[RISC-V Assembly manual], [RISC-V ELF spec], [RISC-V Calling Conventions], [GNU Assembler Directives]
Flow from assembly program to the corresponding binary executable is depicted in the figure below.
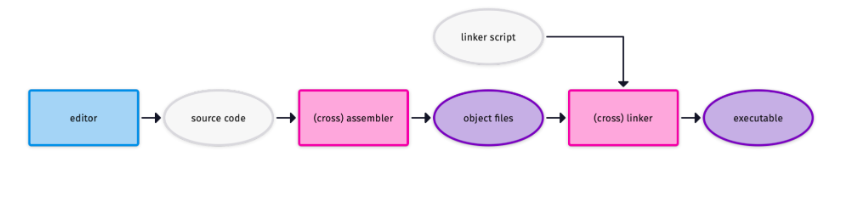
Let's setup tools to compile and debug the RISC-V Assembly programs.
-
Qemu Emulator: Qemu Emulator to run and simulate RISC-V programs.
sudo apt-get install qemu-system-misc qemu-user-static binfmt-support opensbi u-boot-qemu -
Cross Compiler Toolchain: GNU Compiler Toolchain to compile the assembly programs.
sudo apt-get install gcc-riscv64-linux-gnu -
Debugger: In order to debug the assembly programs install GDB-multiarch.
sudo apt-get install gdb-multiarch
Let's take an example assembly program as follows
.text
.global _start
_start:
addi x10, x0, 7
addi x17, x0, 93
add t0, x10,x17
ecall
-
Creating Object File from assembly by running:
riscv64-linux-gnu-as -o example.o example.S -
To obtain executable from the object file using the toolchain (linux) linker file, run the following command
riscv64-linux-gnu-ld -o example example.o -
The disassembly of the executable can be obtained by running.
riscv64-linux-gnu-objdump -sd example💡
riscv64-linux-gnu-objdump --Hfor more dump options -
Emulating and Debugging
qemu-riscv64-static -g 1234 exampleAfter running the above command, leave the terminal window as it is, open another terminal window and run
gdb-multiarch exampleThe debugger will open. Now, run the following command to connect the debugger with the qemu port
1234(gdb) target remote :1234Now, it's connected. In order to look at the code on terminal for debugging, obtain chucnk of source code on the terminal window by specifying the number of lines.
(gdb) display /3i $pcHere,
3is the number of lines of source code andirepresents the instructions.
Other gdb options:
sito step each instruction for debugging.cto continue to iterate through the whole program.qto quit the debugger.
Below are some of the widely GNU binary utilities by RISC-V toolchain. For all the available utilities, visit the documentation.
prefix: riscv64-linux-gnu or riscv64-unknown-elf
- (prefix)-objdump [--help, --info]
- (prefix)-objcopy [--help, --info]
- (prefix)-readelf
- elf2hex
To emulate a full system, a further step is necessary. A whole system needs a boot and system image to start up. You can download pre-baked images from DQIB. Download the file for riscv64-virt and extract the file. There is helpful information in a readme.txt. However, you should be able to emulate the system by typing this command:
qemu-system-riscv64 -machine virt -cpu rv64 -m 1G -device virtio-blk-device,drive=hd -drive file=image.qcow2,if=none,id=hd -device virtio-net-device,netdev=net -netdev user,id=net,hostfwd=tcp::2222-:22 -bios /usr/lib/riscv64-linux-gnu/opensbi/generic/fw_jump.elf -kernel /usr/lib/u-boot/qemu-riscv64_smode/uboot.elf -object rng-random,filename=/dev/urandom,id=rng -device virtio-rng-device,rng=rng -nographic -append "root=LABEL=rootfs console=ttyS0"