This is the official codebase of the paper PEER: A Comprehensive and Multi-Task Benchmark for Protein Sequence Understanding, accepted by NeurIPS 2022 Dataset and Benchmark Track (OpenReview link).
Minghao Xu*, Zuobai Zhang*, Jiarui Lu, Zhaocheng Zhu, Yangtian Zhang, Chang Ma, Runcheng Liu, Jian Tang (*equal contribution)
- [2022/09/19] The initial release! We release source codes and configs for 14 tasks in the PEER benchmark.
- [2022/10/16] Full PEER benchmark released! We newly release the source codes and configs for three protein function prediction tasks from FLIP.
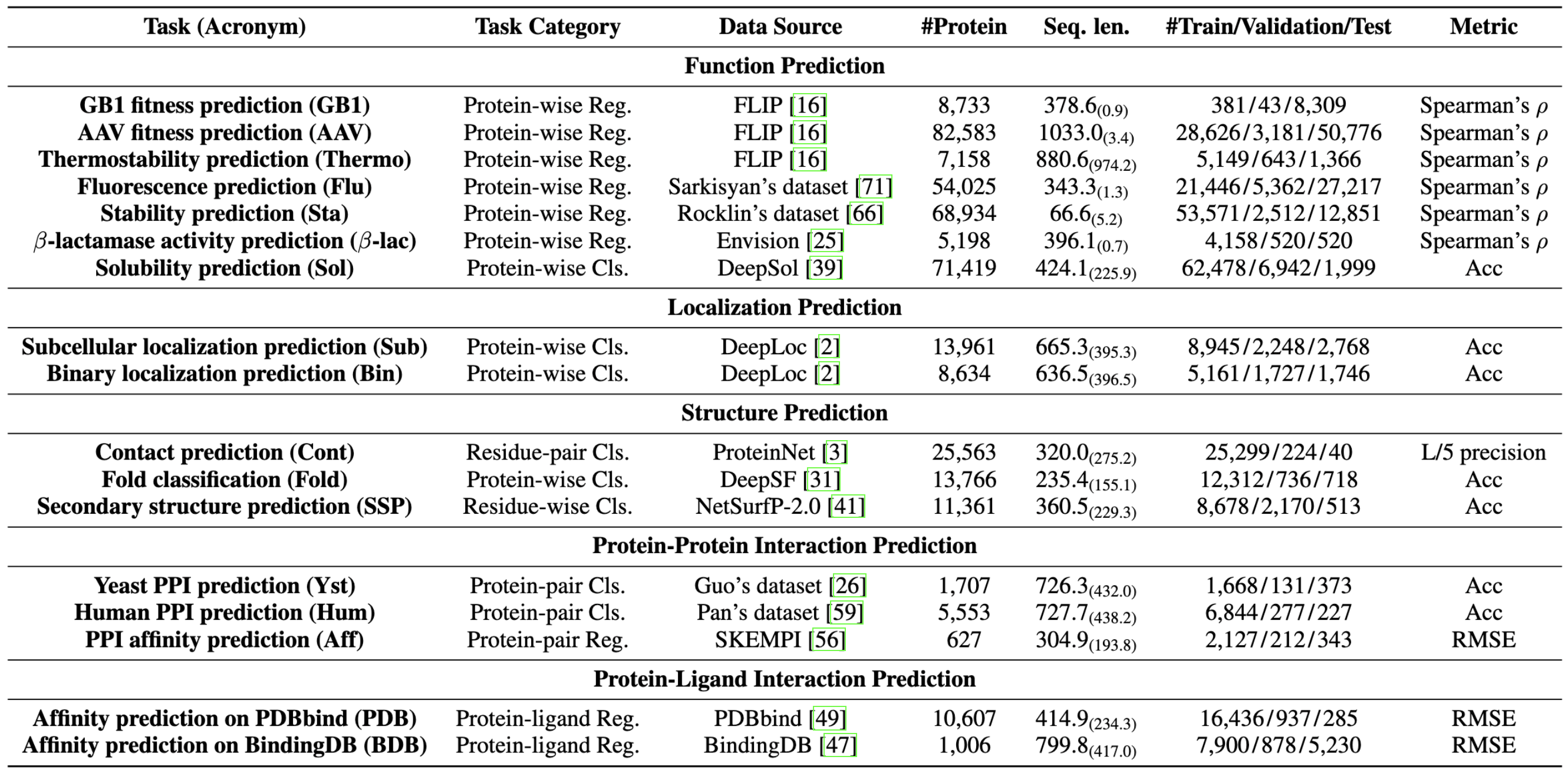
PEER is a comprehensive and multi-task benchmark for protein sequence understanding. It contains 17 tasks of protein understanding lying in 5 task categories including protein function prediction, protein localization prediction, protein structure prediction, protein-protein interaction prediction and protein-ligand interaction prediction. On this benchmark, we evaluate different types of sequence-based methods for each task including traditional feature engineering approaches, different sequence encoding methods as well as large-scale pre-trained protein language models under both single-task learning and multi-task learning settings.
This codebase is based on PyTorch and TorchProtein, an extension of TorchDrug specific to protein applications. It supports training and inference with multiple GPUs or multiple machines.
You may install the dependencies of TorchProtein and PEER benchmark as below. Generally, they work with Python 3.7/3.8 and PyTorch version >= 1.8.0.
conda create -n protein python=3.7
conda activate protein
conda install pytorch==1.8.0 cudatoolkit=10.2 -c pytorch
conda install scikit-learn pandas decorator ipython networkx tqdm matplotlib -y
conda install pytorch-scatter pytorch-cluster -c pyg -c conda-forge
pip install fair-esm transformers easydict pyyaml lmdb
python -m pip install git+https://github.com/DeepGraphLearning/torchdrug/We provide a yaml based config for each benchmark experiment in our paper.
The configs of all baselines for single-task and multi-task learning are stored in ./config/ with the following folder structure:
config
└── single_task
├── ESM
│ ├── Task_ESM.yaml
│ ├── Task_ESM_fix.yaml
├── ProtBert
├── LSTM
├── BERT
├── CNN
├── ResNet
├── DDE
├── Moran
├── multi_task
├── ESM
│ ├── CenterTask_AuxiliaryTask_ESM.yaml
├── BERT
├── CNN
In each config, we give a suggested GPU configuration, considering the tradeoff between dataset size and computational resource. We assume Tesla-V100-32GB GPUs as the computational resource. You can change this default configuration based on your own computational resource.
Note. The benchmark results can be reproduced by taking the mean and std of three runs with --seed 0, --seed 1 and --seed 2.
Single-GPU. By setting gpus: [0], the experiment is performed under a single GPU.
You can use the following command to run with seed 0, where all datasets will be automatically downloaded in the code.
Single-task learning experiment:
python script/run_single.py -c config/single_task/$model/$yaml_config --seed 0Multi-task learning experiment:
python script/run_multi.py -c config/multi_task/$model/$yaml_config --seed 0Multi-GPU. By setting gpus: [0,1,2,3], the experiment is performed under a single machine with 4 GPUs.
You can use the following command to run with seed 0.
Single-task learning experiment:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=4 script/run_single.py -c config/single_task/$model/$yaml_config --seed 0Multi-task learning experiment:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=4 script/run_multi.py -c config/multi_task/$model/$yaml_config --seed 0Multi-Machine. By setting gpus: [0,1,2,3,0,1,2,3], the experiment is performed under 2 machines with 4 GPUs in each machine.
You can use the following command to run with seed 0.
Single-task learning experiment:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nnodes=2 --nproc_per_node=4 script/run_single.py -c config/single_task/$model/$yaml_config --seed 0Multi-task learning experiment:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nnodes=2 --nproc_per_node=4 script/run_multi.py -c config/multi_task/$model/$yaml_config --seed 0At the website of TorchProtein, we maintain a leaderboard for each benchmark task. We also maintain an integrated leaderboard among different methods by taking the mean reciprocal rank (MRR) as the metric. In the future, we will open the entrance to receive new benchmark results of new methods from the community.
This codebase is released under the Apache License 2.0 as in the LICENSE file.
If you find this codebase helpful in your research, please cite the following paper.
@article{xu2022peer,
title={PEER: A Comprehensive and Multi-Task Benchmark for Protein Sequence Understanding},
author={Xu, Minghao and Zhang, Zuobai and Lu, Jiarui and Zhu, Zhaocheng and Zhang, Yangtian and Ma, Chang and Liu, Runcheng and Tang, Jian},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.02096},
year={2022}
}