ROS 2 with Neovim
Neovim setup to work with ROS 2 Humble in Ubuntu 22.04.
This configuration can be used to develop ROS components in
- C++
- Python
This repository is meant to be used as a starting point for Neovim. Therefore, it is configured as a single init.lua file.
The file contains explanation for the different plugins used and their configurations.
The goal is that you use this repository and begin your Neovim configuration. You can add and remove plugins based on your needs.
Installation
I have a provided a config script to speed up the process of configuring Neovim for you. This script with install all the dependencies, download a version of Neovim, and deploy the configuration files to the correct path.
By default ./deploy.sh will download Neovim version v0.9.2, which is the latest stable release, to ~/open_source/Neovim/.
You can change the version and path by calling the script with ./deploy --path <YOUR_PATH> --version <VERSION>. NOTE: The version can be a branch or a tag from the Neovim repository.
Post Installation
The first time you open Neovim, it will install all the Treesitter configurations, as well as the LSPs, Linters, and DAPs using Mason. This is equivalent to running :TSUpdate and :MasonToolsInstall
Plugins
You can check the plugins that are loaded in your Neovim configuration with :Lazy
ROS Related Configurations
Colcon Commands
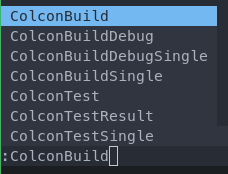
:ColconBuild-> Build ROS packages in current working directory:ColconBuildSingle <ROS_PKG>-> Build the given <ROS_PKG>:ColconBuildDebug-> Build ROS packages with Debug symbols:ColconBuildDebugSingle <ROS_PKG>-> Build the given <ROS_PKG> with Debug symbols:ColconTest-> Runcolcon test:ColconTestSingle <ROS_PKG>-> Runcolcon test --packages-select <ROS_PKG>:ColconTestResult-> Runcolcon test-result --all
C++
LSP
Clang is the LSP here configured. If you use the previously listed commands, this configuration is already taken cared of. Additionally, it generates a compile_commands.json that is needed by clang.
Linters
- clang-tidy: Requires a
.clang-tidyconfig file - cpplint
Formatting
- clang-format: Requires a
.clang-formatconfig file
Python
LSP
Pyright is the LSP here configured
Linters
- ruff: Requires a
pyproject.tomlconfig file
Formatting
- black: Requires a
pyproject.tomlconfig file
Use cases hints
General
-
Open file tree
:NvimTreeToggle -
Open current file in tree
:NvimTreeFindFile -
Open search files
:Telescope find_files -
Grep local files
:Telescope live_grep -
Open keymaps
:Telescope keymaps -
Open old files
:Telescope oldfiles -
Open multi-file search and replace
:Spectre -
Open diagnostics
:TroubleToggle -
Open diagnostics for current file
:TroubleToggle document_diagnostics -
Open diagnostics for whole workspace
:TroubleToggle workspace_diagnostics -
Open Git
:Git -
Compare changes
:DiffviewOpen <BRANCH1>..<BRANCH2>
LSP
NOTE: space is the leader key. You can check the actual commands used by the keybindings in the init.lua
- Expand diagnostics
space + e - Hover Documentation
K - Switch between header and source
Shift + Tab - Type definition
space + D - Type definition
space + D - Go to definition
gd - Go to declaration
gD - Code Action
space + ca - Rename
space + rn
Debugging
For debugging files you can use the following commands
Note: Make sure to compile the C++ files with debug symbols enabled
- Add breakpoint to current line
:DapToggleBreakpoint - Open Debugger UI
F2 - Start debugger
:DapContinue- Select the desirable Configuration (e.g. Launch File)
- You can then use the UI to step over/into or
:DapStepOver
Snippets
A collection of snippets have been configured for C++ and Python. You can find them in the snippets dir
To explore the available snippets do :Telescope luasnip
Comments
This repository is heavily inspired on kickstart, which is a similar Neovim configuration for general purposes.
Please, check out their great explanation on how to configure and extend a Neovim configuration.