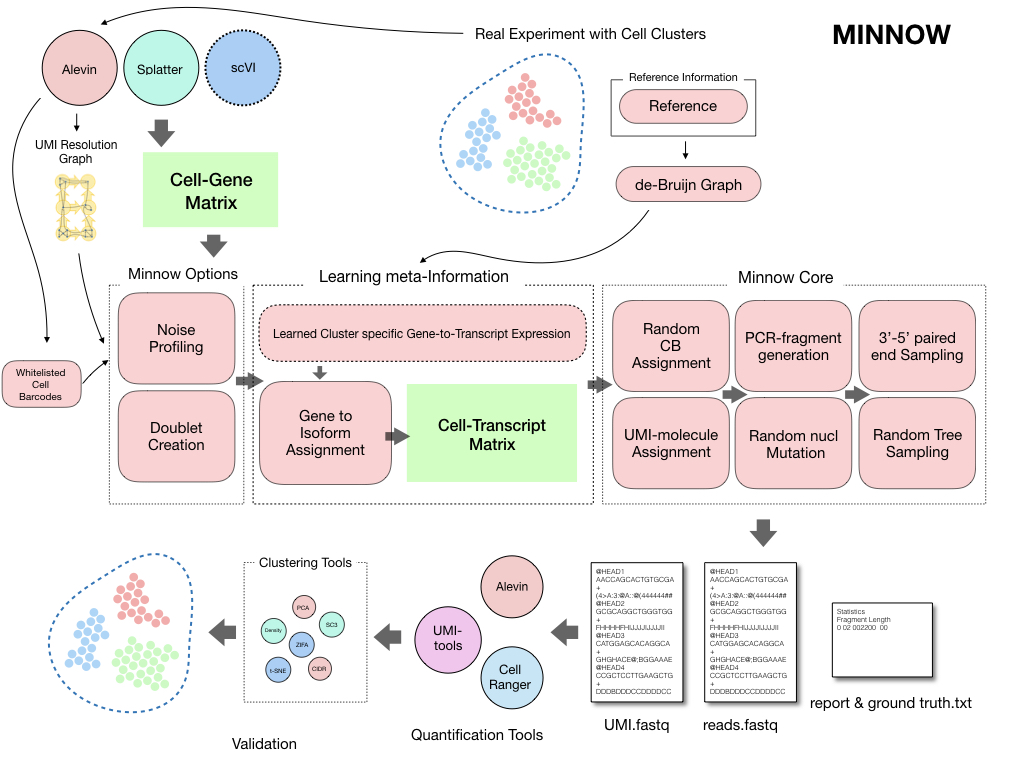
Most analysis pipelines validate their results using known marker genes (which are not widely available for all types of analysis) and by using simulated data from gene-count-level simulators. Typically, the impact of using different read-alignment or UMI deduplication methods has not been widely explored. Assessments based on simulation tend to start at the level of assuming a simulated count matrix, ignoring the effect that different approaches for resolving UMI counts from the raw read data may produce. Here, we present minnow, a comprehensive sequence-level droplet-based single-cell RNA-seq (dscRNA-seq) experiment simulation framework. Minnow accounts for important sequence-level characteristics of experimental scRNA-seq datasets and models effects such as PCR amplification, CB (cellular barcodes) and UMI (Unique Molecule Identifiers) selection, and sequence fragmentation and sequencing.
Minnow is a read level simulator for droplet based single cell RNA-seq data. Minnow simulates the reads by sampling sequences from the underlying de-Bruijn graph (using --dbg) of the reference transcriptome or alternatively just samples sequences from the reference transcriptome. As the --dbg option also enables other features of the software, it is useful to describe those.
[docker](docker pull hrksrkr/minnow)
conda install minnow -c bioconda
Minnow is written in C++14 and tested in a ubuntu server, please let us know if you have difficulty compiling it in your own machine.
git clone https://github.com/COMBINE-lab/minnow.git
cd minnow
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
makeGiven the above steps run withot error, the binary will be stored within the build/src.
In terms of input currently minnow works in two different modes, 1. alevin-mode and 2. splatter-mode. Although it can be be made to work with other matrices given the input is provided with correct format.
This works now with binary flag --binary as most by default alevin writes a binary files. The minimal requirement of alevin directory are quants_mat.gz, quants_mat_rows.txt, quants_mat_cols.txt.
A typical example (minimal)
src/minnow simulate --alevin-mode --binary --g2t <transcript_to_gene_file> -m <alevin_dir_run_on_real_data> -r <fasta_file> --PCR 8 -e 0.001 -p 2 -o <output>Optionally using whitelist produced by alevin
src/minnow simulate --alevin-mode --binary --g2t <transcript_to_gene_file> -m <alevin_dir_run_on_real_data> -r <fasta_file> --PCR 8 -e 0.001 -p 2 -o <output> --useWhiteListIn splatter-mode, just like in alevin mode minnow accepts at least three different files, in the same format, quants_mat.csv, quants_mat_cols.txt, quants_mat_rows.txt. Although splatter matrix is a gene to cell matrix. While running splatter it is easy to create this format by inserting few lines after running splatter.
Below is an example,
sim <- splatSimulate(
nGenes=num_genes,
batchCells=num_cells,
verbose = FALSE
)
write.table(rownames(sim), file= file.path(out_dir, "quants_mat_rows.txt"), quote=FALSE, col.names=FALSE, row.names=FALSE)
write.table(colnames(sim), file= file.path(out_dir, "quants_mat_cols.txt"), quote=FALSE, col.names=FALSE, row.names=FALSE)
write.table(counts(sim), file= file.path(out_dir, "quants_mat.csv"), quote=FALSE, col.names=FALSE, row.names=FALSE, sep=",")
Run TwoPaCo
# delete non unique k-mers of length <READ_LEN>
fixFasta --klen <READ_LEN+1> --input <fasta_file> --output <fixed_fasta_file>
# delete duplicated sequences
seqkit rmdup -s <fixed_fasta_file> > <dedup_fasta>
# run TwoPaCo to produce gfa
TwoPaCo/build/graphconstructor/twopaco -k <READ_LEN+1> -t 10 -f 20 <dedup_fasta> --outfile dbg.bin --tmpdir /tmp/
TwoPaCo/build/graphdump/graphdump <tr.gfa> -k <READ_LEN+1> -s <fasta_file> -f gfa1 dbg.bin
The above process are required to be executed sequencially,
for ease of use we uploaded the de-Bruijn graph and reference transcripts are uploaded in zenodo.
Minnow accepts a de-Bruijn graph in gfa format. (produced by TwoPaCo)
In --dbg mode minnow accepts few additional options, such as --gfa (required), --bfh (optional), --rspd (optional). The repository currently contains two different probability files estimated from 10X pbmc 4k dataset. If --dgb option is provided without any of --bfh, --geneProb or --countProb is provided, those default files will be read.
In default mode weibull distribution is used.
gene prob file - data/hg/geneLebelProb_pbmc_4k.txt
gene prob file - data/hg/countProb_pbmc_4k.txt
transcript to gene - data/hg/hg_t2g.tsv
src/minnow simulate --alevin-mode --binary --g2t <transcript_to_gene_file> -m <alevin-dir>/alevin --PCR <PCR-cycle> -r <fasta_file> -e <error_rate < 1> -p <#threads> 2> -o <out_dir> --useWhiteList --dbg --gfa <gfa_file> --geneProb <gene_prob_file> --rspd <fragment_length_dist_file> -s <#samples>
src/minnow simulate --alevin-mode --binary --g2t <transcript_to_gene_file> -m <alevin-dir>/alevin --PCR <PCR-cycle> -r <fasta_file> -e <error_rate < 1> -p <#threads> 2> -o <out_dir> --useWhiteList --dbg --gfa <gfa_file> --bfh <bfh_file> --rspd <fragment_length_dist_file> -s <#samples>
src/minnow simulate --splatter-mode --g2t <transcript-gene> -m <alevin-dir> --PCR <PCR-cucle> -r <fasta_file> -e <error-rate> -p <#threads> -o <out_dir> --dbg --gfa <gfa_file> --bfh <bfh_file>src/minnow simulate --splatter-mode --g2t /mnt/scratch6/avi/data/cgat/references/metadata/hg_t2g.tsv -m ../example_data/splatter_data_100_Cells_50K_Genes_pbmc/ --PCR 7 -r /mnt/scratch6/avi/data/cgat/references/txome/hg_transcriptome.fasta -e 0.01 -p 25 -o <out_dir> --useWeibull --testUniqness --reverseUniqness- Doublets
- Empty-drops
- Retained intron
- Clusters