About the SDK program architecture of computer vision algorithms written in C++ and OpenCV.
The computer vision algorithms in this notion are contained object location(Template Matching, Pattern Matching, Feature Matching), flat-field-correction, contrast stretching, variance..., etc.
The following content will introduce the software architecture and the usage and effects of each API.
You can find for more details form my notion.
| Win 10 | Ubuntu 1604 |
|---|---|
| Visual studio 2017 | GCC 7.5.0 |
| Package | Version |
|---|---|
| OpenCV | 3.4.9 |
- To CMakeLists.txt enable "add_executable"
- To main.cpp, and select the function you want to execute by the index.
- Execute the following command
Windows
$ cd build
$ build.bat
$ bin\Release\ipo_cv.exe
Ubuntu
$ cd build
$ cmake ..
$ make
$ ./bin/ipo_cv
- To CMakeLists.txt enable "add_library"
- Execute the following command
Windows
$ cd build
$ build.bat
Ubuntu
$ cmake ..
$ make
This algorithm is refer to threshold operator from Halcon. Inspect the differences between images. The input image and mean of the image are compared pixel by pixel.
enum class DynamicThresholdTypes {
DYNAMIC_THRES_LIGHT = 0,
DYNAMIC_THRES_DARK = 1,
DYNAMIC_THRES_LIGHT_AND_DARK_INRANGE = 2,
DYNAMIC_THRES_LIGHT_OR_DARK_OUTRANGE = 3,
};
/**
* @param src Input image (CV_8UC1 or CV_8UC3).
* @param dst Output image (CV_8UC1).
* @param blur_ksize Blurring kernel size.
* @param offset The sensitivity of the dynamic threshold operator.
* @param mode (DynamicThresholdTypes) switch to the select mode.
* @return 0:ok; -1:error
**/
int ipo::DynamicThreshold(const cv::Mat &src,
cv::Mat &dst,
const int &blur_ksize,
const int &offset,
const DynamicThresholdTypes &mode)
 LIGHT || DARK || LIGHT_AND_DARK_INRANGE || LIGHT_OR_DARK_OUTRANGE
LIGHT || DARK || LIGHT_AND_DARK_INRANGE || LIGHT_OR_DARK_OUTRANGE
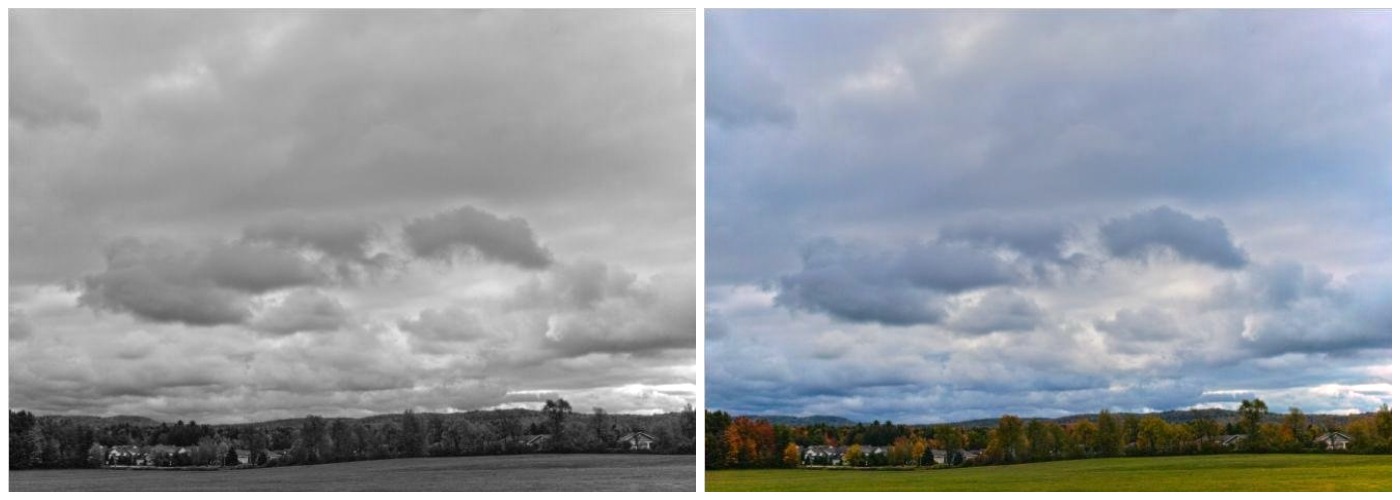
This algorithm is refer to threshold operator from ImageJ. Contrast stretching is an Image Enhancement method that attempts to improve an image by stretching the range of intensity values. For example, Search for each pixel and set 255 if its pixel value is higher than high_value, and then set 0 if it's lower than low_value. The pixel value in the range of low_value and high_value will do contrast stretching.
/**
* @param src input image (CV_8UC1 or CV_8UC3).
* @param dst output image (CV_8UC1 or CV_8UC3).
* @param low_value low threshold.
* @param high_value height threshold.
* @return 0:ok; -1:error
**/
int ipo::Stretching(const cv::Mat &src,
cv::Mat &dst,
const int &low_value,
const int &high_value)
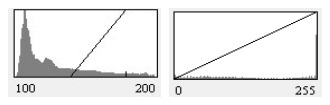 origin histogram || histogram after stretching
origin histogram || histogram after stretching
 CV_8UC1 || CV_8UC3
CV_8UC1 || CV_8UC3
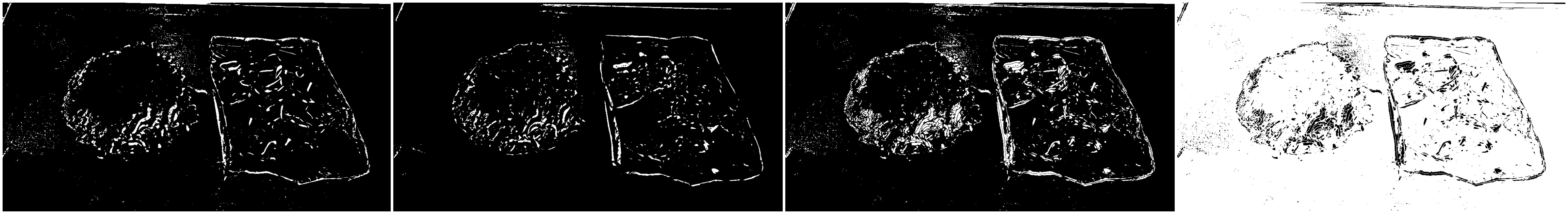
This algorithm is refer to threshold operator from ImageJ. Highlight edges in the image by replacing each pixel with the neighborhood variance. Variance link to wiki
/**
* @param src input image (CV_8UC1 or CV_8UC3).
* @param dst output image (CV_8UC1).
* @param kernel_size filter kernel size
* @return 0:ok; -1:error
**/
int ipo::Variance(const cv::Mat &src,
cv::Mat &dst,
const int &kernel_size)
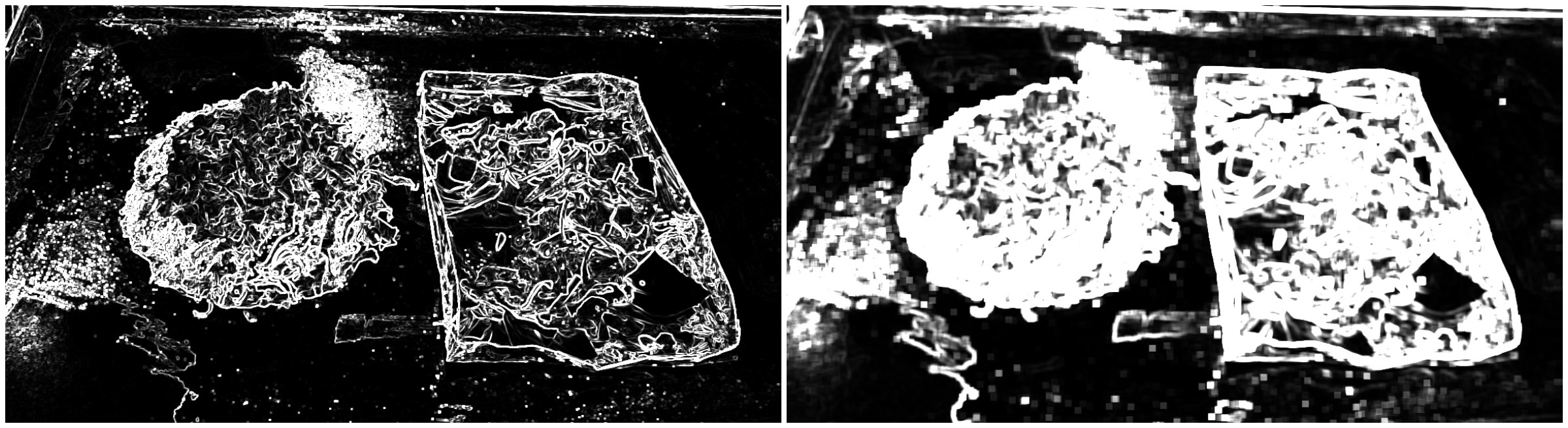 kernel_size = 3 || kernel_size = 10
kernel_size = 3 || kernel_size = 10
Highlight edges in the image by replacing each pixel with the neighborhood variance.
/**
* @param src input image (CV_8UC3).
* @param dst output image (CV_8UC1).
* @param r the r channel of the RGB color space
* @param g the g channel of the RGB color space
* @param b the b channel of the RGB color space
* @param tolerance the tolerance of the RGB color
* @return 0:ok; -1:error
**/
int ipo::FindTheSpecifiedColorByRGB(const cv::Mat &src, cv::Mat &dst,
const int &r,
const int &g,
const int &b,
const double &tolerance);
Get the intersection of two lines.
/**
* @param x1_start the start point by the first line (line 1)
* @param x1_end the end point by the first line (line 1)
* @param x2_start the start point by the second line(line 2)
* @param x2_end the end point by the second line (line 2)
* @return the intersection of two lines
**/
cv::Point ipo::TwoLineIntersection(const cv::Point &x1_start,
const cv::Point &x1_end,
const cv::Point &x2_start,
const cv::Point &x2_end);
Rotate with the center point of the picture, and its boundary will be adjusted according to the picture boundary after rotation.
/**
* @param src input image(CV_8UC1 || CV_8UC3)
* @param angle rotate angle(CV_8UC1 || CV_8UC3)
* @return rotated image
**/
cv::Mat ipo::ImageRotateByCenterAndAdjustBoundary(const cv::Mat &src,
const double &angle);
- Feature Matching: OpenCV doc Use feature descriptors to compare and match using the Euclidean distance between the template image and the searching image. Use feature descriptors to compare and match using the Euclidean distance between the template image and the searching image.
- Template Matching: OpenCV doc And then find 3 points with the highest score to calculate the homography matrix, and using this matrix to find angle and coordinate.
- Positioning() : Pass the enum type of algorithm you want to execute by the constructor.
- int SetGoldenSampleImage() : Set the golden image.
- int SetRect() : Set ROI rectangle.
- int SetAttribute() : Set the attribute that algorithm needs.
- cv::Mat GetResult() : Get result image.
enum PositioningTypeEnums {
FEATURE_MATCHING = 0,
TEMPLATE_MATCHING = 1,
};
enum PositioningRectEnums {
TEMPLATE_IMG_RECT = 0,
SEARCHING_IMG_RECT = 1,
};
enum FeatureAttributeEnums {
HESSIAN_THRESHOLD = 0, // 100~3000
LOWE_RATIO = 1, // 0~1.0
};
enum TemplateAttributeEnums {
ANGLE_TOLERANCE = 0, // 0~180
NUMBER_OF_LEVELS = 1, // 1~5
THRESHOLD_SCORE = 2, // 0~1.0
};
class Positioning {
public:
Positioning(const PositioningTypeEnums &type);
~Positioning();
int SetGoldenSampleImage(const cv::Mat &golden_sample_img);
int SetRect(const PositioningRectEnums &rect_type, const cv::Rect &rect);
int SetAttribute(const int &attribute_type, const double &value);
cv::Mat GetResult(const cv::Mat &sample_img);
};
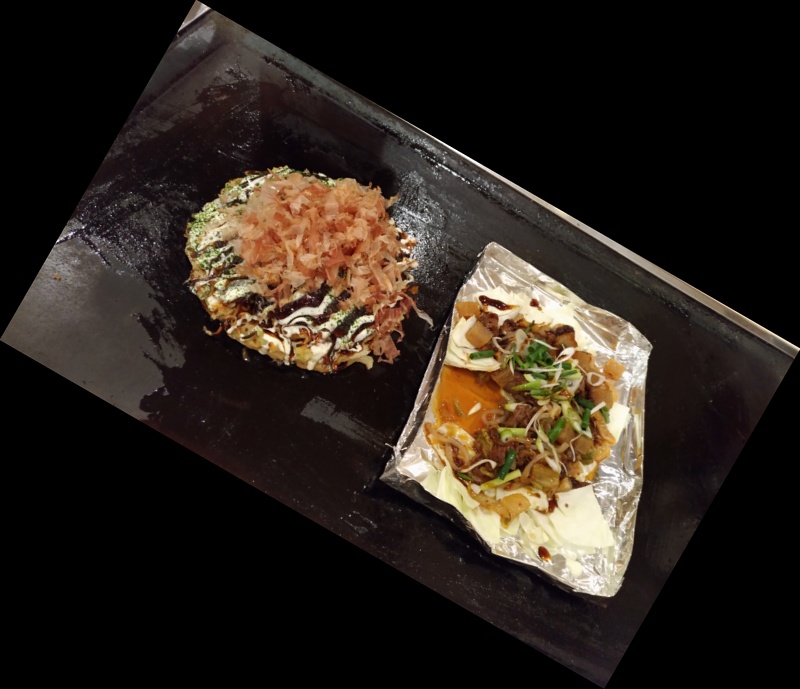
 Golden image || sample image || result : feature matching || result : template matching
Golden image || sample image || result : feature matching || result : template matching
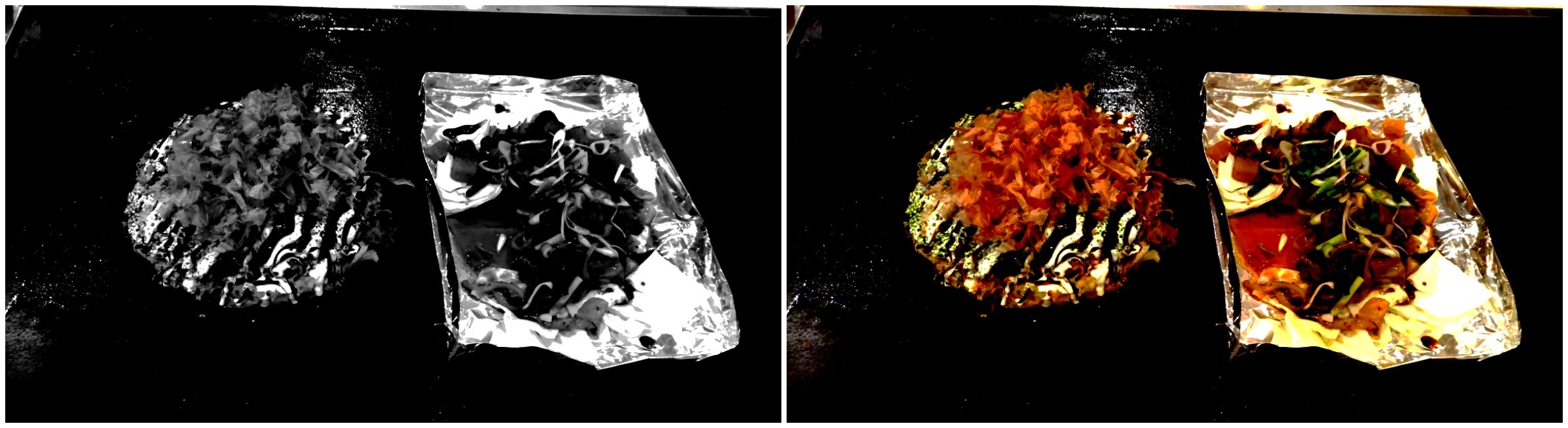
wiki Image Source: A technique used to improve quality in digital imaging. It cancels the effects of image artifacts caused by variations in the pixel-to-pixel sensitivity of the detector and by distortions in the optical path.
- int SetDarkAndBrightFieldImage() : Set dark field image, bright field image and mean_pixel_value for imageaverage brightness.
- cv::Mat GetResult() : Get result image.
class FlatFieldCorrection {
public:
FlatFieldCorrection();
~FlatFieldCorrection();
int SetDarkAndBrightFieldImage(const cv::Mat &dark_field_img,
const cv::Mat &bright_field_img,
const int &mean_pixel_value);
cv::Mat GetResult(const cv::Mat &src);
};
 input image : original image || dark field image || bright field image
input image : original image || dark field image || bright field image
 Output image : CV_8UC1 || CV_8UC3
Output image : CV_8UC1 || CV_8UC3
Breakpad is a set of client and server components which implement a crash-reporting system. It can catch the core dump if it occurs in the program, you can know where it happened.
- In CMakeList.txt
- build .pdb
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS_RELEASE "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS_RELEASE} /Zi")
- choose shared/static/exe to build
# SHARED
#set(CMAKE_SHARED_LINKER_FLAGS_RELEASE "${CMAKE_EXE_LINKER_FLAGS_RELEASE} /DEBUG /OPT:REF /OPT:ICF")
# EXE
set(CMAKE_EXE_LINKER_FLAGS_RELEASE "${CMAKE_EXE_LINKER_FLAGS_RELEASE} /DEBUG /OPT:REF /OPT:ICF")
- This program will produce the dump file:
#ifdef _WIN32
#include "client/windows/handler/exception_handler.h"
bool callback(const wchar_t *dump_path, const wchar_t *id,
void *context, EXCEPTION_POINTERS *exinfo,
MDRawAssertionInfo *assertion, bool succeeded) {
if (succeeded)
std::cout << "Create dump file success" << std::endl;
else
std::cout << "Create dump file failed" << std::endl;
return succeeded;
}
#endif
int main() {
#ifdef _WIN32
const wchar_t *dumpPath = L"../dump_file/log";
google_breakpad::ExceptionHandler eh(
dumpPath, NULL, callback, NULL,
google_breakpad::ExceptionHandler::HANDLER_ALL);
#endif
std::cout << "main start" << std::endl;
// A program that will cause a core dump.
int *a = NULL;
*a = 0x1;
std::cout << "main end" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
- Put .dll & .pdb & .dmp in the same folder location.
- Double click to open .dmp file (with Visual Studio).