Configure note templating locally in frontmatter and insert values using prompts.
Is this Obsidian plugin for you? You should use this plugin if
Note: configuration in GIFs uses old YAML property names. All other YAML in this readme is up to date.
Notes are created by running intents.
Intents group together templates and are the core unit of configuration in this plugin. They represent the different intents for creating a note. Eg: "I intend to create a meeting note".
The frontmatter of any note can hold a list of intents. The easiest way to edit frontmatter is to enable the source property display mode in the Obsidian settings.
Example: simple intents
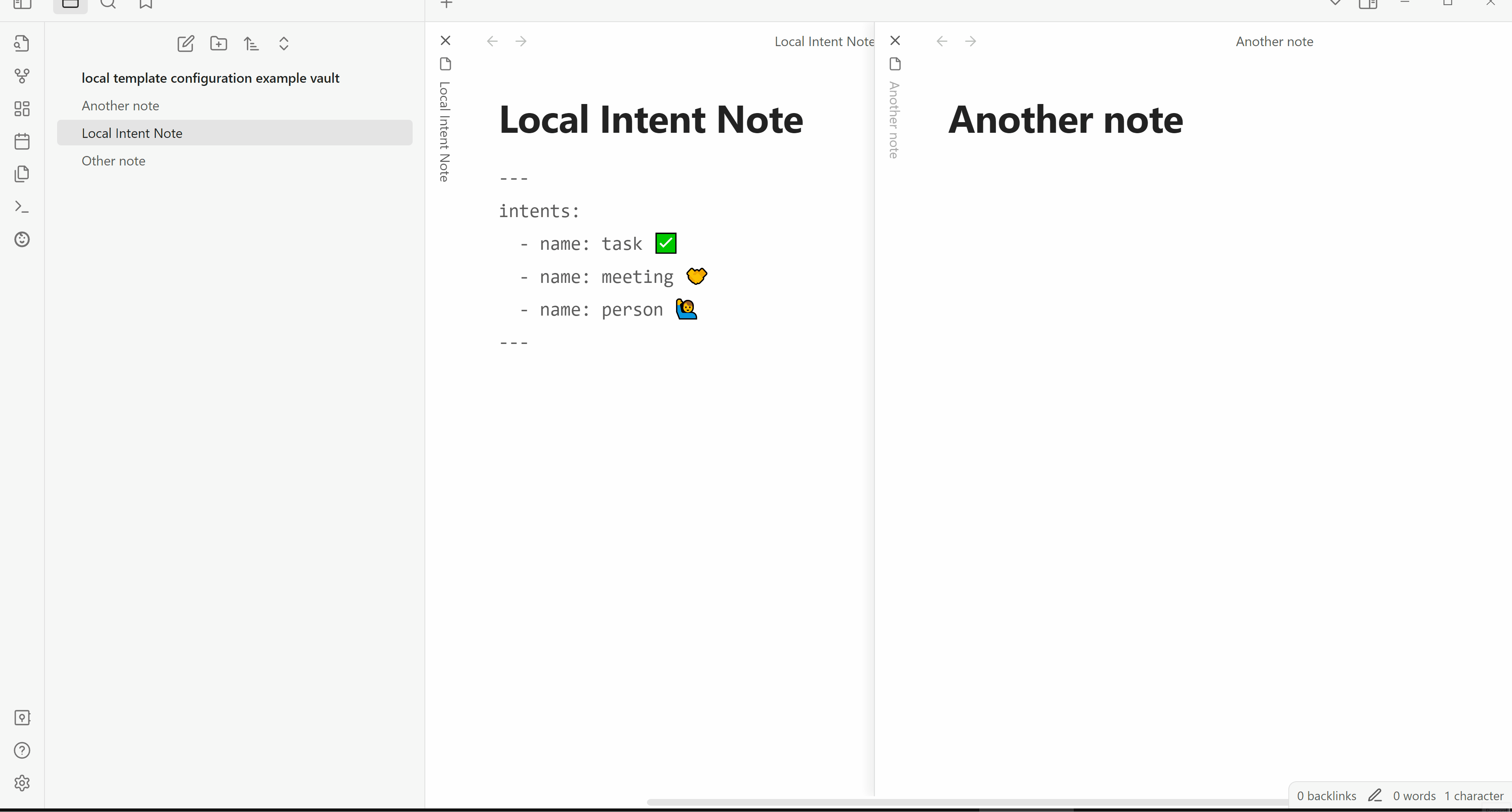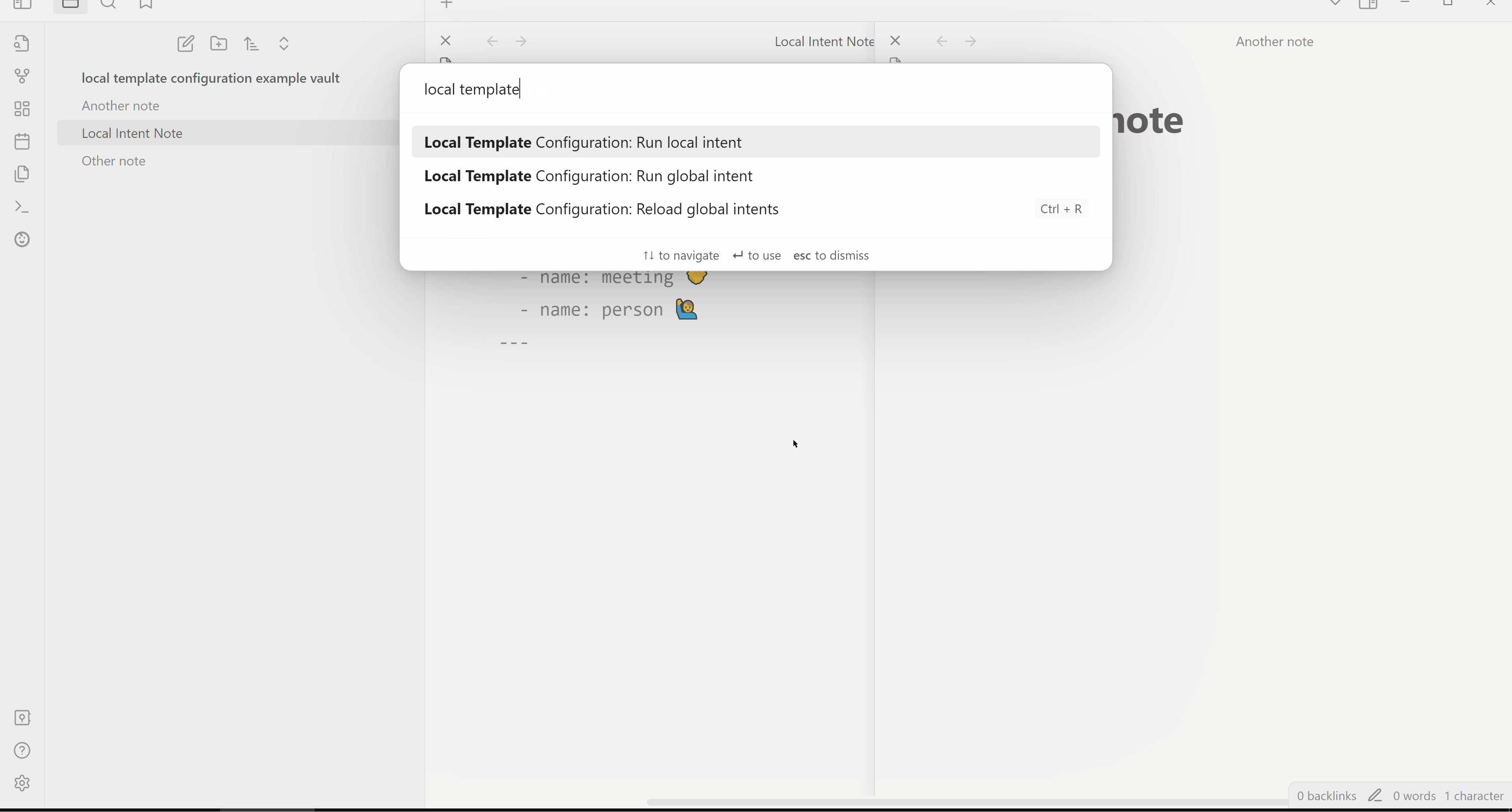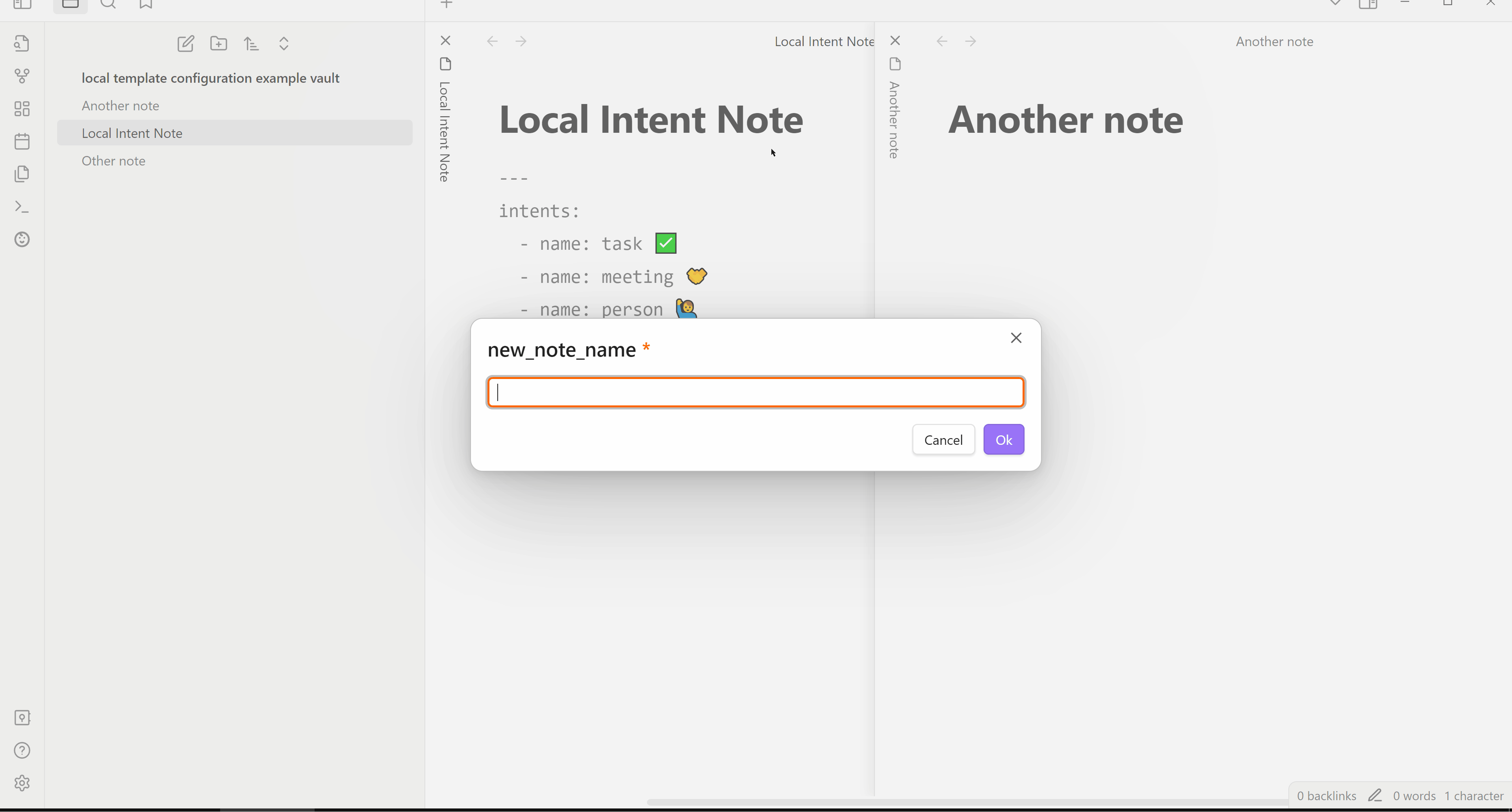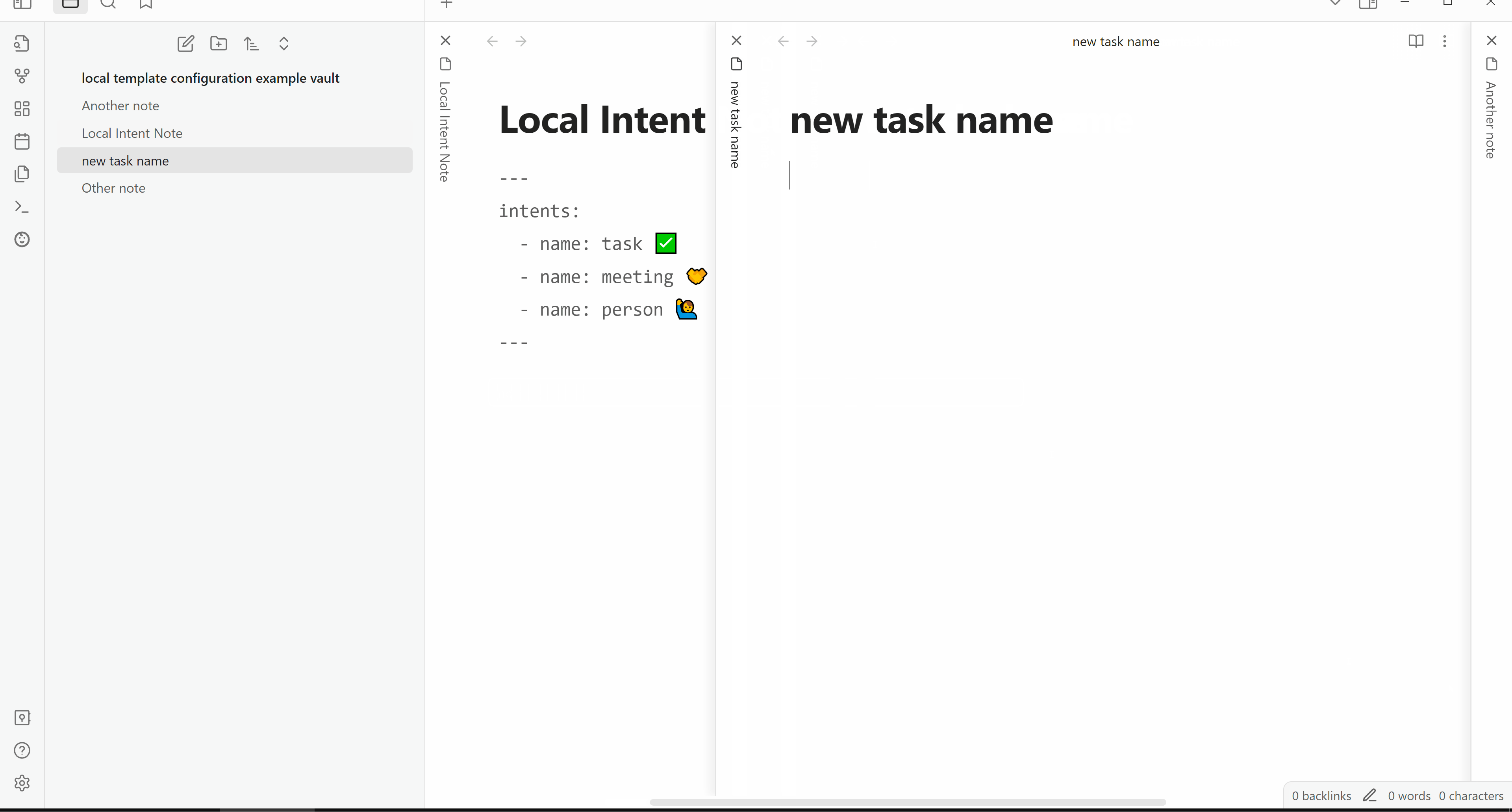
---
intents_to:
- make_a: task ✅
- make_a: meeting 🤝
- make_a: person 🙋♂️
---The Run note intent command is the simplest way to run an intent.
To run a note intent, you have to select the note that contains that intent.
Another plugin called "Filtered Opener" is required to select a note from your vault. To select a note, Filtered Opener displays a list of every note in your vault. Filtered Opener can also be configured to display a subset of your notes using filters. Please install the Filtered Opener plugin as it is required to use this plugin.
After selecting a note, you will be shown its list of intents to chose from. If a note only has one intent, that intent will be selected automatically.
Global intents are intents that are in the global intents note.
Global intents can be ran in the context of any other note. A context note is used to resolve relative paths and before running the global intent, it imports and merges the global intents before the resulting merged intent is ran.
The Run global intent command runs a global intent in the global context.
The global context is the note containing global intents.
Paths relative to the global context are resolved relative to the root folder of your vault.
When global intents are configured, a command is created for each global intent called Create ${intent.name} for note.
This command lets you run a global intent in the context of a note.
The global intents note is configured by setting the Global Intents Note Path in the plugin settings.
This note must be reloaded by using the Reload global intents command for changes to apply.
Intents can have many note templates.
A note template contains a path to a note. The new note will contain the contents of this template note.
The properties of templates are:
| property name | required | Default | description |
|---|---|---|---|
called |
Yes | The display name of the template | |
at_path |
Yes | An alternative for outputs_to_pathname that allows using variable values. The example below uses the new_note_name variable to format the name of the new note |
|
is_disabled |
No | false | see disabling intents, templates and variables |
| Additional properties covered in New Note Properties |
Example: intents with templates
---
intents_to:
- make_a: "task ✅"
with_templates:
- called: "default"
at_path: "Templates/task template.md"
- called: "graded"
at_path: "Templates/graded task template.md"
- called: "worksheet"
at_path: "Templates/worksheet task template.md"
- make_a: "meeting 🤝"
with_templates:
- called: "default"
at_path: "Templates/meeting template.md"
- called: "project review"
at_path: "Templates/project review meeting template.md"
- called: "standup"
at_path: "Templates/standup meeting template.md"
- make_a: "person 🙋♂️"
with_templates:
- called: "default"
at_path: "Templates/person template.md"
- called: "work colleague"
at_path: "Templates/work colleague person template.md"
---Both intents and templates can have a new note pathname and a list of variables.
Template new note properties overwrite intent new note properties.
Example: Task intent has 3 different templates with different output folders and note names.
The properties of new notes are:
| property name | required | Default | description |
|---|---|---|---|
outputs_to_pathname |
No | A note called new_note_name in the same folder as the context note |
The output location and name of the new note |
outputs_to_templated_pathname |
No | ./{{new_note_name}} is the template representation of the above |
An alternative for outputs_to_pathname that allows using variable values. The example below uses the new_note_name variable to format the name of the new note |
with_variables |
No | A list of variables | |
is_disabled |
No | false | see disabling intents, templates and variables |
Example:
- A task intent that
outputs_to_templated_pathname. - A "graded task" template with an additional
date_releasedvariable and a custom output pathname. - A "worksheet task" template with an additional
worksheet_numbervariable and a custom output pathname.
---
intents_to:
- make_a: task ✅
outputs_to_templated_pathname: ./✔ tasks/✅ {{new_note_name}}
with_variables:
- called: deadline
of_type: natural_date
with_templates:
- called: default ✅
at_path: Templates/task template.md
- called: graded 🎓
at_path: Templates/graded task template.md
outputs_to_templated_pathname: ./✔ tasks/🎓 {{new_note_name}}
with_variables:
- called: date_released
of_type: natural_date
- called: percent
- called: worksheet 📃
at_path: Templates/worksheet task template.md
outputs_to_templated_pathname: "./📃 worksheets/📃 Worksheet #{{worksheet_number}} - {{new_note_name}}"
with_variables:
- called: worksheet_number
of_type: number
is_over: 1
---There are multiple types of variables but all variables contain a common set of properties:
| property name | required | Default | description |
|---|---|---|---|
called |
Yes | The name of the variable, used when inserting values into templates. see using variable values. For the purpose of demonstration this property uses lowercase and underscores instead of spaces but it can contain any characters eg emojis. |
|
of_type |
No | text | The type of the variable. See variable types. |
is_required |
No | false | If true, when you enter an invalid value the note creation process will stop and an error message will be shown. |
that_prompts |
No | The text that is displayed when prompting. | |
described_as |
No | Text that will be shown bellow the prompt. | |
is_initially |
No | The value that will be in the prompt initially. | |
uses_selection |
No | false | See prepopulating prompts using selection. |
replaces_selection_with_templated |
No | [[{{new_note_name}}]] | Template text that replaces the selection if uses_selection is enabled |
hinted_as |
No | The value displayed inside the prompt when it is empty. | |
is_disabled |
No | false | See disabling intents, templates and variables |
There are multiple ways to use variable values. See using variable values.
Each type of variable has its own parameters and validation.
A simple text prompt. Text is the default variable type.
| property name | required | Default | description |
|---|---|---|---|
matches_regex |
No | A regular expression used to validate the text |
Example:
---
with_variables:
- called: word_starting_with_auto
of_type: text
matches_regex: ^auto
---A simple number prompt. Any number including integers and floats.
| property name | required | Default | description |
|---|---|---|---|
is_over |
No | the minimum allowed value | |
is_under |
No | the maximum allowed value |
Example:
---
with_variables:
- called: a_number
of_type: number
is_over: -10.8
is_under: 11.22
---A natural date provided the natural language dates plugin.
| property name | required | Default | description |
|---|---|---|---|
format |
No | Defaults to natural date setting | The output format of the natural date |
is_after |
No | The date must be after this date. A natural language date | |
is_before |
No | The date must be before this date. A natural language date |
Example:
---
with_variables:
- called: some_date
of_type: natural_date
format: "YYYY-MM-dd"
is_after: yesterday # today or later
is_before: next year
---A path to a note chosen from a list of notes. Uses same Filtered Opener plugin as when selecting a note.
The Filtered Opener plugin takes the name of the filter set (note_filter_set_name) to display a list of notes to chose from.
| property name | required | Default | description |
|---|---|---|---|
note_filter_set_name |
No | Allows all notes | The name of the note filter set. |
Example:
---
with_variables:
- called: some_note
of_type: note
note_filter_set_name: maps of content
---A path to a folder chosen from a list of folders. Uses same Filtered Opener plugin as when selecting a note.
The Filtered Opener plugin takes the name of the filter set (folder_filter_set_name) to display a list of folders to chose from.
| property name | required | Default | description |
|---|---|---|---|
in_folder |
No | Vault root folder | A folder to start searching from, defaults to the vault folder. |
at_depth |
No | Depth configured in Filtered Opener | The depth of folders to include, for a folder structure of root/inner/leaf, a depth of 2 will show notes down to the leaf level. |
includes_roots |
No | false |
When false notes only at the specified depth are shown. When true notes at all levels down to the specified depth are shown. |
folder_filter_set_name |
No | Allows all folders | The name of the folder filter set. |
Example:
---
with_variables:
- called: a_project_folder
of_type: folder
in_folder: "/🏗 projects"
at_depth: 1
includes_roots: false
folder_filter_set_name: default
---When using variables, text in the format of {{variable_name}} is replaced with the value of the variable.
If the variable called variable_name is not in the current intent, the {{variable_name}} text will not be changed.
When creating a new note, variables in the template are also replaced before the new file is created.
If you are already familiar with the Templater plugin, it will run its templating after the variables of this plugin are replaced.
This is a text variable that is added to every intent automatically.
It holds the name of the new note and can be used in outputs_to_templated_pathname to add other text, including other variables, to the new note name.
It can also be used with a folder variable to chose the output folder of the new note eg to create a project
If an intent disables new_note_name and doesn't set outputs_to_pathname, by default the name of the new note will be the name of the intent and it will be created in the same folder as the context note.
Intents, templates and variables can be disabled by setting is_disabled to true.
- Disabled intents and templates are ignored and not shown when one must be selected.
- Disabled variables are ignored, their prompts are not shown and they wont be replaced when using variable values.
Disabled items are still imported and can be un-hidden by setting their is_disabled property to false.
When running an intent, selected text can be used to pre-populate the prompts for variables.
The selection will be split using the delimiters configured in the plugin settings and then assigned to variables by the order that they appear in the variable list.
To enable this for a variable, set uses_selection to true.
If a variable is assigned a valid value from the selection, the value will be accepted and the variable prompt will be skipped. If the value is not valid, the prompt will be shown prepopulated with the selected value.
The full schema used by this plugin is shown in the Intents Schema File.
When debugging intents, check the developer console. If an intent has properties that aren't in this schema, an error will be shown.
Notes can import intents from other notes using the intents_imported_from property.
The intents_imported_from property accepts any number of paths to configuration notes.
Example: Import single note
---
intents_imported_from: "some/configuration note.md"
---Example: Import a list of notes
---
intents_imported_from: ["some/configuration note.md", "other/configuration note.md" ]
---The intents of the imported notes are loaded first and are then merged with note intents.
If a note with an intent imports an intent with the same name, the current note intent properties will overwrite the properties of the imported intent.
Overwriting properties of imported intents is useful to:
- add and change templates
- eg: use a template in the same folder by overwriting the template path with a relative one
- add variables
- enabling and disabling intents, templates and variables
- you use templates to create notes
- you want to insert variables into your templates and use prompts to capture their values
- you want to group your templates by intent
- eg: a task, a meeting, …
- some of your intents have multiple templates
- tasks: a normal task, a graded task, a research task
- meetings: daily stand-up meeting, project catch-up meeting, catch-up with a colleague
- you want to extend/override your prompts and templates on a note by note basis
- use a template note next to your note (relative path)
- add prompts to an existing intent/template
- add more intents/templates
- …
- auto-populate variable prompts with selected text
- use multiple cursors to create multiple notes
- replace the selected text with a link to the new note
- use a template to change the replacement text
- supports many variable types eg text, number
- and other types of variable providers eg: natural date, note, folder
- import other config notes
Contextual Note Templating (CNT) functionality compared to:
- Note from template: Both plugins show prompts and use the selection to pre-populate fields that can be inserted into many note properties eg output folder, name, note title and body.
- The major difference is that CNT shows one field at a time and extends the functionality of a single field.
- CNT extends fields into Variables.
- Each variable has its own configurable prompt and its type adds validation and post processing.
- Hotkeys for templates:
- Instead of creating hotkeys (commands) for each template, this plugin creates commands for each Intent.
---
intents_to:
- make_a: task
---This intent will create an empty note named the value of new_note_name in the same folder as the context note.
Create an empty note in a folder called tasks next to the context note.
---
intents_to:
- make_a: task
outputs_to_templated_pathname: "./tasks/{{new_note_name}}"
---Create an empty note in a folder in the root of the vault called vault tasks.
---
intents_to:
- make_a: task
outputs_to_templated_pathname: "/vault tasks/{{new_note_name}}"
---Chose a folder and place a task in its own folder in that folder.
---
intents_to:
- make_a: task
with_variables:
- called: output_folder
is_required: true
of_type: folder
in_folder: ✅ tasks
at_depth: 1
includes_roots: false
folder_filter_set_name: default
outputs_to_templated_pathname: "{{output_folder}}/{{new_note_name}}/{{new_note_name}}"
---Adding a simple template.
---
intents_to:
- make_a: task
with_templates:
- called: simple task
at_path: "/path /to /templates folder /simple task template.md"
---Using a template next to a context note.
---
intents_to:
- make_a: task
with_templates:
- called: simple task
at_path: "./simple task template.md"
---This intent creates a project note with an emoji in the project note name.
This intent disables new_note_name and replaces it with a new_project_name variable so that it doesn't replace new_note_name in the project note.
---
intents_to:
- make_a: project
with_variables:
- called: new_note_name
is_disabled: true
- called: new_project_name
outputs_to_templated_pathname: "./{{new_project_name}}/🏗 {{new_project_name}}"
with_templates:
- called: default
at_path: "/path /to /templates /project template.md"
---This creates a project note with an intent that contains the project name in the task name template.
Because new_note_name is disabled, it wont be replaced but new_project_name will.
Project note template:
---
intents_to:
- make_a: task
outputs_to_templated_pathname: "./tasks/{{new_project_name}}-{{new_note_name}}"
with_templates:
- called: simple task
at_path: "./simple task template.md"
---
# Note for {{new_note_name}} project!
Contents of the project note template!This intent creates a project note with an intent that has the project name in the task name, created in its own folder in a category folder.
In this case the 🏗 projects folder contains subfolders that categorize projects.
This intent disables new_note_name and replaces it with a new_project_name variable so that it doesn't replace new_note_name in the project note.
---
intents_to:
- make_a: project
with_variables:
- called: new_note_name
is_disabled: true
- called: new_project_name
- called: output_folder
is_required: true
of_type: folder
in_folder: 🏗 projects
at_depth: 1
includes_roots: false
outputs_to_templated_pathname: "{{output_folder}}/{{new_project_name}}/🏗 {{new_project_name}}"
with_templates:
- called: default
at_path: "/path /to /templates /project template.md"
---Because new_note_name is disabled, it wont be replaced but new_project_name will.
Project note template:
---
intents_to:
- make_a: task
outputs_to_templated_pathname: "./tasks/{{new_project_name}}-{{new_note_name}}"
with_templates:
- called: simple task
at_path: "./simple task template.md"
---
# Note for {{new_project_name}} project!This repository uses code from the following projects:
Code credits are also placed in comments above code.