- Quick start
- How to use
- Reference manual
- MainFrame, applications
- GSON
- Datasets
- Building an IGP server
- Applications
- Contributing to InteractiveGraph
- Build & Debug
- Build & Release
- LICENSE
InteractiveGraph provides a web-based interactive operating framwork for large graph data, which may come from a GSON file, or an online Neo4j graph database.
InteractiveGraph also provides three applications built on the framework: GraphNavigator, GraphExplorer and RelFinder.
GraphNavigator: online demo https://grapheco.github.io/InteractiveGraph/dist/examples/example1.html
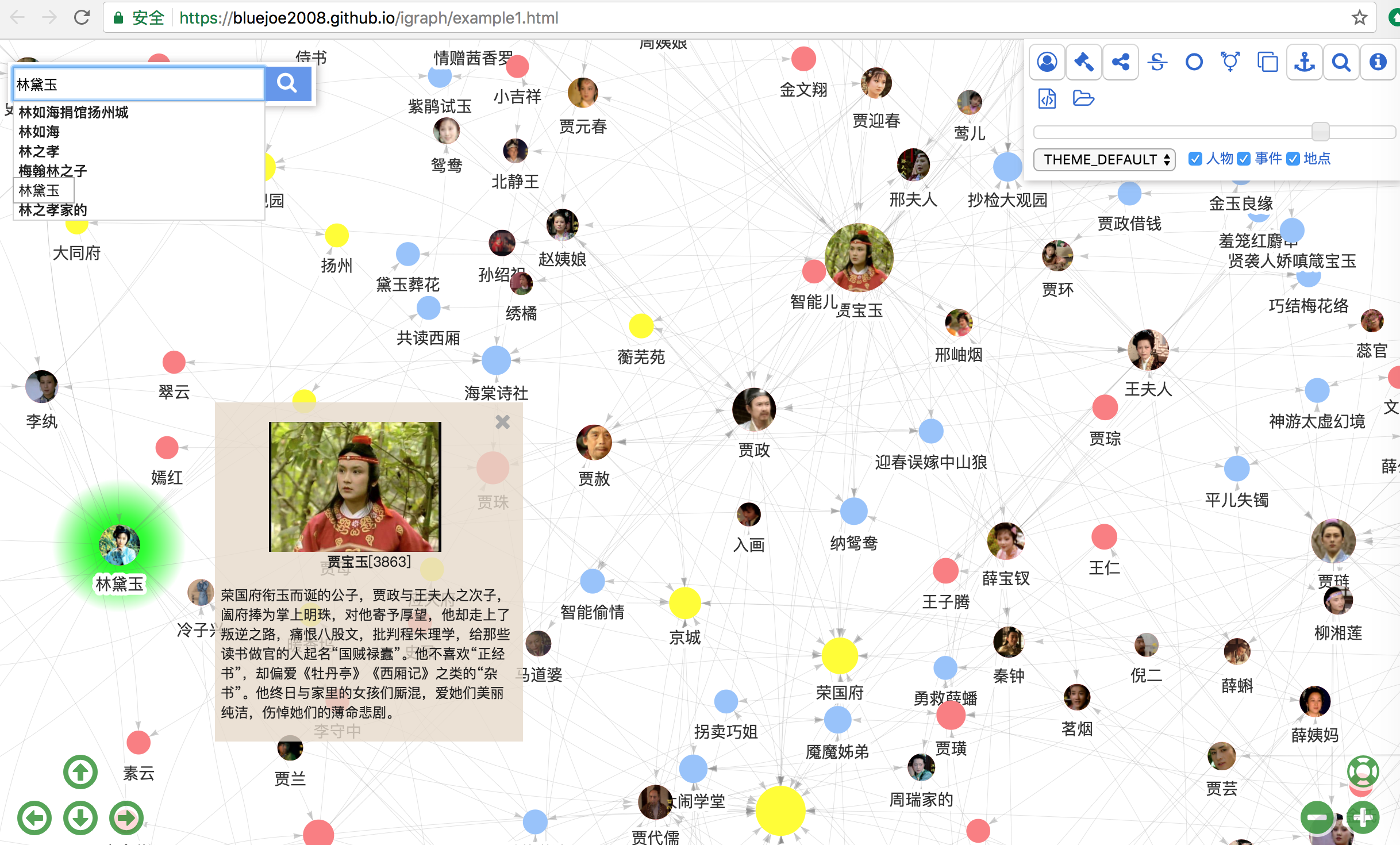
GraphExplorer: online demo
https://grapheco.github.io/InteractiveGraph/dist/examples/example2.html
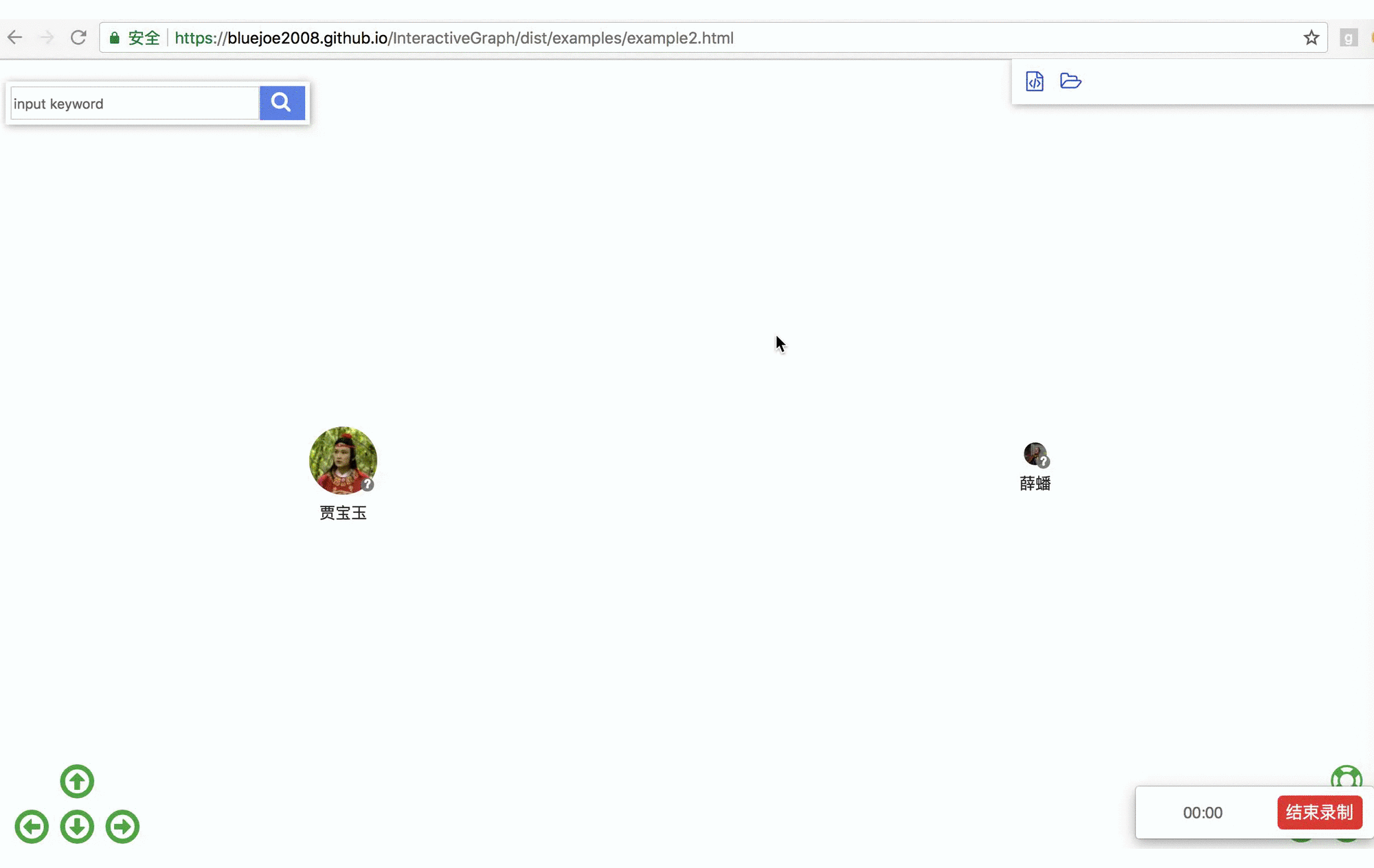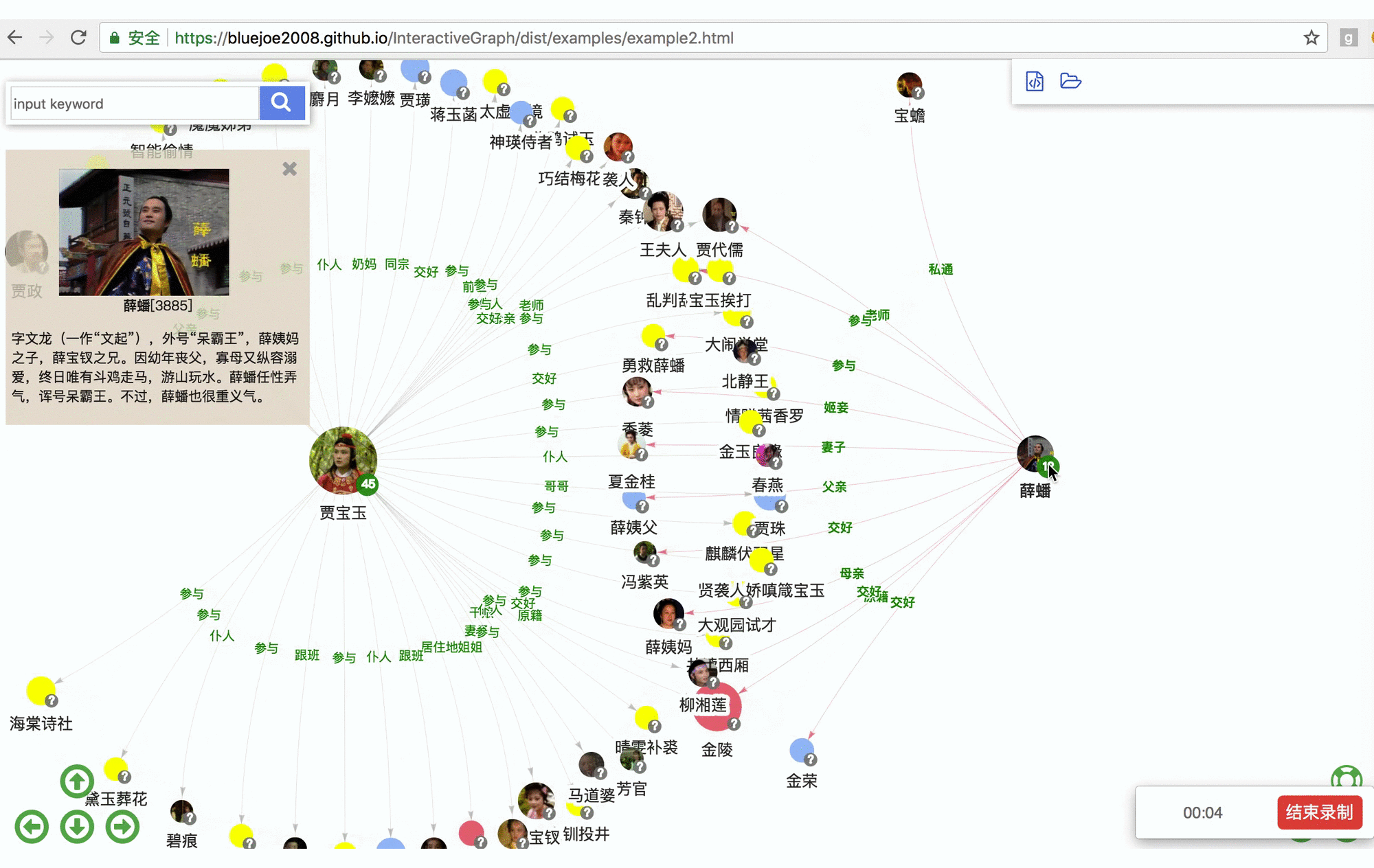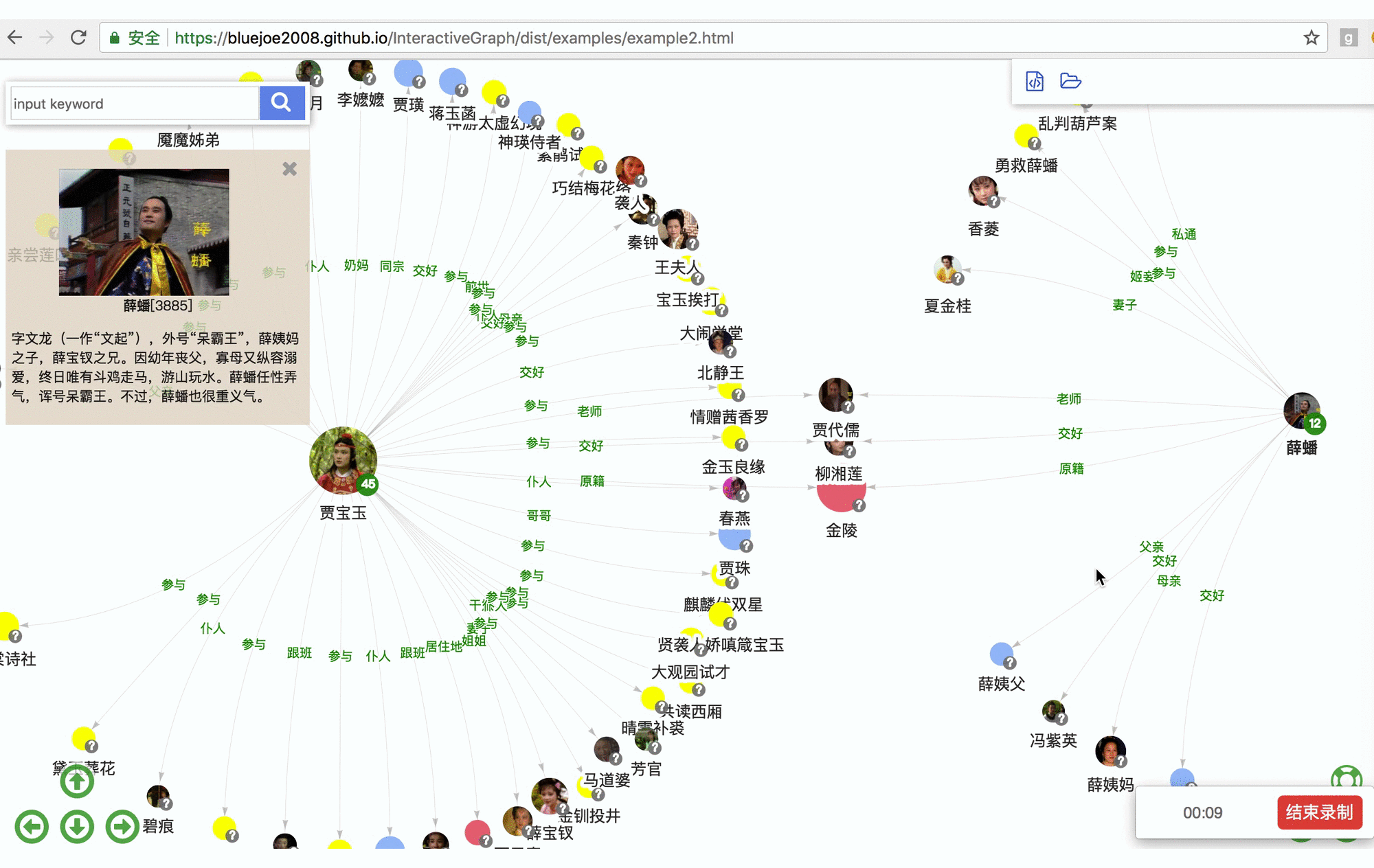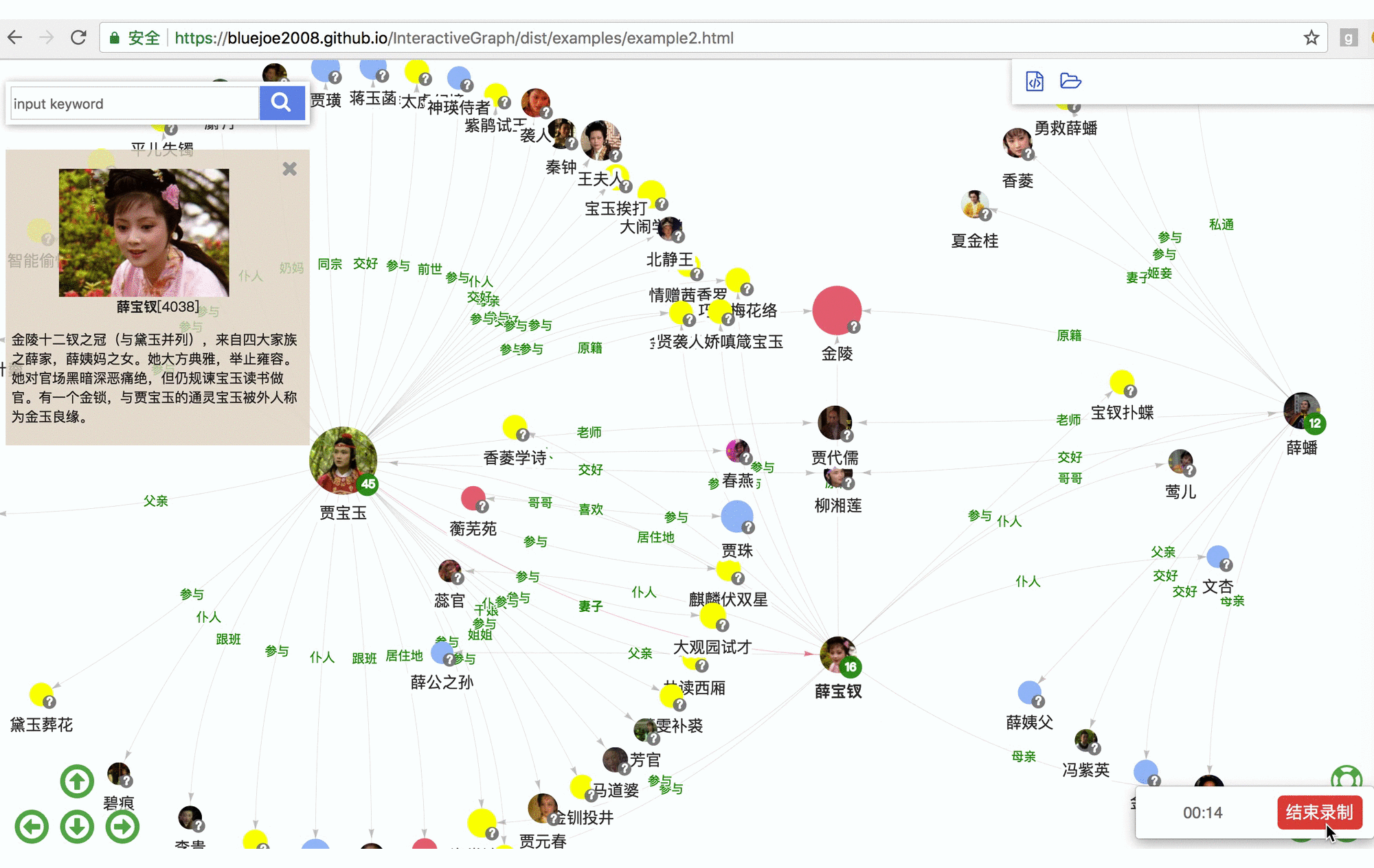
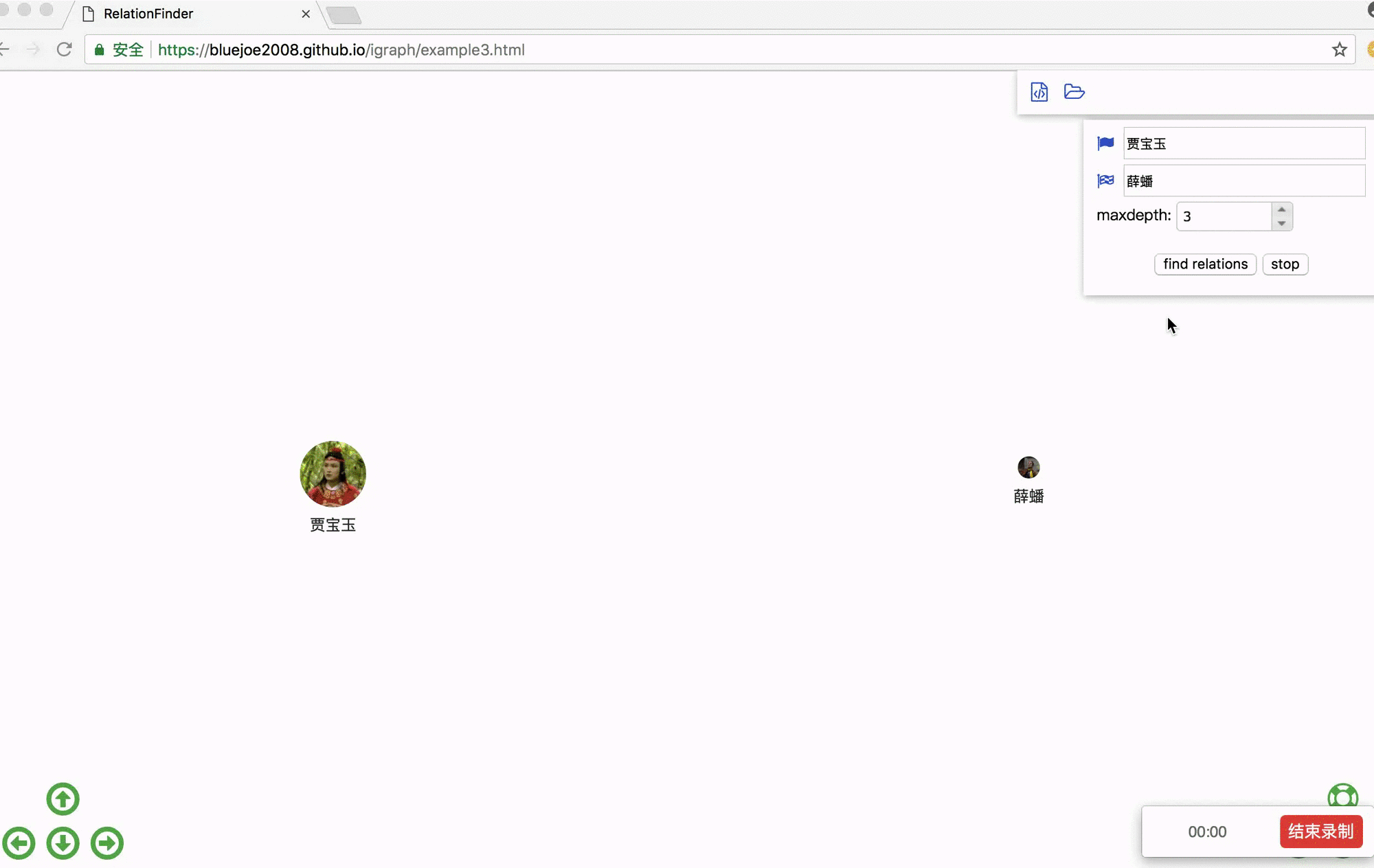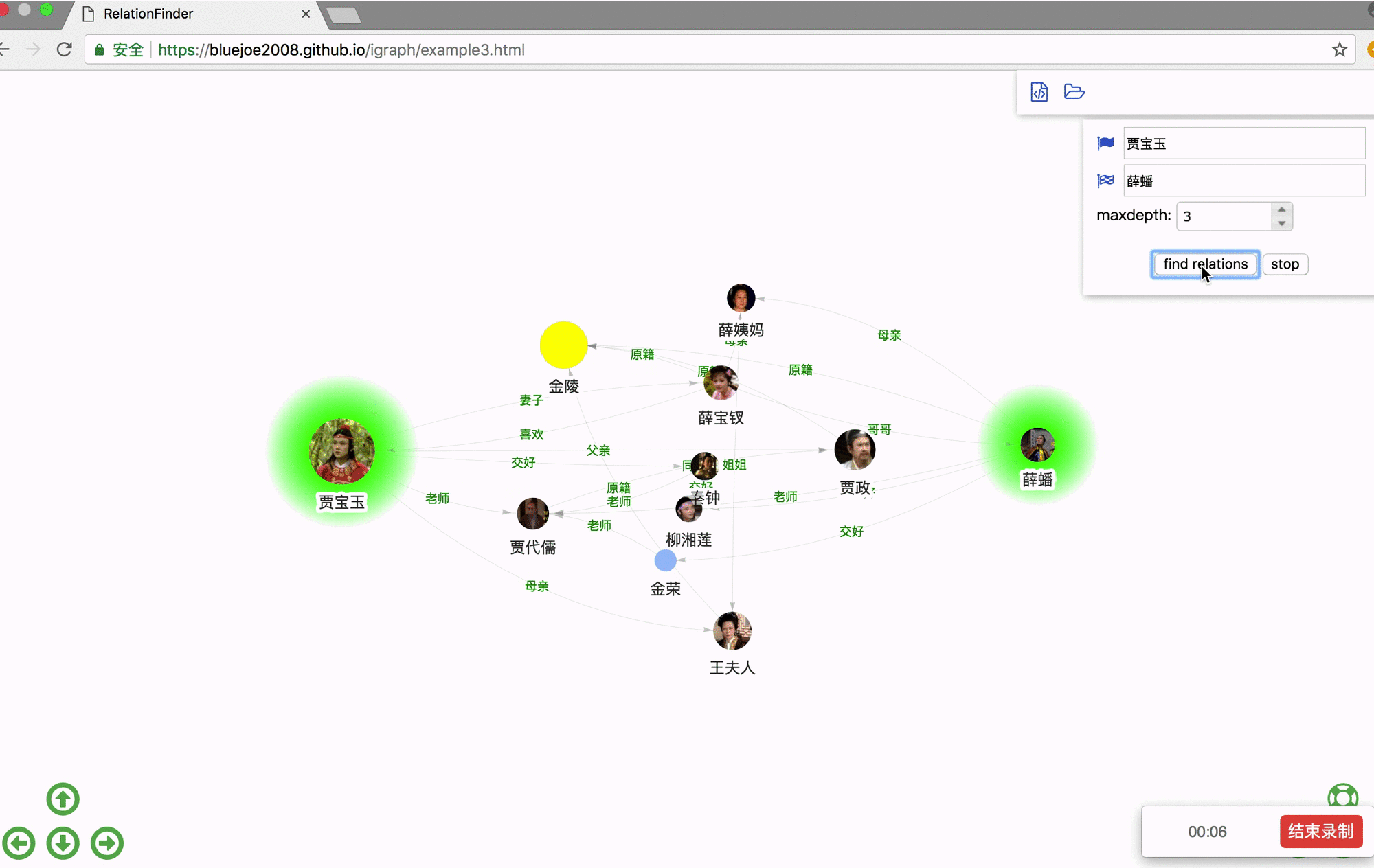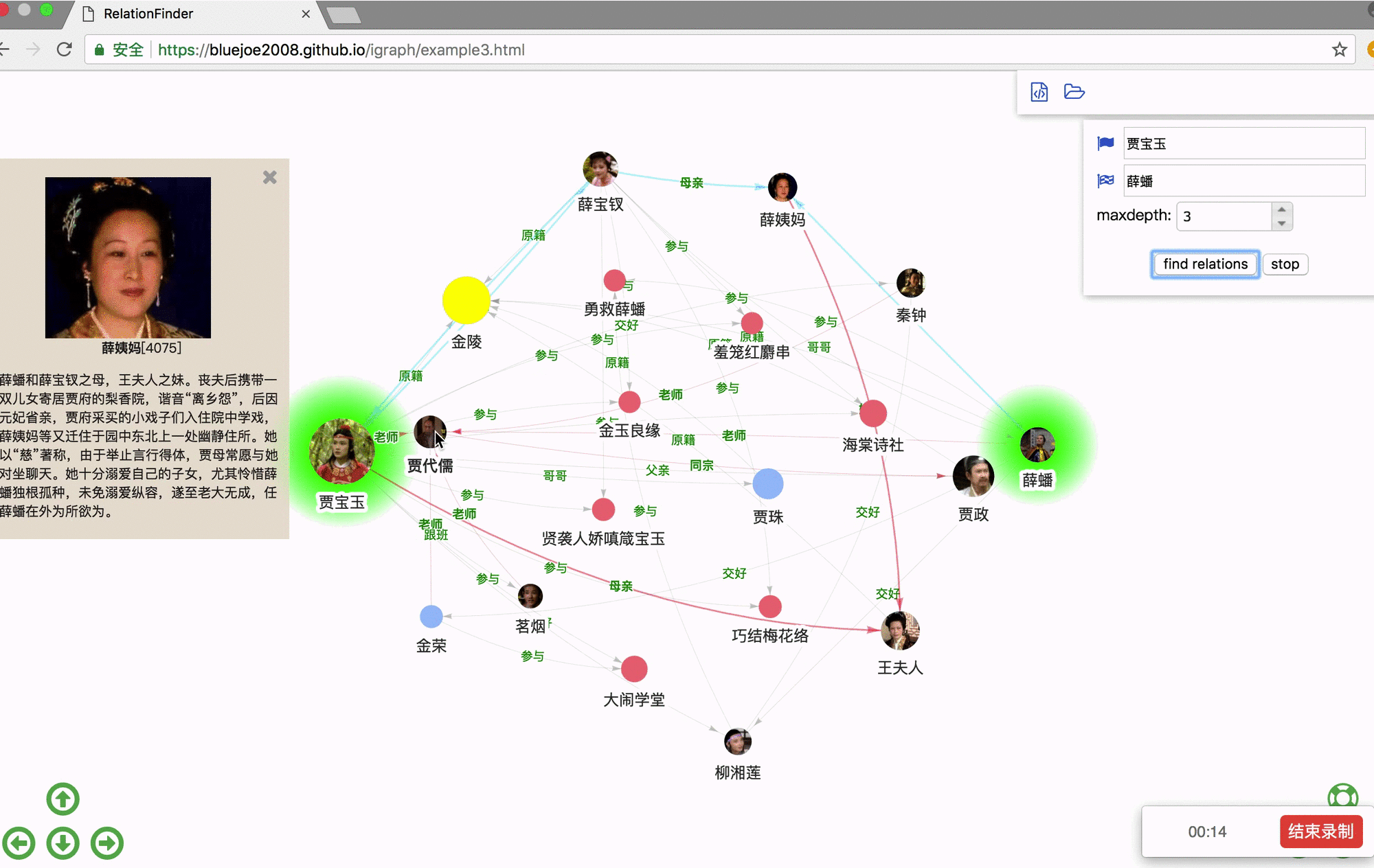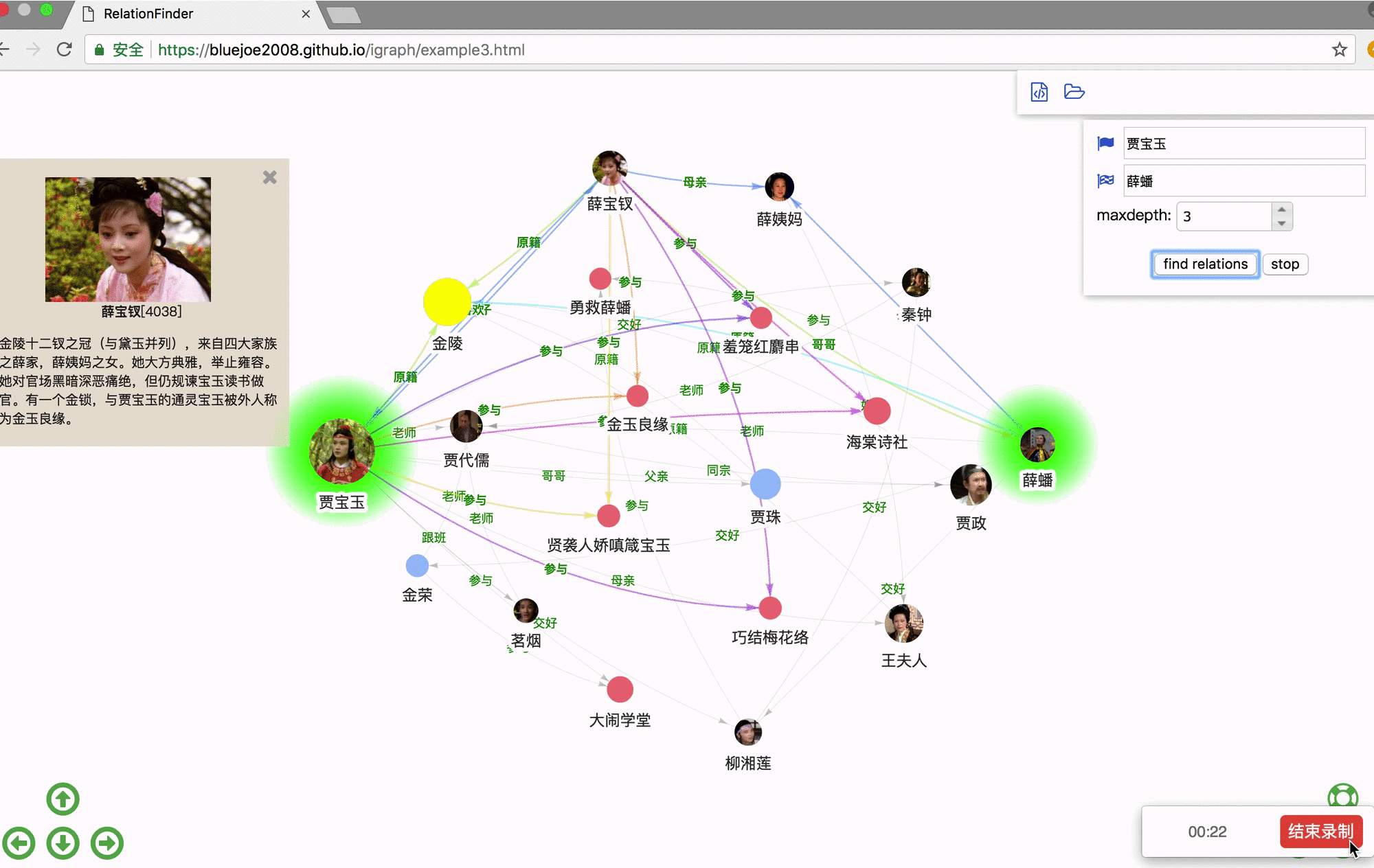
RelFinder: online demo https://grapheco.github.io/InteractiveGraph/dist/examples/example3.html
Step 1. download examples.zip:
https://github.com/grapheco/InteractiveGraph/releases
Step 2. unzip and deploy examples.zip as a webapp in a Web server (Apache, Tomcat, etc). A Web server is required, otherwise the graph data loading via AJAX will get an error.
Step 3. visit the webapp in Web browser, url may looks like: https://localhost:8080/examples/example1.html
change example1.html to examples2.html or examples3.html, etc.
Step 1. download interactive-graph-<VERSION>.zip(interactive-graph-0.1.0.zip, for example) from dist directory:
https://github.com/grapheco/InteractiveGraph/dist/
Step 2. unzip interactive-graph-<VERSION>.zip, two files will be got: interactive-graph.min.js and interactive-graph.min.css.
Step 3. import the .js and .css files in HTML page, like that:
<script type="text/javascript" src="./lib/interactive-graph-0.1.0/interactive-graph.min.js"></script>
<link type="text/css" rel="stylesheet" href="./lib/interactive-graph-0.1.0/interactive-graph.min.css">Step 4. use functions and classes defined in igraph namespace:
<script type="text/javascript">
igraph.i18n.setLanguage("chs");
var app = new igraph.GraphNavigator(document.getElementById('graphArea'));
app.loadGson("honglou.json");
</script>As shown above, a GraphNavigator application object is created and used to load graph data from honglou.json.
For more details, see https://github.com/grapheco/InteractiveGraph/blob/master/dist/examples/example1.html.
To develop custom applications, it is a good idea to write new application classes derived on GraphNavigator and other application classes. Furthermore, users can create new application classes via using a MainFrame class directly.
InteractiveGraph is written in TypeScript. Visit https://grapheco.github.io/InteractiveGraph/dist/api/index.html to get online API documents.
This project depends on some open sourced components including visjs, npm, gulp, jQuery, jQueryUI, Font Awesome and so on.
More dependencies, see https://github.com/grapheco/InteractiveGraph/blob/master/package.json.
InteractiveGraph provides a MainFrame, which actually is a facade of Web UI, event handling and graph data connection.
As shown above, MainFrame consists of a main graph rendering canvas, a set of navigation buttons, and serveral controls: search bar, tool bar, info box, highlight control and so on.
Some controls have Web UI, such as InfoBoxCtrl, MessageBoxCtrl, etc. While others work with no UI, such as HighlightNodeCtrl, ExpansionCtrl, etc. A Control class and two derived classes UIControl(controls with UI) and BGControl(backgroud control with no UI) are defined in InteractiveGraph.
All controls are listed in the table below.
| control | function | type |
|---|---|---|
| ConnectCtrl | show a load data dialog | UIControl |
| ExpansionCtrl | expands a graph node on double click | BGControl |
| HighlightNodeCtrl | highlight selected graph nodes | BGControl |
| InfoBoxCtrl | show a infomation box on click on a graph node | UIControl |
| MessageBoxCtrl | show a message box on demand | UIControl |
| RelFinderCtrl | finding relations between graph nodes | BGControl |
| RelFinderDialogCtrl | show a dialog for user to launch a finding task | UIControl |
| SearchBarCtrl | show a search bar for keyword input | UIControl |
| ToolbarCtrl | show a tool bar | UIControl |
MainFrame and controls communicate with applications through events. For example, when the window is resizing, MainFrame and all controls will receive FRAME_RESIZE events.
To subscribe a event, call a on(event, handler) method on MainFrame or a Control. To cancel the subscription, use off(event, handler) instead.
To fire an event to MainFrame, use MainFrame.emit(event, args) or MainFrame.fire(event, args) method. Unlike the emit() method, fire() put default context objects including mainFrame, htmlMainFrame, theme into args before emition. To fire an event to a Control, use emit(event, args) method.
MainFrame loads data via a Connector which may connect to a LocalGraph or a RemoteGraph. A LocalGraph loads all data once from a GSON object or file, while a RemoteGraph interacts with a remote graph server each time if no cache data is available.
An application always employe an embedded MainFrame to load a GSON file via loadGson() method:
app.loadGson("honglou.json");
Or calling connect() method to load an interactive graph from remote IGP server:
app.connect("http://localhost:9999/graphserver/connector-bolt");
MainFrame loads data from a LocalGraph in GSON format. GSON is actually an enhanced JSON format for graph data. The enhancement is GSON recoginzes functions, which is not valid in JSON.
GSON consists of some data items, it is defined as follow:
export interface GSON {
"data": {
nodes: object[];
edges?: object[];
}
"dbinfo"?: object;
"categories"?: object;
"translator"?: {
"nodes"?: (node: object) => void;
"edges"?: (node: object) => void;
};
}Here, translator defines translator functions for graph nodes and edges, which will be invoked on loading. An example is shown below, in which description of each node is evaluated on loading time.
"translator": {
"nodes": function (node) {
//set description
if (node.description === undefined) {
var description = "<p align=center>";
description += "<img src='" + node.image + "' width=150/><br>";
description += "<b>" + node.label + "</b>" + "[" + node.id + "]";
description += "</p>";
node.description = description;
}
},
}Two GSON datasets are provided in examples as .json files: honglou.json, WorldCup2014.json.
The honglou dataset comes from the Chinese famous novel Dream of the Red Chamber(also called The Story of the Stone, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dream_of_the_Red_Chamber), in which Jia Baoyu, Lin daiyu, and Xue baochai are famous characters. The honglou dataset defines 300+ entities represent persons, locations, and events in the novel, and 500+ links between them.
nickel2008@github provides this dataset. Maybe there are some mistakes in the dataset, but it is good enough to use as an example graph.
The world cup 2014 data set comes from http://visjs.org/examples/network/exampleApplications/worldCupPerformance.html. The edges in particular (~9200) are very computationally intensive to draw.
The next screenshot shows how WorldCup2014.json is rendered in GraphNavigator (empowered by visjs).
An RemoteGraph is always provided by an IGP(interactive graph protocol, see https://github.com/grapheco/InteractiveGraph/blob/master/IGP.md) server. To build an IGP server, refer to the InteractiveGraph-neo4j project and other 3-party projects.
| project | description | language |
|---|---|---|
| InteractiveGraph-neo4j | InteractiveGraph-neo4j(https://github.com/grapheco/InteractiveGraph-neo4j) serves GSON files, Neo4j databases as InteractiveGraph providers, it generates InteractiveGraphs for remote frontend InteractiveGraph clients on demand. | Scala+Java+Spring |
| InteractiveGraph-RDF | InteractiveGraph-RDF(https://github.com/grapheco/InteractiveGraph-RDF) serves RDF stores as InteractiveGraph providers | Scala+Java+Spring |
It would be highly appreciated if you commit any codes or documents to InteractiveGraph. If you have any good idea, please fork this project and create pull requests.
-
To contribute new applications, you may define new application class derived from
BaseApp. -
To contribute any controls, you may define new control class derived from
UIControlandBGControl. -
To contribute new themes.
-
To contribute new tool button, you may define new ButtonInfos. Note that
Font Awesomeicons are available in button icon! -
To contribute new data sets or modification, you may submit data in GSON format!
Step 1. use npm run build or gulp build to build InteractiveGraphBrowser, which generates interactive-graph.js and interactive-graph.css in build dir.
Step 2. open src/test/webapp/example1.html in Web browser (Google Chrome, for example).
Step 1. use gulp release if you want to get a distribution version, which will output examples and interactive-graph-<VERSION> in dist dir.
Step 2. open dist/examples/example1.html in Web browser.
InteractiveGraph is licensed under the BSD 2-Clause "Simplified" License.
Please cite this project as reference if you used it:
InteractiveGraph: a web-based interactive operating framwork for large graph data[EB/OL]. https://github.com/grapheco/InteractiveGraph, 2018-09-09
Furthermore, it is appreciated if you let us know how you use InteractiveGraph in your projects!!! Please fill the use case table (https://github.com/grapheco/InteractiveGraph/wiki/use-case-collection) with your name (github username), organization, and project.













