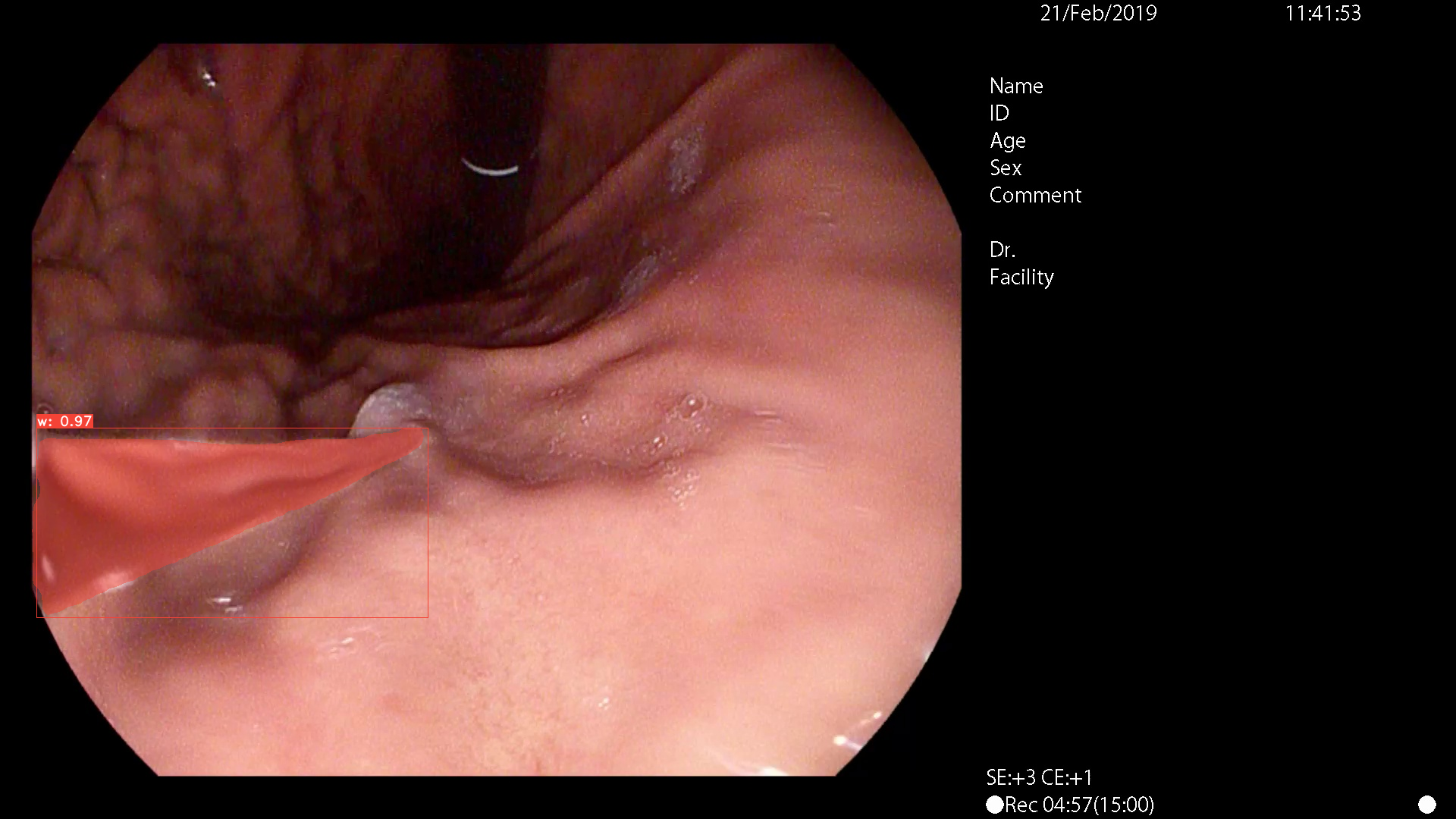
paper:
YOLACT: Real-time Instance Segmentation YOLACT++: Better Real-time Instance Segmentation
Xu Jing
通过labelme我们标注了自己的训练集,我们将标注的训练集经过如下处理后即可得到coco样式的数据
$ cd labelme-master/examples/instance_segmentation
$ python3 labelme2coco.py water water_coco --labels labels.txt
其中labels.txt文件为labelme标注的label名称列表,如下:
__ignore__
_background_
water
会在当前文件夹下的water_coco文件下生成JPEGImages文件夹内存放了所有的image及annotations.json为coco类型的标注文件。
- clone yolact项目
$ git clone https://github.com/dbolya/yolact.git
$ cd yolact
- 安装相关环境
# anaconda
$ conda env create -f environment.yml
# Pytorch 1.0.1 (or higher) 和 TorchVision建议手动安装
# Cython needs to be installed before pycocotools
$ pip3 install cython
$ pip3 install opencv-python pillow pycocotools matplotlib
如果想使用YOLACT++,请编译DCNv2
$ cd external/DCNv2
$ python3 setup.py build develop
- 打开
yolact-master/data/config.py
# 修改dataset_base
# ----------------------- DATASETS ----------------------- #
dataset_base = Config({
'name': 'water', # 起个名字
# Training images and annotations
'train_images': './myData/coco/JPEGImages/train', # 训练集的路径
'train_info': './myData/coco/annotations/train/annotations_train.json', # 标签的路径
# Validation images and annotations.
'valid_images': './myData/coco/JPEGImages/val', # 验证集路径
'valid_info': './myData/coco/annotations/train/annotations_val.json', #验证集标签的路径
# Whether or not to load GT. If this is False, eval.py quantitative evaluation won't work.
'has_gt': True,
# A list of names for each of you classes.
'class_names': ('water'), # 修改成自己的class name 是一个truple
# COCO class ids aren't sequential, so this is a bandage fix. If your ids aren't sequential,
# provide a map from category_id -> index in class_names + 1 (the +1 is there because it's 1-indexed).
# If not specified, this just assumes category ids start at 1 and increase sequentially.
'label_map': {1:1} # 修改成自己的label map
})
- 修改数据名称和
num_classes。(num_classes=数据集标签类数+1)
# ----------------------- YOLACT v1.0 CONFIGS ----------------------- #
yolact_base_config = coco_base_config.copy({
'name': 'yolact_base',
# Dataset stuff
'dataset': dataset_base, # 数据源
'num_classes': 1 + 1, # 类别数量 = label + 1
# Image Size
'max_size': 550,
# Training params
'lr_steps': (280000, 600000, 700000, 750000),
'max_iter': 800000,
-
下载预训练权重放至根目录里的
weights文件夹下 -
在训练过程中按
ctrl+c能够保存当前训练权重并保存在weight文件夹里。命名为:<config>_<epoch>_<iter>.pth -
训练
使用默认为8的batch size训练:
$ python3 train.py --config=yolact_base_config
根据根据实际情况可以适当调节batch size的大小,如果显卡性能低可以减小batch size大小:
$ python3 train.py --config=yolact_base_config --batch_size=5
从中断的权重继续训练:
$ python3 train.py --config=yolact_base_config --resume=weights/yolact_base_10_32100.pth --start_iter=-1
$ python3 train.py --config=yolact_plus_resnet50_config
帮助:
$ python3 train.py --help
- image
# Display qualitative results on the specified image.
$ python3 eval.py --trained_model=weights/yolact_base_54_800000.pth --score_threshold=0.15 --top_k=15 --image=my_image.png
# Process an image and save it to another file.
$ python3 eval.py --trained_model=weights/yolact_base_54_800000.pth --score_threshold=0.15 --top_k=15 --image=input_image.png:output_image.png
# Process a whole folder of images.
$ python3 eval.py --trained_model=weights/yolact_base_54_800000.pth --score_threshold=0.15 --top_k=15 --images=path/to/input/folder:path/to/output/folder
$ python3 eval.py --trained_model=weights/yolact_plus_resnet50_1086_100000.pth --score_threshold=0.15 --top_k=15 --images=./test:./result
- video
# Display a video in real-time. "--video_multiframe" will process that many frames at once for improved performance.
# If you want, use "--display_fps" to draw the FPS directly on the frame.
$ python3 eval.py --trained_model=weights/yolact_base_54_800000.pth --score_threshold=0.15 --top_k=15 --video_multiframe=4 --video=my_video.mp4
# Display a webcam feed in real-time. If you have multiple webcams pass the index of the webcam you want instead of 0.
$ python3 eval.py --trained_model=weights/yolact_base_54_800000.pth --score_threshold=0.15 --top_k=15 --video_multiframe=4 --video=0
# Process a video and save it to another file. This uses the same pipeline as the ones above now, so it's fast!
$ python3 eval.py --trained_model=weights/yolact_base_54_800000.pth --score_threshold=0.15 --top_k=15 --video_multiframe=4 --video=input_video.mp4:output_video.mp4
$ python3 eval.py --trained_model=weights/yolact_plus_resnet50_1086_100000.pth --score_threshold=0.50 --top_k=15 --video_multiframe=4 --display_fps --video=test.mp4:test_res.mp4
python3 eval.py --trained_model=weights/yolact_plus_resnet50_1086_100000.pth --score_threshold=0.50 --top_k=15 --display_fps --video=test.mp4:test_res.mp4
- help
python3 eval.py --help
@inproceedings{yolact-iccv2019,
author = {Daniel Bolya and Chong Zhou and Fanyi Xiao and Yong Jae Lee},
title = {YOLACT: {Real-time} Instance Segmentation},
booktitle = {ICCV},
year = {2019},
}
For YOLACT++, please cite
@misc{yolact-plus-arxiv2019,
title = {YOLACT++: Better Real-time Instance Segmentation},
author = {Daniel Bolya and Chong Zhou and Fanyi Xiao and Yong Jae Lee},
year = {2019},
eprint = {1912.06218},
archivePrefix = {arXiv},
primaryClass = {cs.CV}
}