable to carefully designed adversarial perturbations of their input signals that induce misclassification. In this work, we propose a white-box steganography-inspired adversarial attack that generates imperceptible adversarial perturbations against a speaker identification model. Our approach, FoolHD, uses a Gated Convolutional Autoencoder that operates in the DCT domain and is trained with a multi-objective loss function, in order to generate and conceal the adversarial perturbation within the original audio files. In addition to hindering speaker identification performance, this multi-objective loss accounts for human perception through a frame-wise cosine similarity between MFCC feature vectors extracted from the original and adversarial audio files. We validate the effectiveness of FoolHD with a 250-speaker identification x-vector network, trained using VoxCeleb, in terms of accuracy, success rate, and imperceptibility. Our results show that FoolHD generates highly imperceptible adversarial audio files (average PESQ scores above 4.30), while achieving a success rate of 99.6% and 99.2% in misleading the speaker identification model, for untargeted and targeted settings, respectively.
Fig 1. Block diagram of the proposed approach.
Code available here.
Adversarial audio samples available here.
If you would like to cite our work, please use:
@article{shamsabadi2020foolhd,
title={FoolHD: Fooling speaker identification by Highly imperceptible adversarial Disturbances},
author={Ali Shahin Shamsabadi and Francisco Sepúlveda Teixeira and Alberto Abad and Bhiksha Raj and Andrea Cavallaro and Isabel Trancoso},
year={2020},
eprint={2011.08483},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.SD}
}
The authors would like to thank Thomas Rolland and Catarina Botelho for their contributions in the implementation of the x-vector speaker identification network. This work was supported by Portuguese national funds through Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT), with reference UIDB/50021/2020, and BD2018 ULisboa. We also wish to thank the Alan Turing Institute (EP/N510129/1), which is funded by the U.K. Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council, for its support throughout the project PRIMULA.