Lesion Detection for Colonoscopy
Check out our presentation and demo video: Lesion Detection for Colonoscopy App Deployed with Rasa Unity CNN Models | SJSU CMPE 257 ML Demo
A gastroenterologist is a doctor who diagnoses patients for colon cancer, which is one of the most common diagnosed cancers throughout the world. Detecting these lesions in the colon usually requires using an endoscope device with a camera that goes to the patient’s colon area. This lesion detection is also a difficult challenge for specialists, which could result in human error. So AI/ML engineers have stepped in to provide assistance to these specialists to increase the accuracy and the early diagnosis rate for lesion detection. After consulting with some medical tech companies about the data set they would want to use for AI/ML, we have determined we will need to either create a data set from scratch from several YouTube videos where specialists identified lesions in the colon or find a data set that has already been created doing a similar process just mentioned. For creating the data set, we would extract out the frames from these videos, label a sample of the frames with “lesion or not lesion” to do semi-supervised learning. We plan to read multiple publications on the latest Deep Neural Network architectures that are being used to identify lesions in the colon. The goal that some of these companies are aiming to do is perform non-invasive techniques to treat or remove the patients colon cancer usually a procedure known as Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) and lesion detection will help in the process of using automated robotic surgery to cut out the lesion from the patient, ultimately reducing the mortality rate of colorectal cancer.
- Lesion-Detection
The following software can be installed in Anaconda or Docker:
- Rasa 3.1.0 (Rasa Chatbot Server)
- Rasa 3.1.1 SDK (Rasa Actions Server)
- TensorFlow-GPU 2.7.3 (Needed for Rasa Actions Server)
- OpenCV-Python 4.5.5.64 (Needed for Rasa Actions Server)
- Scikit-Learn 0.24.2
- Seaborn 0.11.2
- Matplotlib 3.5.1
- Pandas 1.3.4
- Jupyter 1.0.0
- Ngrok version latest
CUDA:
- Nvidia CUDA 11.6
- cudatoolkit==11.3.1
- CUDNN==8.2.1
1. Open your terminal and clone this project repository
git clone https://github.com/shreyahunur/Lesion-Detection.git2. Go to the Lesion Detection Project:
rem change "path/to" with your path to the project
cd path/to/Lesion-Detection- Updated CNN_Polyp_Classification Notebook Notebook
- Updated YOLOv4_Polyp_Detection Notebook
- Updated UNet_Polyp_Segmentation Notebook
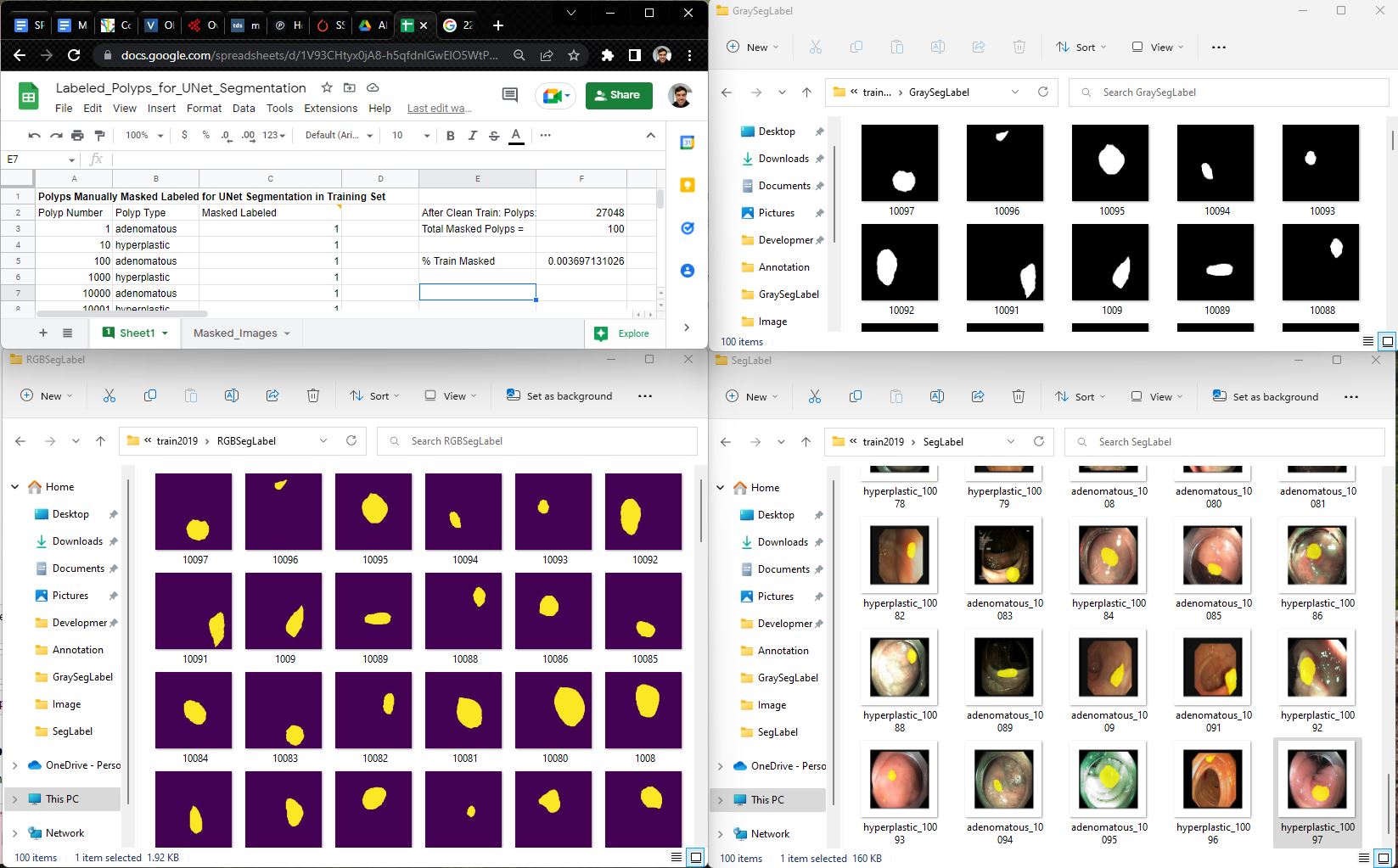
- Created 200 Masked Binary Labels out of 28K+ Training Images. During the CMPE257 Project, 100 Masked Binary Labels were created
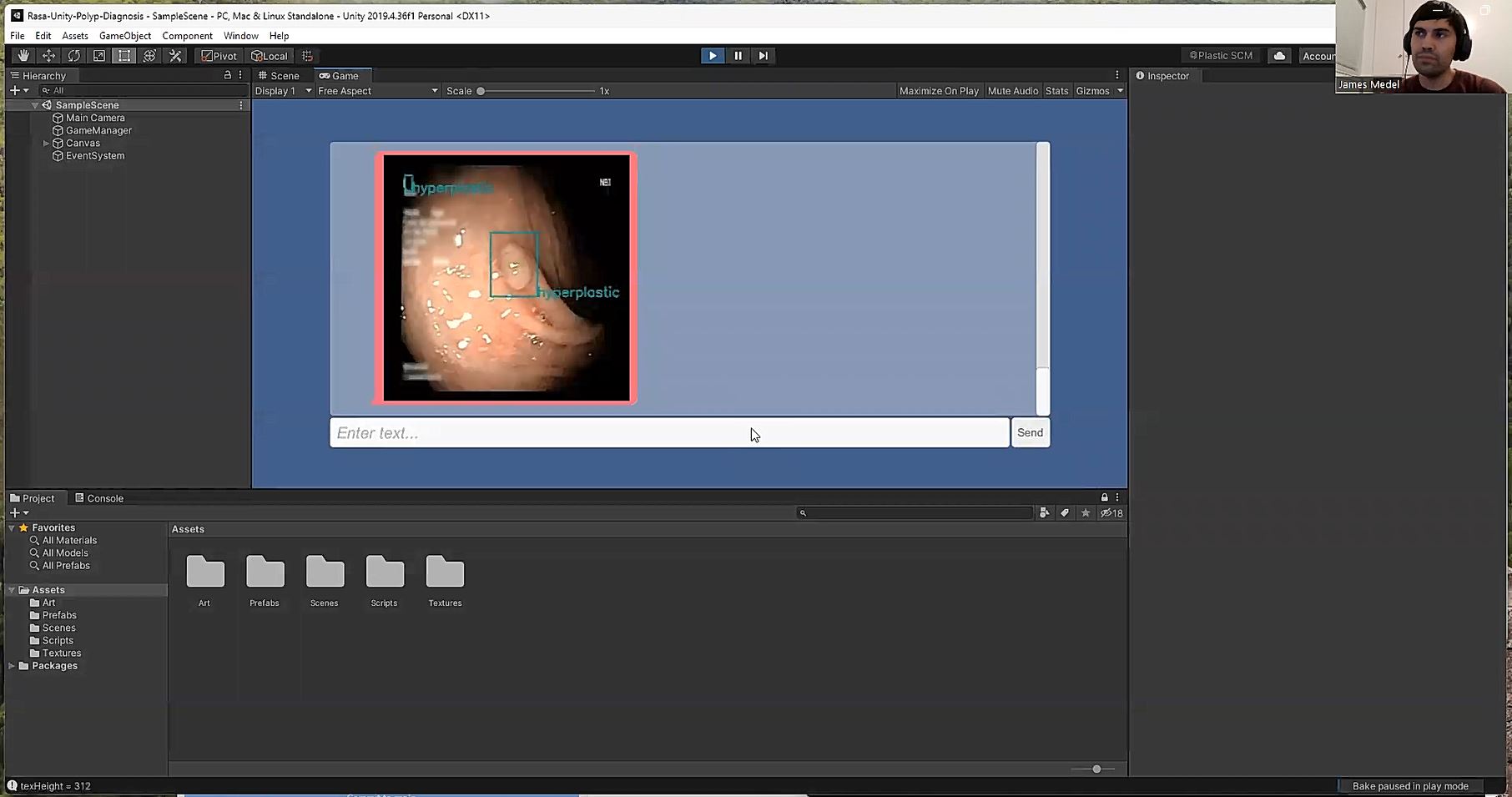
- Integrated Our DL Models into Rasa AI System for Backend
- Integrated Unity with Rasa for Frontend
- Created CNN_Polyp_Classification Notebook
- Trained custom CNN on 11.2K data augmented images, validated on 2.8K augmented images, tested on 2K augmented images (took 6K subset of 28K+ training images to create 14K)
- Precision is 88%, Recall is 90%, Accuracy 91%, Loss is 19.6% Loss is ** as average across training, validation and testing
- CNN consists of a 1st Conv2D layer with 32 filters of kernel size 3x3, MaxPooling2D with 2x2 pooling size, a 2nd Conv2D with 64 filters of kernel size of 3x3, MaxPooling2D, Flatten layer, 1st Dense layer with 64 neurons and a 2nd Dense layer with 1 neuron since we're doing binary classification
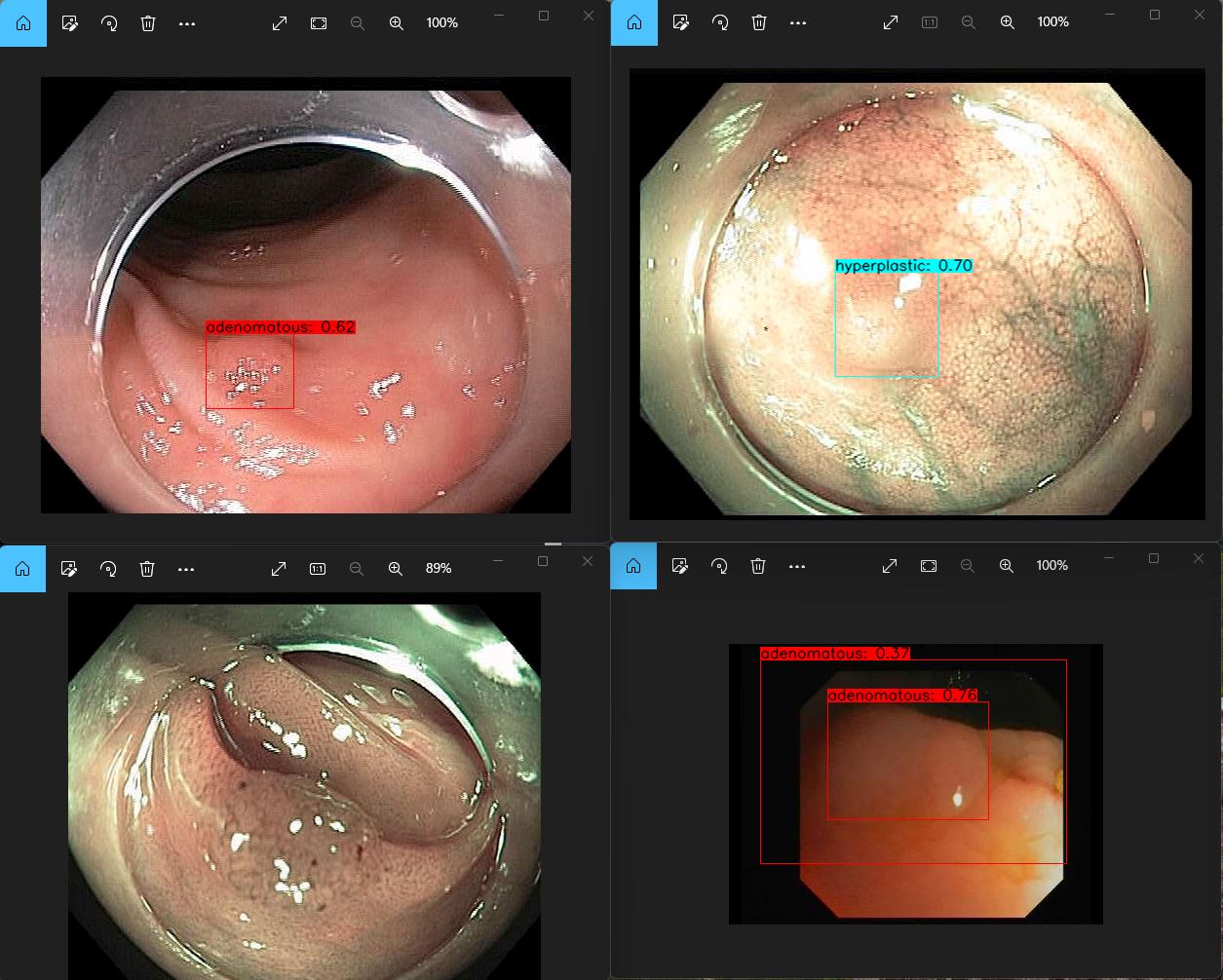
- Created YOLOv4_Polyp_Detection Notebook
- Uses Python to automate setting up Darknet YOLOv4 environment to then build YOLOv4 Darknet model on Windows Laptop in Jupyter Notebook, able to automate training of Darknet YOLOv4 from running Python code in command line, but not able to automate training Darknet YOLOv4 model in Jupyter notebook, so in notebook instruct user to manually train Darknet YOLOv4 model from command line, instruct user to manually evaluate Darknet YOLOv4 model from command line and manually run Darknet YOLOv4 polyp detector model on polyp images.
- Trained YOLOv4 on 7K images over 6 hours on ASUS ROG Zephyrus Laptop (GTX 2070, GPU 8GB RAM, CUDA 11.6)
- 3 different versions of saved YOLOv4 models over iterations, the model that had the best metrics with fastest detection time was YOLOv4 (1K iterations) v1 with Precision 75%, Recall 60%, F1 Score 67%, mAP 83%, Avg IOU 54% and Detection Time 1 sec
- Created UNet_Polyp_Segmentation Notebook
- Created 100 Masked Binary Labels out of 28K+ Training Images. Initially there wasnt masked labels. Performed Data Augmentation to create 2K images and masked labels. Trained UNet on 1.2K images, validated on 320 images, tested on 400 images.
- IOU Score is 21%, F1 Score is 33.5%, Accuracy 91.5%, Loss is 1.085 Loss is ** as average across validation and testing
- Created Rasa Chatbot Stories for Doctor, Surgeon and Physician as App Frontend
- Integrating CNN, YOLOv4 and UNet Models into Rasa as App Backend for DL Model Deployment
- 3 Rasa Custom Action classes were created for where the DL models would be run to do polyp classification, detection and segmentation
- Currently there is filler code for these custom actions that print what each does and the Keras Rasa integration code is commented out. Still resolving integration issues.
- Researched various Object Detection Models in Resarch Papers (Faster RCNN, YOLOv3, YOLOv4, YOLOv5, SSD, RetinaNet, DetNet, RefineDet, ATSS)
For metrics, refer to the following Jupyter notebooks.
For more info on our CNN Polyp Classification model, check out our notebook below:
For more info on our UNet Polyp Segmentation model, check out our notebook below:
For this notebook above, we manually created our own segmentation labeled images:
For more info on our YOLOv4 Polyp Detection model, check out our notebook below:
At the end of YOLOv4 Polyp Detection notebook, you will know how to train it to be able to detect polyps like the following:
We have made conversational chatbot using Rasa with four different entities interacting with chatbot. The entities were Doctor, Physician, Surgeon and Student. Our goal here with the conversations was to eventually lead to our DL models being deployed in Rasa to classify, detect or segment polyps in images and return those reports to the care providers. The conversation flow between each entity and chatbot is as follows:
- Doctor: -> Doctor will ask about symptoms regarding colon cancer. -> Doctor will ask about types of treatments we can use to cure it?
https://enric1994.github.io/synth-colon/ Case 8_Colonoscopy with NBI and ESD for colonic lateral spreading tumors
For example, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3_4b086YEdY Case 14_Colonoscopy with chromoendoscopy and hybrid ESD technique for recurrent colonic adenoma
For example, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gdqOigwvUQA
Artificial Intelligence in Colorectal Cancer Screening, Diagnosis and Treatment. A New Era: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8161764/
Artificial intelligence in gastrointestinal endoscopy, ScienceDirect: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2468448120302721
Deep learning driven colorectal lesion detection in gastrointestinal endoscopic and pathological imaging: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8610875/
Artificial Intelligence- Assisted Polyp Detection System for Colonoscopy, based on the largest available collection of clinical video data for machine learning: :https://www.giejournal.org/article/S0016-5107(19)31325-2/fulltext#relatedArticles
Deep learning for diagnosis of precancerous lesions in upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8160615/
A novel machine learning-based algorithm to identify and classify lesions and anatomical landmarks in colonoscopy images: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00464-021-08331-2 https://wd.vghtpe.gov.tw/ecdt/Fpage.action?muid=2388&fid=5621
EARLIER DIAGNOSIS OF CANCER OF THE COLON THROUGH COLONIC ENDOSCOPY (COLONOSCOPY): https://acsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/1097-0142%28197409%2934%3A3%2B%3C912%3A%3AAID-CNCR2820340720%3E3.0.CO%3B2-P
Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Polyp Detection for Colonoscopy: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016508518304153?via%3Dihub
Artificial Intelligence-Based Classification of Multiple Gastrointestinal Diseases Using Endoscopy Videos for Clinical Diagnosis: https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/8/7/986/htm
Colonoscopy polyp detection and classification: Dataset creation and comparative evaluations: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0255809 Development and Validation of a Deep Neural Network for Accurate Evaluation of Endoscopic Images From Patients With Ulcerative Colitis
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0016508520302122?via%3Dihub