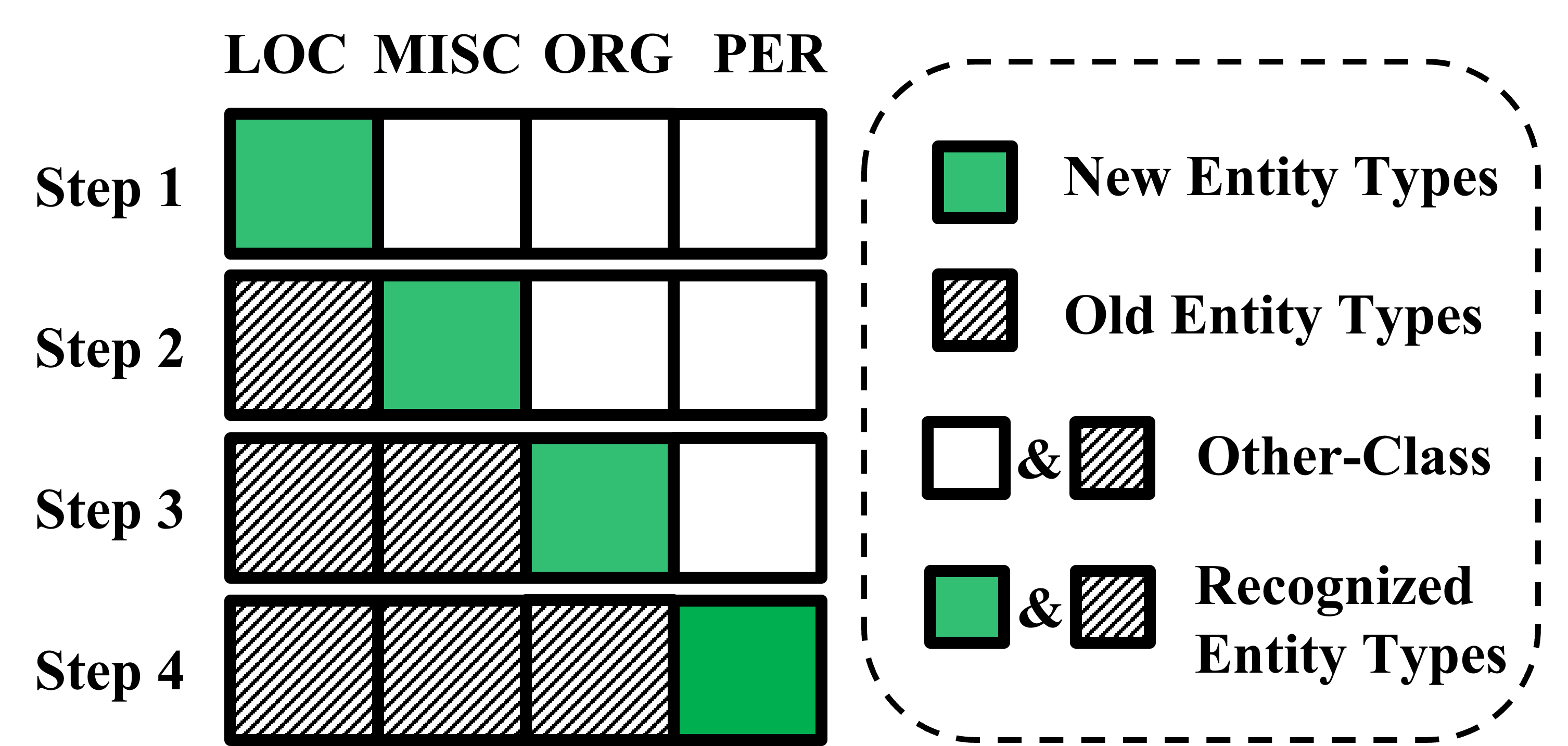
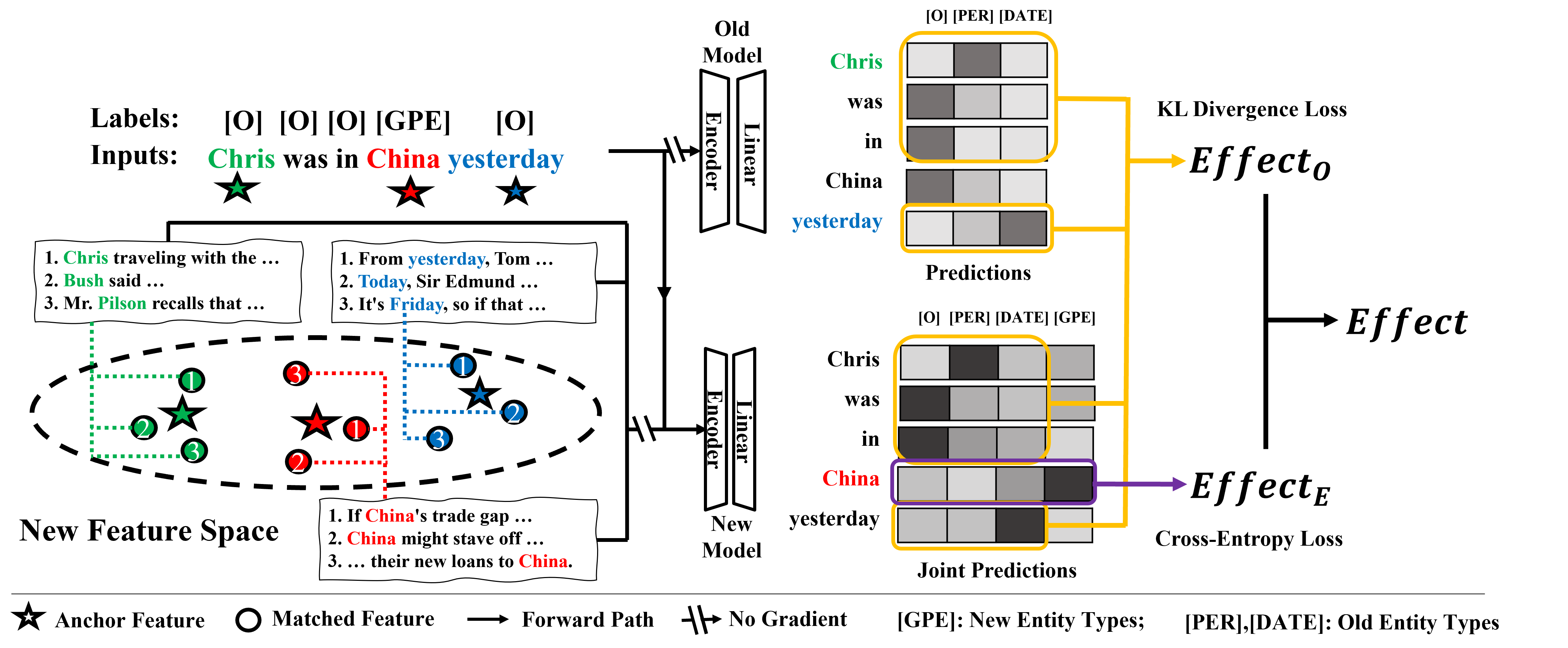
Distilling Causal Effect from Miscellaneous Other-Class for Continual Named Entity Recognition (EMNLP2022)
This repo provides the source code for our method
- CFNER : a causal framework for Continual Named Entity Recognition
Besides, we also provide re-implementation of the following methods for a fair comparison:
- Self-Training (ST) : ST first utilizes the old model to annotate the Other-class tokens with old entity types. Then, the new model is trained on new data with annotations of all entity types. Finally, the cross-entropy loss on all entity types is minimized.
- ExtendNER: ExtendNER has a similar idea to ST, except that the old model provides the soft label (i.e., probability distribution) of Other-class tokens. Specifically, the cross-entropy loss is computed for entity types’ tokens, and KL divergence loss is computed for Other-class tokens. During training, the sum of cross-entropy loss and KL divergence loss is minimized.
- LUCIR : LUCIR develops a framework for incrementally learning a unified classifier for the continual image classification tasks. The total loss consists of three terms: (1) the cross-entropy loss on the new classes samples; (2) the distillation loss on the features extracted by the old model and those by the new one; (3) the margin-ranking loss on the reserved samples for old classes. In our re-implementation, we compute the cross-entropy loss for new entity types, the distillation loss for all entity types, and the margin-ranking loss for Other-class samples instead of the reserved samples.
- PODNet : PODNet has a similar idea to LUCIR to combat the catastrophic forgetting in continual learning for image classification. The total loss consists of the classification loss and distillation loss. To compute the distillation loss, PodNet constrains the output of each intermediate convolutional layer while LUCIR only considers the final feature embeddings. For classification, PODNet used NCA loss instead of the cross-entropy loss. In our re-implementation, we constrain the output of each intermediate stage of BERT as PODNet constrains each stage of a ResNet.
- config/ : the directory of configurations for each models
- datasets/ : the directory of datasets
- src/ : the directory of the source code
- main_CL.py : the python file to be executed
.
├── config
│ ├── conll2003
│ ├── ontonotes5
│ ├── i2b2
│ └── default.yaml
├── datasets
│ └── NER_data
│ ├── conll2003
│ ├── i2b2
│ └── ontonotes5
├── main_CL.py
└── src
├── config.py
├── dataloader.py
├── model.py
├── trainer.py
├── utils_log.py
├── utils_plot.py
└── utils.py
Reference environment settings:
python 3.7.13
torch 1.12.1+cu116
transformers 4.14.1
If you want to repreduce the results or use the same data splits of our paper, please download the ./datasets/ foloder in this link and skip Step 1 and 2.
Download data and preprocess them as the following format (word + \t + NER_tag):
SOCCER O
- O
JAPAN B-location
GET O
LUCKY O
WIN O
, O
CHINA B-person
IN O
SURPRISE O
DEFEAT O
. O
Then, save the training/testing/developing set to a txt file named train.txt/test.txt/dev.txt and move them to the corresponding directory in ./datasets/NER_data/{dataset_name}/
Take CoNLL2003 as an example:
- specify the arguments of the function spilt_dataset in the file ./src/dataloader.py as follow:
if __name__ == "__main__":
spilt_dataset(['datasets/NER_data/conll2003'], 'train', domain2entity['conll2003'], 1, 1, 'BIO')
# the parameters nb_class_fg=1 and nb_class_pg=1 represent that the model learns 1 entity in the first CL step and learns 1 entity in the following CL steps.
- execute the python file dataloader.py as follow:
python ./src/dataloader.py
Then, the program will split the dataset with the Greedy Sampling Algorithm for continual learning and store the split dataset in train_fg_1_pg_1.pth. Note that only training set needs to be split!
Specify your configurations (e.g., ./config/i2b2/fg_8_pg_2/i2b2_ours.yaml) and run the following command
python3 main_CL.py --exp_name {your_experiment_name} --exp_id {your_experiment_id} --cfg {your_configuration}
Then, the results as well as the model checkpoint will be saved automatically in the directory ./experiments/{your_experiment_name}/{your_experiment_id}/
| Dataset | Method | FG-1-PG-1 | **** | FG-2-PG-2 | **** | FG-8-PG-1 | **** | FG-8-PG-2 | **** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| **** | Mi-F1 | Ma-F1 | Mi-F1 | Ma-F1 | Mi-F1 | Ma-F1 | Mi-F1 | Ma-F1 | |
| I2B2 | Finetune Only | 17.43 | 13.81 | 28.57 | 21.43 | 20.83 | 18.11 | 23.60 | 23.54 |
| **** | PODNet | 12.31 | 17.14 | 34.67 | 24.62 | 39.26 | 27.23 | 36.22 | 26.08 |
| **** | LUCIR | 43.86 | 31.31 | 64.32 | 43.53 | 57.86 | 33.04 | 68.54 | 46.94 |
| **** | ST | 31.98 | 14.76 | 55.44 | 33.38 | 49.51 | 23.77 | 48.94 | 29.00 |
| **** | ExtendNER | 42.85 | 24.05 | 57.01 | 35.29 | 43.95 | 23.12 | 52.25 | 30.93 |
| **** | CFNER(Ours) | 62.73 | 36.26 | 71.98 | 49.09 | 59.79 | 37.30 | 69.07 | 51.09 |
| OntoNotes5 | Finetune Only | 15.27 | 10.85 | 25.85 | 20.55 | 17.63 | 12.23 | 29.81 | 20.05 |
| **** | PODNet | 9.06 | 8.36 | 34.67 | 24.62 | 29.00 | 20.54 | 37.38 | 25.85 |
| **** | LUCIR | 28.18 | 21.11 | 64.32 | 43.53 | 66.46 | 46.29 | 76.17 | 55.58 |
| **** | ST | 50.71 | 33.24 | 68.93 | 50.63 | 73.59 | 49.41 | 77.07 | 53.32 |
| **** | ExtendNER | 50.53 | 32.84 | 67.61 | 49.26 | 73.12 | 49.55 | 76.85 | 54.37 |
| **** | CFNER(Ours) | 58.94 | 42.22 | 72.59 | 55.96 | 78.92 | 57.51 | 80.68 | 60.52 |
| Method | FG-1-PG-1 | **** | FG-2-PG-1 | **** |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| **** | Mi-F1 | Ma-F1 | Mi-F1 | Ma-F1 |
| Finetune Only | 50.84 | 40.64 | 57.45 | 43.58 |
| PODNet | 36.74 | 29.43 | 59.12 | 58.39 |
| LUCIR | 74.15 | 70.48 | 80.53 | 77.33 |
| ST | 76.17 | 72.88 | 76.65 | 66.72 |
| ExtendNER | 76.36 | 73.04 | 76.66 | 66.36 |
| Ours | 80.91 | 79.11 | 80.83 | 75.20 |
If you find the code useful, please consider citing this work
Junhao Zheng, Zhanxian Liang, Haibin Chen, and Qianli Ma. 2022. Distilling Causal Effect from Miscellaneous Other-Class for Continual Named Entity Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, pages 3602–3615, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. Association for Computational Linguistics.