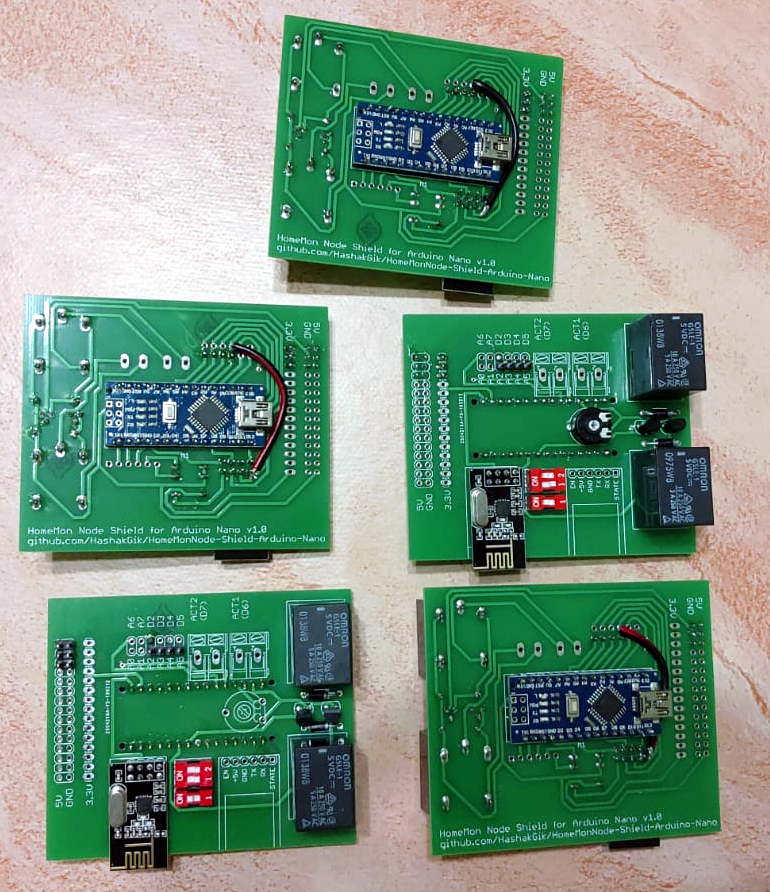
The HomeMon project is a simple wireless sensor network for domotic use. It comprises sensor nodes which broadcast their state over a meshed peer-to-peer network and a viewer application capable of displaying data received from a sink node.
This Arduino nano sketch uses the HomeMon node shield.
Each node can sense up to eleven local and sixteen remote signals, and drive up to two actuators when triggering conditions are met.
For debugging purposes, a node emulator is also available.
- The nodes share the same firmware and each of them can act as a sink, by simply connecting it to a PC (via serial or bluetooth)
- Configuration is done via serial/bluetooth interface (connect at 9600 bauds, 1 stop bit, no parity and 8 data bits, type
helpfor a list of available commands) and stored on the internal EEPROM for persistent storage - New sensors can be attached at runtime to 16-characters signals (e.g. temperature sensor on pin A3 attached to variable bathroom_temp)
- Triggering conditions can be set at runtime between two signals (either local or remote) or a signal and a constant (e.g. "turn on the lamp connected to actuator 1 when people_number > 0" or "turn on the boiler connected to actuator 2 when bathroom_temp < outside_temp")
- The nodes communicate between each other via a radio interface and with the client PC via USB or bluetooth
- If the bluetooth, the radio, or both interfaces are not available, a node will still work correctly.
- The code is composed of mostly C-style functions and global variables, in order to keep the stack as small as possible, but the input signals are modeled by a hierarchy of C++-style classes for easier extendability.