Sign up for IBM Cloud at: https://ibm.biz/HyperProtectHIPAA
- Account setup
- Deploy a Sample App with CareKit
- Deploy a Hyper Protect Virtual Server instance
- Deploy a IBM Hyper Protect DBaaS for MongoDB instance
- Integrate IBM Hyper Protect with the Sample App
- Integrate IBM Hyper Protect SDK for iOS into the Sample App
- Troubleshooting
Goal : At the end of this section, you should have pre-requisite accounts needed to successfully complete this lab
IBM Cloud Account:
An IBM Cloud Account is required for this lab. If you need to create one, please go to: https://ibm.biz/HyperProtectHIPAA
CareKit requires XCode 11.4+
- First
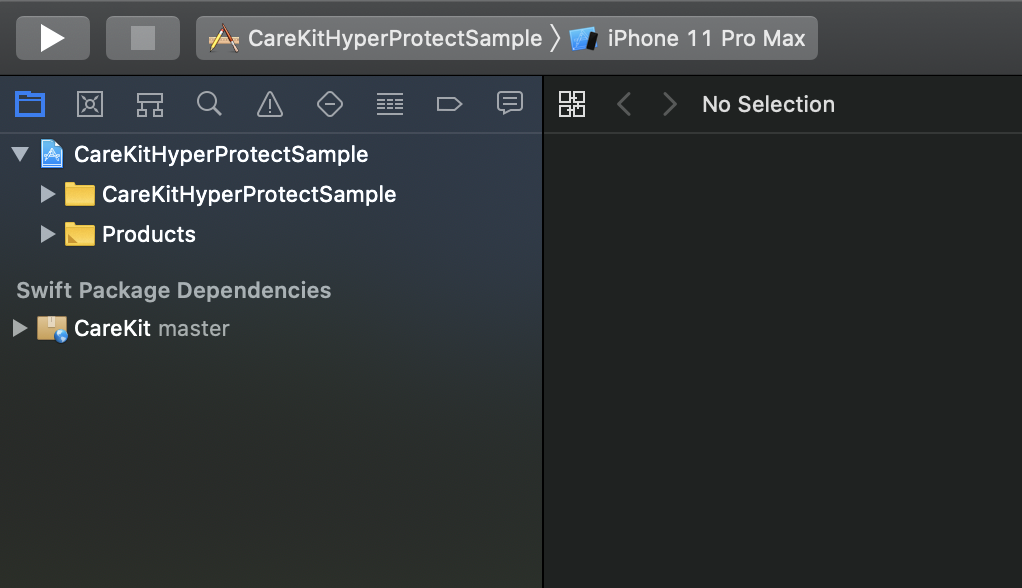
git clone https://github.com/THINKLab2020/CareKitHyperProtectSample.git - Click on 'CareKitHyperProtectSample.xcodeproj' to open up the project in XCode. Once the dependencies are downloaded, you should see this:
- Hit Run to build the sample app. The first run might take a while since it's building everything from source, but subsequent runs will be much quicker.
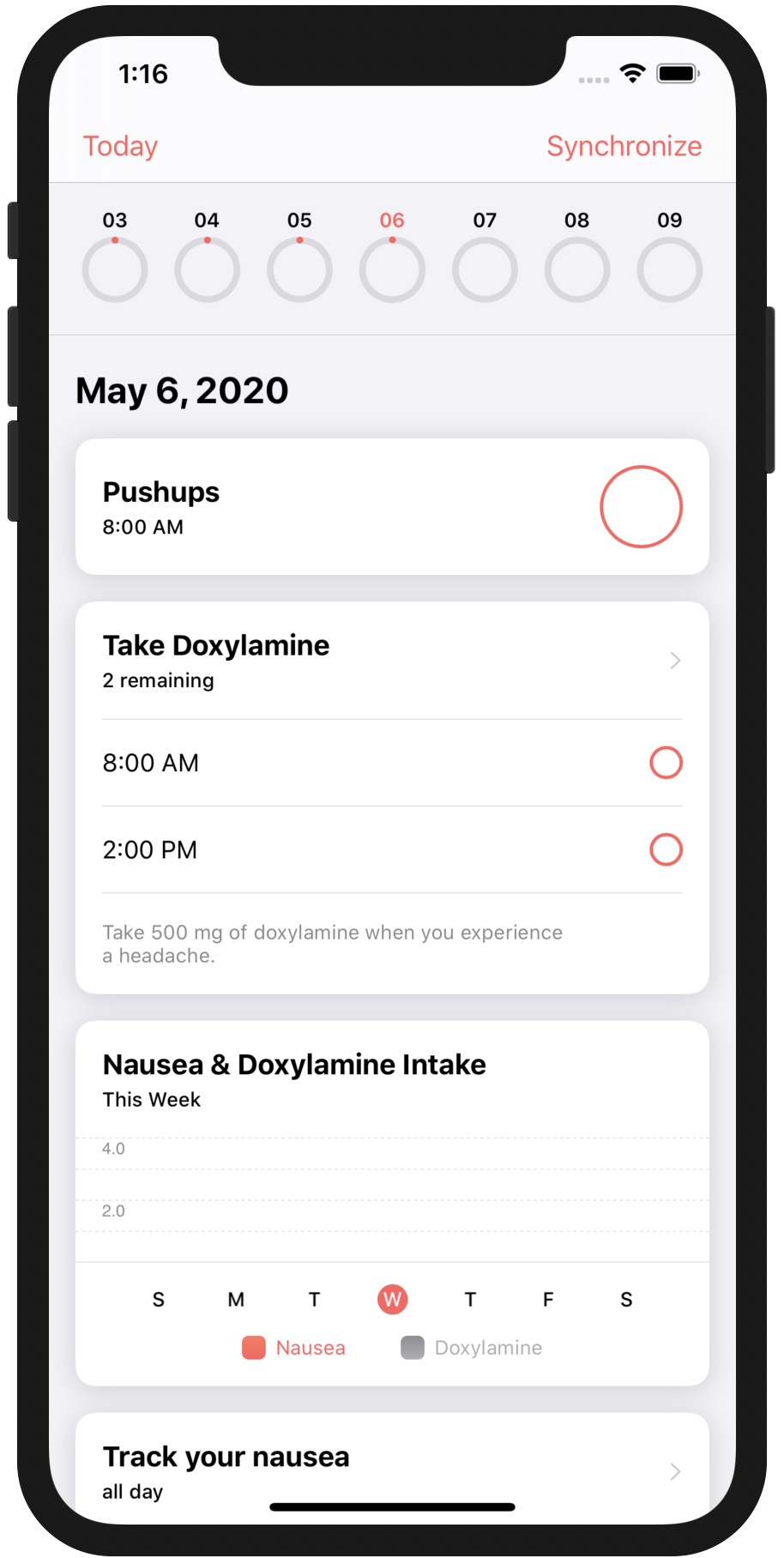
- You should see an app in the simulator:
- The first view you see are tasks that were programmatically set up using
OCKTasks. Tasks look at the populateSampleData() in the AppDelegate.swift file to see how this was done.
let thisMorning = Calendar.current.startOfDay(for: Date())
let aFewDaysAgo = Calendar.current.date(byAdding: .day, value: -4, to: thisMorning)!
let beforeBreakfast = Calendar.current.date(byAdding: .hour, value: 8, to: aFewDaysAgo)!
let afterLunch = Calendar.current.date(byAdding: .hour, value: 14, to: aFewDaysAgo)!
let schedule = OCKSchedule(composing: [
OCKScheduleElement(start: beforeBreakfast, end: nil,
interval: DateComponents(day: 1)),
OCKScheduleElement(start: afterLunch, end: nil,
interval: DateComponents(day: 2))
])
var doxylamine = OCKTask(id: "doxylamine", title: "Take Doxylamine", carePlanUUID: nil, schedule: schedule)-
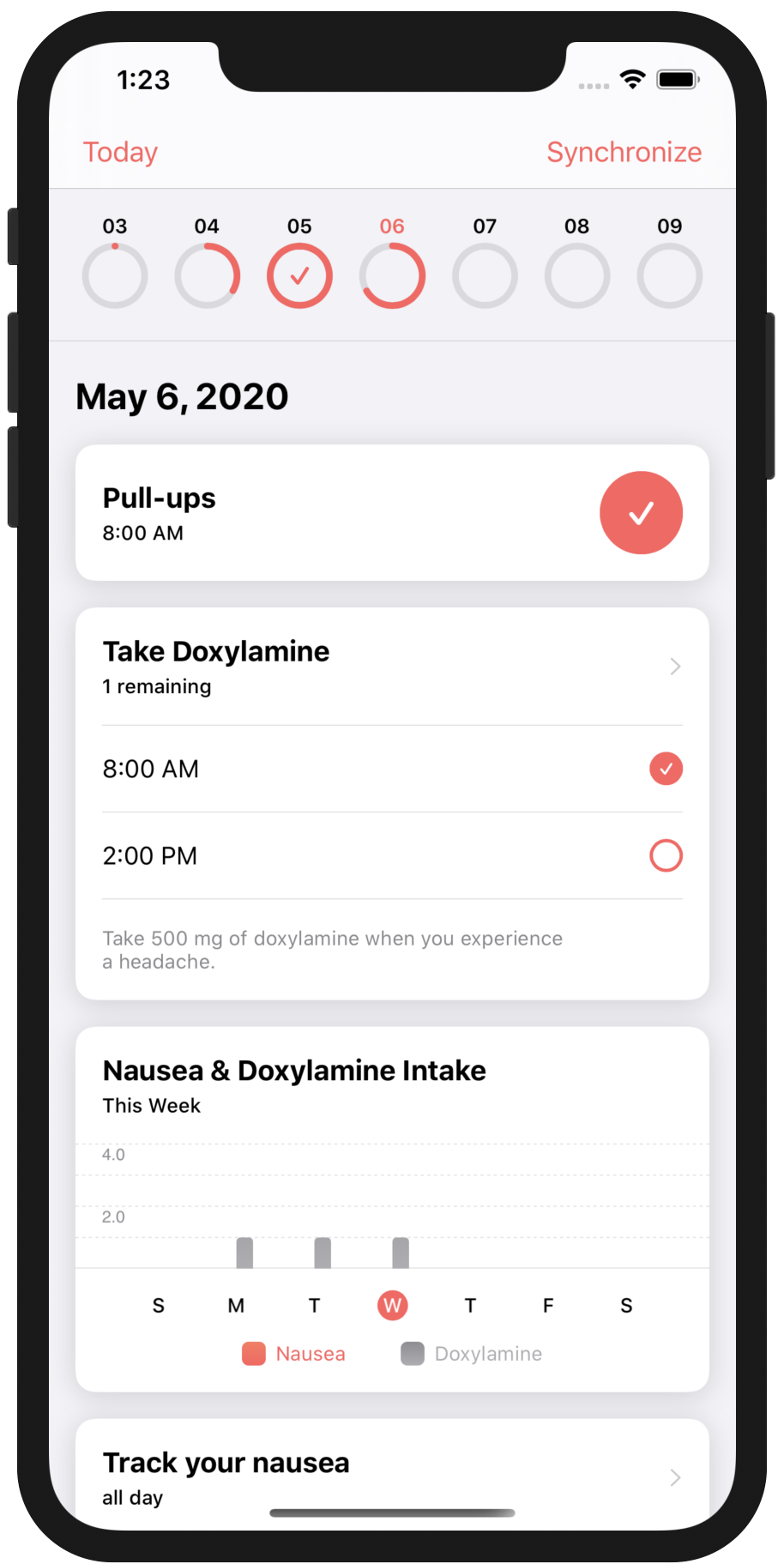
Next, click on some tasks to see the graphs change. These are
outcomesand are programmatically represented byOCKOutcome. Typically you would only explicitly define an outcome programmatically for testing purposes. In regular app operation, outcomes are created as a result of tasks being completed. -
Change or add tasks in the populateSampleData().
- Changing text will be the easiest. You can change the
titleorinstructionof the existingdoxylamineOCKTask. - If you do decide to create a new task, it will need a schedule. You could also re-use the original
doxylaminetasks'schedulefor your new task with some imaginative times. - If you change
id, you'll need to change the arrayidentifiersinCareViewController.swifttoo
- Changing text will be the easiest. You can change the
-
Push build on your new app. In our case, we changed the text from pushups to "pull-ups".
Goal : At the end of this section, you should have a production ready MongoDB instance from IBM Hyper Protect DBaaS and a secure execution environment from IBM Hyper Protect Virtual Servers to deploy the IBM Hyper Protect MBaaS on.
-
Log into the IBM Cloud dashboard (https://cloud.ibm.com). Please refer to the documentation on the README page for further instructions on logging into IBM Cloud, or obtaining an IBM Cloud account
-
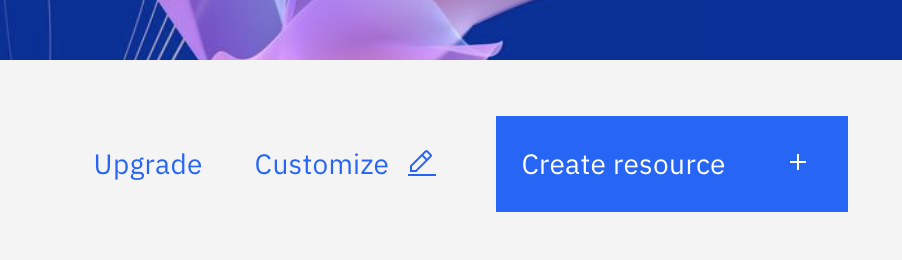
After the IBM Cloud homepage loads, click the blue 'Create Resource' button on the top right of the page, directly underneath the Cloud toolbar. Alternatively, the create resource function is accessible by selecting the 'Add Resource +' option underneath the Resource Summary table.
- The desired destination is the Cloud catalog, where all current available Cloud offerings are listed
- In order to view the full list of Cloud offerings, ensure that the 'Services' tab is selected on the left-hand side of the catalog
-
Within the catalog listings, locate and click on 'Hyper Protect Virtual Servers'.
-
The page defaults to the 'Create' tab, where the various Virtual Server options are able to be selected.
-
Choose the appropriate region to deploy the virtual server in, as well as a suitable pricing plan based on the technical requirements for the Virtual Server. The 'free' payment option will be adequate for this lab
-
Add any necessary tags for labeling the virtual server
- Copy and paste your public ssh key (
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.publocally) into the last field. This is a required step as the Virtual server is only accessible via ssh key. If you do not know how/where to find your ssh key, please follow these instructions. - After all required fields have been properly filled out, click the create button on the bottom right hand side of this page to begin provisioning of the Hyper Protect Virtual Server instance
- Copy and paste your public ssh key (
-
As this will take some time, we will deploy a MongoDB instance in IBM Hyper Protect and then test the connection to this virtual server once that's complete.
Goal : At the end of this section, you should have a production ready MongoDB instance for consumption by the IBM Hyper Protect MBaaS
- Navigate back to the IBM Cloud catalog, and search for the 'Hyper Protect DBaaS for MongoDB' offering
- Choose the appropriate region to deploy the virtual server in, as well as a suitable pricing plan based on the technical requirements needed for the MongoDB service.
- There are several fields listed below the pricing plans, some of which are required, while other fields are optional. Follow the next steps for the required fields.
- The non-essential fields will be left to the default values:
- Create and add a 'Cluster Name' for the database. e.g. My_Mongo_Cluster
- Choose an admin ID name for the MongoDB service, this ID will have full administrative access to the database e.g Example: admin
- Generate a password for the associated database admin user
- PLEASE TAKE NOTE OF USERNAME AND PASSWORD YOU WILL NEEED THEM LATER.
Password requirements: 15 characters minimum, must include 1 capital letter, and 1 number, The use of non-alphanumeric symbols is not required but is recommended
After all required fields have been properly filled out, click the create button on the bottom right hand side of this page to begin provisioning of the Hyper Protect DBaaS for MongoDB
Note: Please allow up to 10 minutes for both services to deploy after the process initiates. There are several security hardening processes and checks happen after you deploy your instances which is why these take longer than regular VM deployments.
Further Documentation:
Connect to your Virtual Server (optional)
Now that both required Cloud services have been deployed, it is time to access the newly provisioned virtual server using ssh protocol
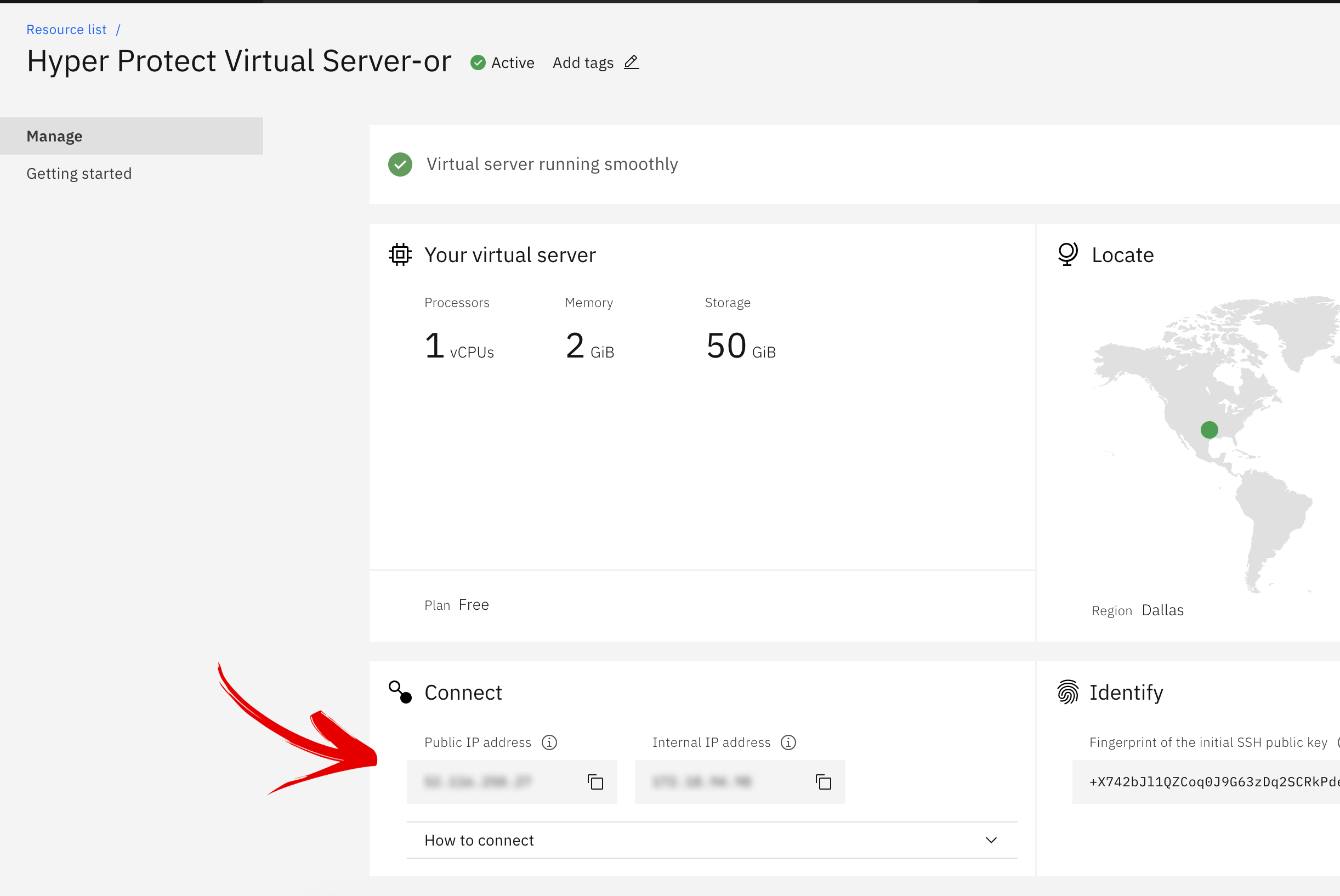
- To obtain the public IP address of the virtual server, navigate to the Cloud dashboard homepage, and click on 'Services' in the Resource Summary box. Once the deployed services are listed, locate the Hyper Protect virtual server instance and click on the name. The public IP address will be displayed on the following screen.
- After finding the public IP address, access a terminal and leverage the ssh protocol to navigate to the virtual server.
Example ssh command:
ssh root@{public_IP}. The ID required for a successful ssh connection must be 'root'
Goal : At the end of this section, you should have a fully running CareKit based app end-to-end that that consumes IBM Hyper Protect Services
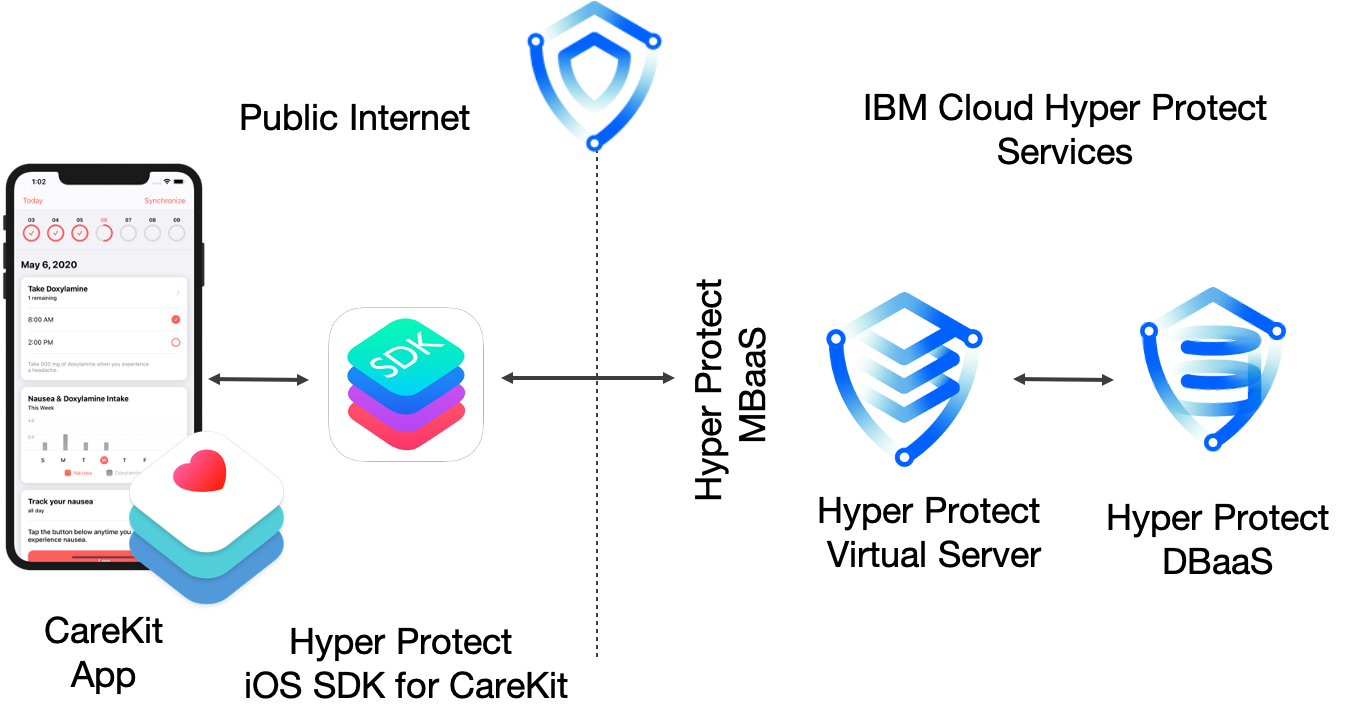
The SDK consists of 2 layers:
- The frontend Swift component that extends CareKit's functionality
- The backend server that acts as a mediator between the frontend and the database
This is what the end to end architecture looks like:
Goal: At the end of this next section, the recently provisioned Hyper Protect Virtual server and Hyper Protect DBaaS Instance should be fully configured with the Backend SDK CareKit application. Follow the illustrated steps below to run the ansible playbook for automated setup.
Prerequisites
Note: if pip3 fails, re-run the commands using just pip
-
Install ansible via pip3 (or pip) with:
sudo pip3 install ansible
-
Install docker-compose via pip3
sudo pip3 install docker-compose
-
Install docker
sudo pip3 install docker
-
Clone the carekit-hyperprotect-lab repository on the local machine using
git clone https://github.com/THINKLab2020/carekit-hyperprotect-lab.gitThis github repository containing the ansible playbooks has been made public for accessibility. -
After the Github repo has been cloned to the local machine, change directories to
carekit-hyperprotect-lab/ansible_setup. -
Use the instructions below to run the Ansible playbook for bringing up the CareKit Backend SDK application. It uses the HPVS and HPDBaaS instances recently provisioned.
-
You will also need a
cert.pemfile from your DBaaS instance. You can download it by clicking on theDownload the CA filelink as shown in this screenshot.
This needs to be placed in the ansible_setup folder from Step 2. In the rare occasion you get a Permission Denied error, run chmod 644 cert.pem to set right permissions.
Pre-requisites : IBM Hyper Protect Virtual Servers and MongoDB in IBM Hyper Protect DBaaS
Three critical modifications need to be made to the playbook files in order to successfully run the hpvs_setup.yml playbook.
The first change is within the ansible.cfg file. Alter the value for environmental variable ansible_ssh_private_key_file with the location and name of your public ssh key. This particular ssh key must be the same key used when deploying the Hyper Protect Virtual Server, as illustrated in a previous section.
With Linux and Mac, the default public ssh key location is:
~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
ansible.cfg:
$ cat ansible.cfg
[defaults]
inventory = inventory.yml
remote_user = root
deprecation_warnings=False
#add public ssh key directory and filename as private_key_file value
ansible_ssh_private_key_file = "{Public_SSH_Key}"The second change occurs within the inventory.yml file. Underneath the commented line, add the public IP address of the Hyper Protect Virtual Server.
inventory.yml:
$ cat inventory.yml
[hosts]
# if running locally local_setup.yml is already pointed towards 'localhost' and no change needs to be made
#add HPVS public IP below this comment
{Public_IP_Address}You can get your public IP by looking at the:
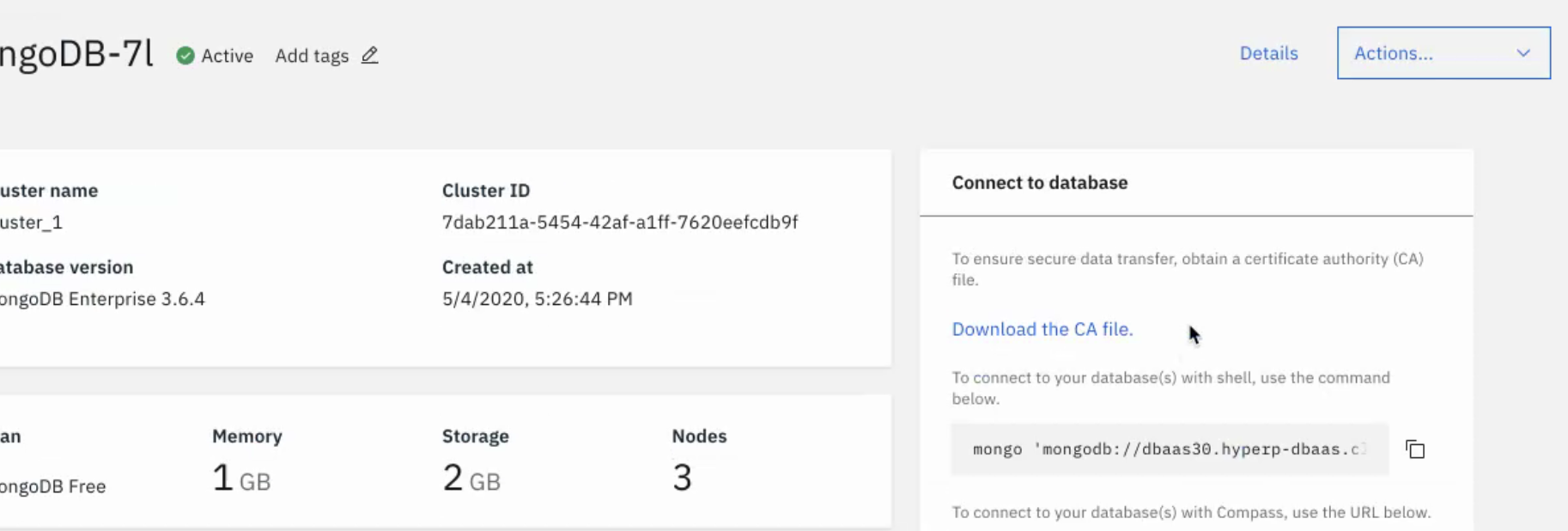
Lastly, the vars.yml file needs to be altered, and the db variable within vars.yml must have it's value set as the HPDBaaS connection string. Prior to modifying the vars.yml file, we must first acquire the MongoDB connection string. See below for further instructions on obtaining the necessary information.
Please goto the MongoDB service you created on the IBM Cloud and then click on the copy icon next to where it says "To connect to your database(s) with Compass, use the URL below."
<>
After the connection string has been obtained, the database admin ID and associated password need to be added to the URI in order to authenticate (you will have noted it down prior - if you haven't - you will need to delete the MongoDB instance and create a new one!).
In the connection string after the mongodb:// portion, please add the userID and password as depicted below. The format must be: {adminID}:{Password}@. Notice that there is a colon separating the admin ID and password, followed by an @ symbol before the start of the first DBaaS replica.
mongodb://{adminID}:{Password}@dbaas31.hyperp-dbaas.cloud.ibm.com:XXXX,dbaas29.hyperp-dbaas.cloud.ibm.com:YYYY,dbaas30.hyperp-dbaas.cloud.ibm.com:ZZZZ/admin?replicaSet=test_cluster
Following the formatting of the connection string, the db variable is ready to be set within the vars.yml file. Edit vars.yml and paste the DBaaS connection string as portrayed below. Make certain that the admin ID and password were formatted into the connection string properly!
$ cat vars.yml
---
# Repo name - change value as needed (MBaaS is default)
repo_name: IBM-HyperProtectMBaaS
db: mongodb://admin:Password123@dbaas30.hyperp-dbaas.cloud.ibm.com:28008,dbaas29.hyperp-dbaas.cloud.ibm.com:28097,dbaas31.hyperp-dbaas.cloud.ibm.com:28191/admin?replicaSet=Cluster_1Now we are ready to run setup playbook! Run the command below to start the setup.
ansible-playbook hpvs_setup.yml
Allow the playbook to run through it's designated tasks and configure the HPVS container.
PLAY [Configure Hyper Protect Virtual Serve*********************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Fact************************************************************\**********************************************************
ok: [169.63.212.6
TASK [Install required system package**************************************************\*\*\*\************************************************
changed: [169.63.212.61] => (item=curl)
changed: [169.63.212.61] => (item=npm)
changed: [169.63.212.61] => (item=docker.io)
changed: [169.63.212.61] => (item=ufw)
changed: [169.63.212.61] => (item=docker-compose)
ok: [169.63.212.61] => (item=gi
TASK [Clone github repo (SDK CareKit****************************************************\**************************************************
changed: [169.63.212.61]
.
PLAY REC******************************************************************\****************************************************************
169.63.212.61 : ok=9 changed=7 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0NOTE 2: If on the TASK [Running setup via docker-compose.yml] there is an error - please re-run the command.
The HPVS configuration should now be complete, follow the validation test section listed below to confirm the setup worked as intended.
Validation Test
To validate that the app is running properly, a simple curl command can be issued to for verification. Please make certain to change the {HPVS_Public_IP} entry to the actual HPVS public address used in the earlier steps.
This curl command should be executed from the local machine, while pointing the cacert argument at the rootCA.crt file, as shown below.
Curl Command
curl --location --request POST 'http://{HPVS_Public_IP}:3000/revisionRecord' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data @verification.jsonAfter the curl command has been issued, if successful you will see a RevisionRecord stored message.
This SDK implements CareKit's Remote Synchronization API and must be coupled with the backend SDK IBM-HyperProtectMBaaS on the server side.
Note, this is a pre-1.0 release and is still in beta
First, we will need to add the carekit-root.der certificate to xcode in order to complete the SSL authentication challenge. The ansible playbook copied the required certificate to the local CareKit lab directory during the bootstrapping Hyper Protect Virtual Server phase. However, we still need to move carekit-root.der to the CareKitHyperProtectSample local directory, specifically within the project folder.
Note: The CareKitHyperProtectSample directory being referenced is the repo that was cloned during the 'Deploy a Sample App with CareKit' portion of the lab.
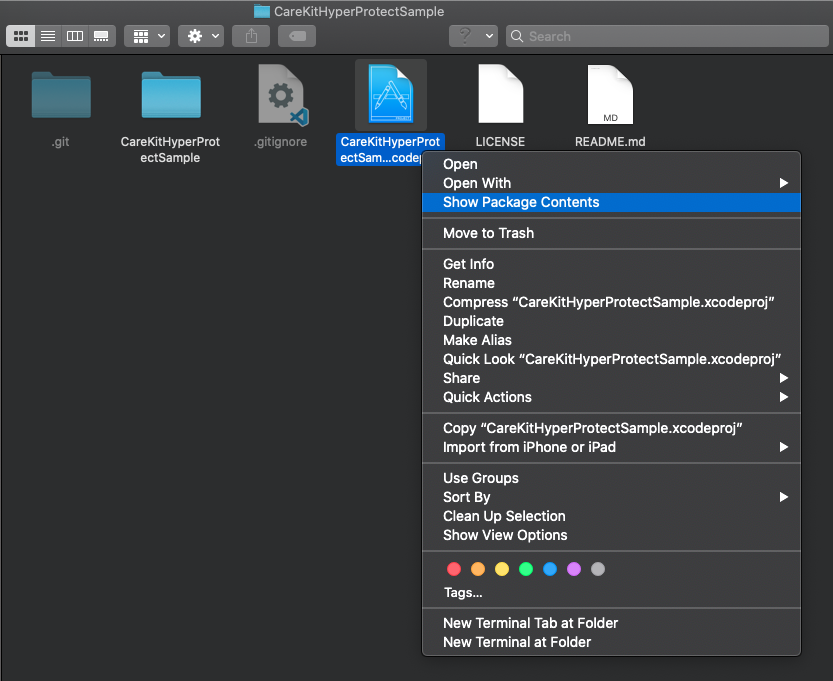
Navigate to the CareKitHyperProtectSample directory, right click on CareKitHyperProtectSample.xcodeproj, and select Show Package Contents.
Once the contents within the project folder are displayed, simply copy over the carekit-root.der certificate.
Now that the carekit-root.der certificate exists within the CareKitHyperProtectSample.xcodeproj folder, we can complete the last step of adding the certificate within the xcode UI.
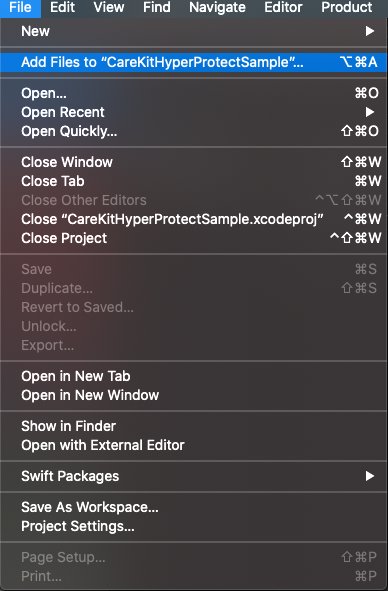
In xcode click on File, and choose the Add Files to "CareKitHyperProtectSample" option.
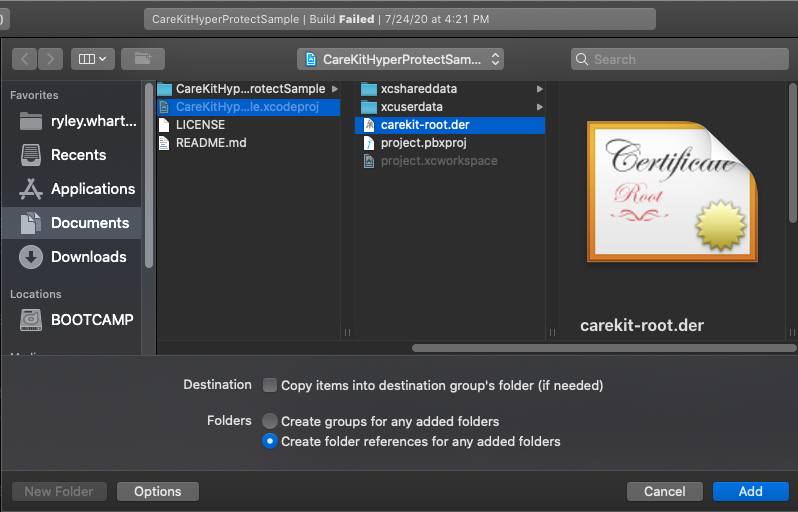
Another screen will appear that should default to the CareKitHyperProtectSample directory, more specifically the project folder mentioned above. The carekit-root.der certificate will be present, as illustrated in the screenshot below. Click on the certificate, and complete the addition by selecting Add on the bottom right of the window.
Now that the root certificate has been added to our sample app, we can proceed with the integration of the Hyper Protect SDK for iOS into the sample app.
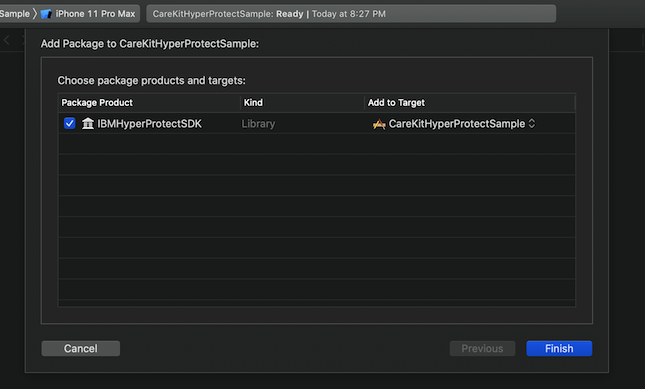
The Hyper Protect SDK package can be imported into XCode using Swift Package Manager:
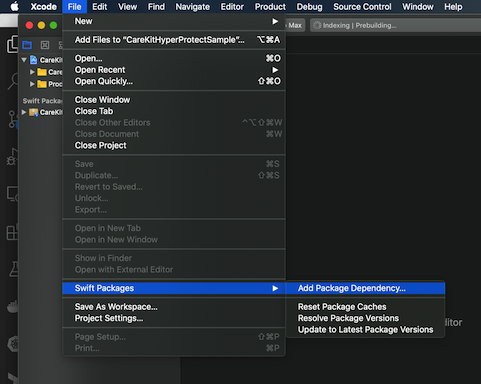
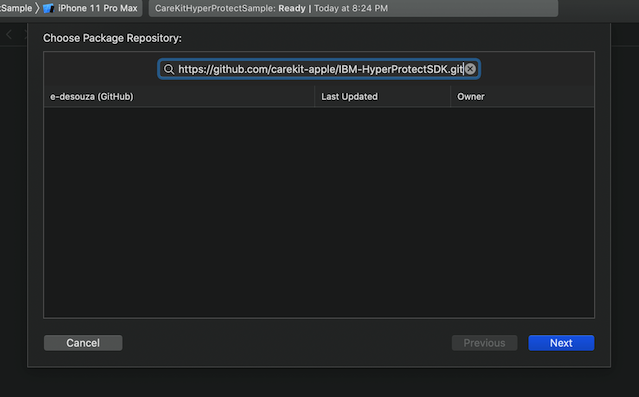
Go to File → Swift Packages → Add Package Dependency
Put in https://github.com/carekit-apple/IBM-HyperProtectSDK.git
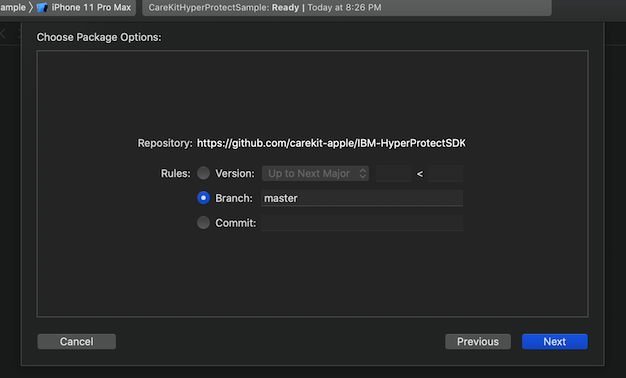
Make sure to change the branch to master
Now import the package in AppDelegate.swift with
import IBMHyperProtectSDKand pass it in to your OCKStore by replacing the below line (still in AppDelegate.swift)
let store = OCKStore(name: "SampleAppStore", type: .inMemory)with this
let remote = IBMMongoRemote(apiLocation: "http://{HPVS_Public_IP}:3000/", apiTimeOut: 2.0)
let store = OCKStore(name: "SampleAppStore", type: .inMemory, remote: remote)and finally make sure to replace {HPVS_Public_IP} with your server IP address e.g.
let remote = IBMMongoRemote(apiLocation: "http://169.63.212.34:3000/", apiTimeOut: 2.0)
let store = OCKStore(name: "SampleAppStore", type: .inMemory, remote: remote)Note: by default if no backend API information is passed in, it will default to http://localhost:3000 .
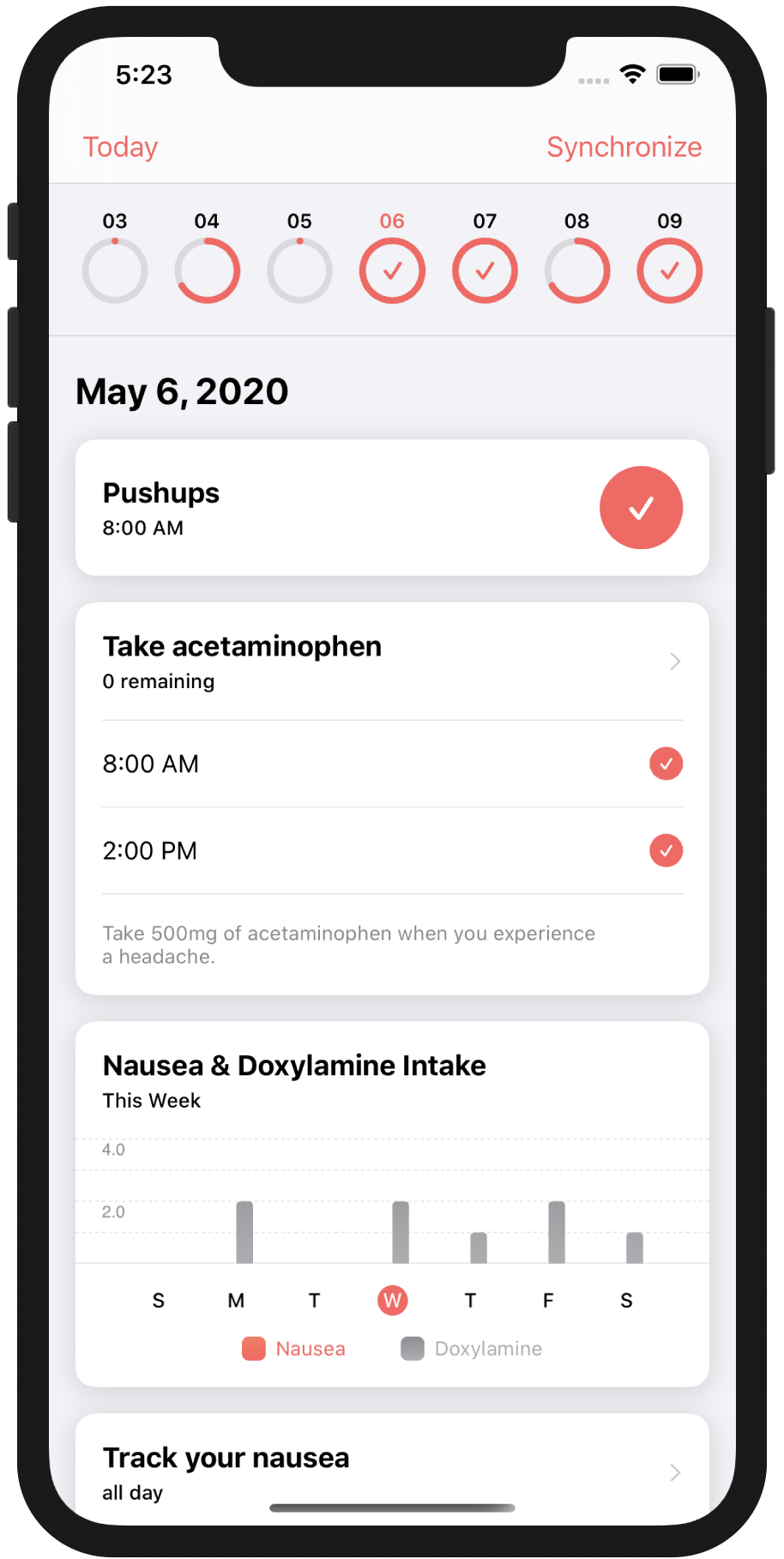
To test synchronization with the MBaaS, run the app and select some outcomes:
Next, stop your app by clicking the square icon at the top left of XCode.
Comment out the programmatic generation of tasks in AppDelegate.swift by commenting store.populateSampleData() like this:
// Manages synchronization of a CoreData store
lazy var synchronizedStoreManager: OCKSynchronizedStoreManager = {
let remote = IBMMongoRemote(apiLocation: [your MBaaS location], apiTimeOut: 2.0)
let store = OCKStore(name: "SampleAppStore", type: .inMemory, remote: remote)
//store.populateSampleData() // COMMENT THIS
let manager = OCKSynchronizedStoreManager(wrapping: store)
return manager
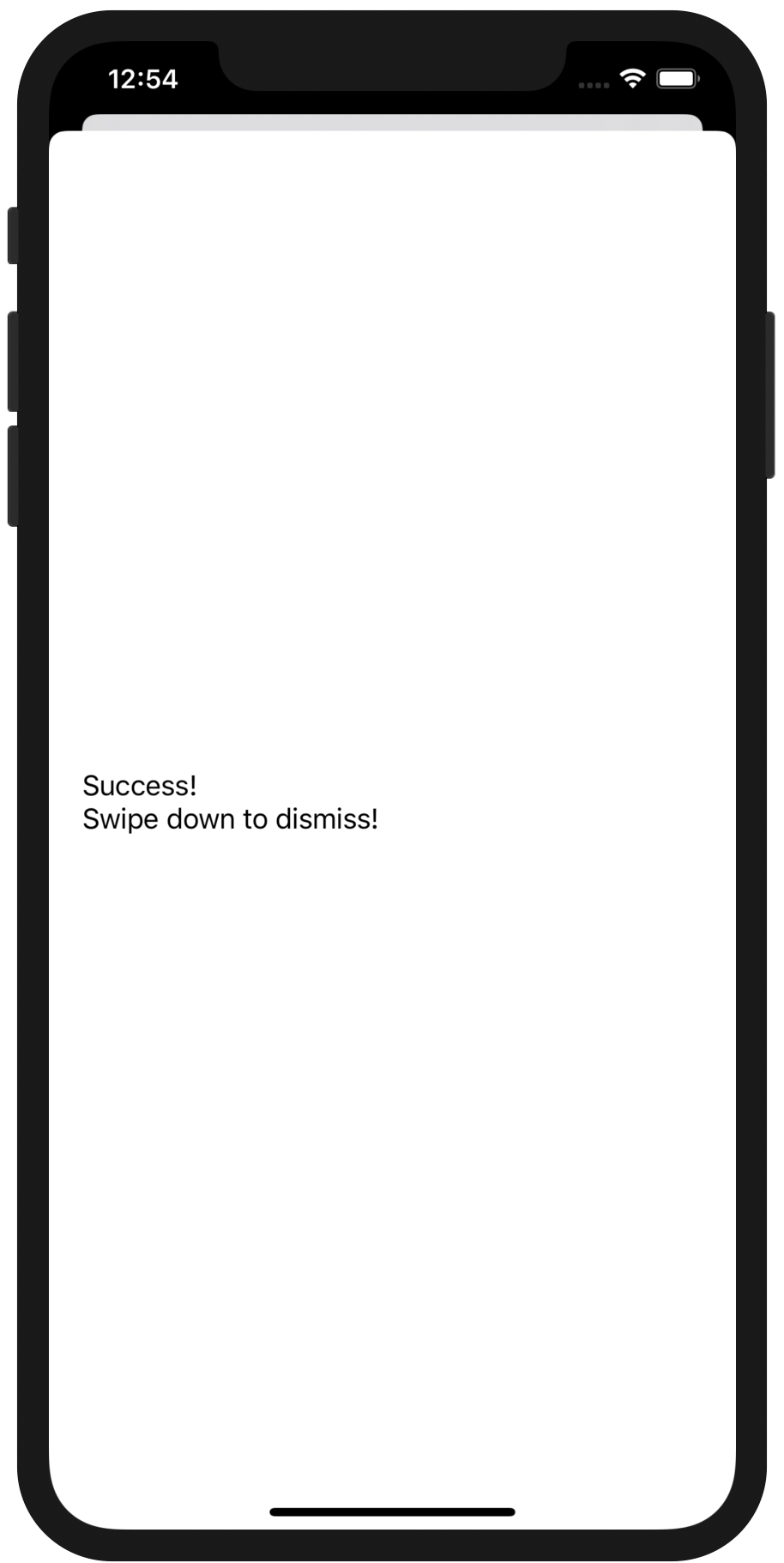
}()Start the app again and notice how it has no Tasks populated. Hit the Synchronize button and if everything worked according to plan, you should see a success message like:
If you swipe down on that message, you should now see the tasks and outcomes you entered during your last run! This can be done across multiple devices and conflicts are automatically resolved!
There are a few potential issues that could arise while running the Ansible automation.
Failure on docker-compose task
Error:
TASK [Running setup via docker-compose.yml] ****************************************************************************************************
fatal: [169.63.212.61]: FAILED! => {"changed": false, "msg": "Failed to import the required Python library (Docker SDK for Python: docker (Python >= 2.7) or docker-py (Python 2.6)) on e7c65ce8b4cd's Python /usr/bin/python3. Please read module documentation and install in the appropriate location. If the required library is installed, but Ansible is using the wrong Python interpreter, please consult the documentation on ansible_python_interpreter, for example via `pip install docker` or `pip install docker-py` (Python 2.6). The error was: No module named 'requests'"Explanation and Resolution:
The Hyper Protect Virtual Server has just installed the docker daemon for the first time. This particular error can be somewhat misleading, as it appears to be missing a pip/python package. However, this error is due to the docker daemon being installed, but not enabling quick enough before docker-compose is called.
- Wait 1-2 minutes and rerun the ansible playbook, no changes are required!
Failure on validation steps using rootCA.crt
Error:
curl: (35) error:04FFF084:rsa routines:CRYPTO_internal:data too large for modulus
Resolution:
The SSL certificates were either created too quickly, causing the signing to fail, or the rootCA.crt file did not copy from the Virtual Server to the local machine properly.
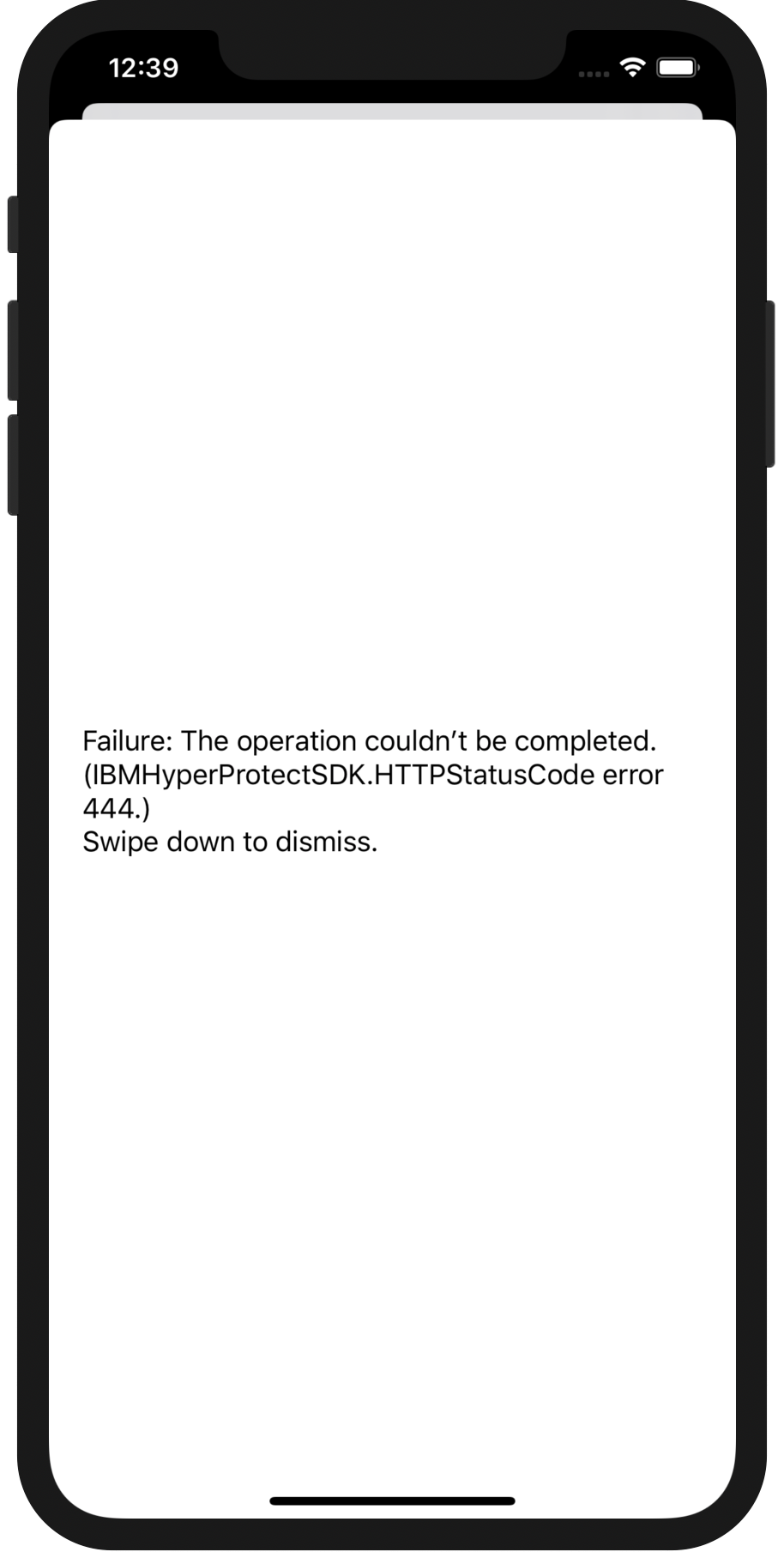
scp root@{Public_IP_Address}:/root/HyperProtectBackendSDK/certs/rootCA.crt {directory_for_ansible}IBMHyperProtectSDK.HTTPStatusCodeError 444
Error:
Resolution:
444 stands for Connection Closed Without Response. This typically means your app couldn't connect to your MBaaS backend so look at the error message in XCode console (it'll have NSURLError...) in it, and ensure the URL is correct.
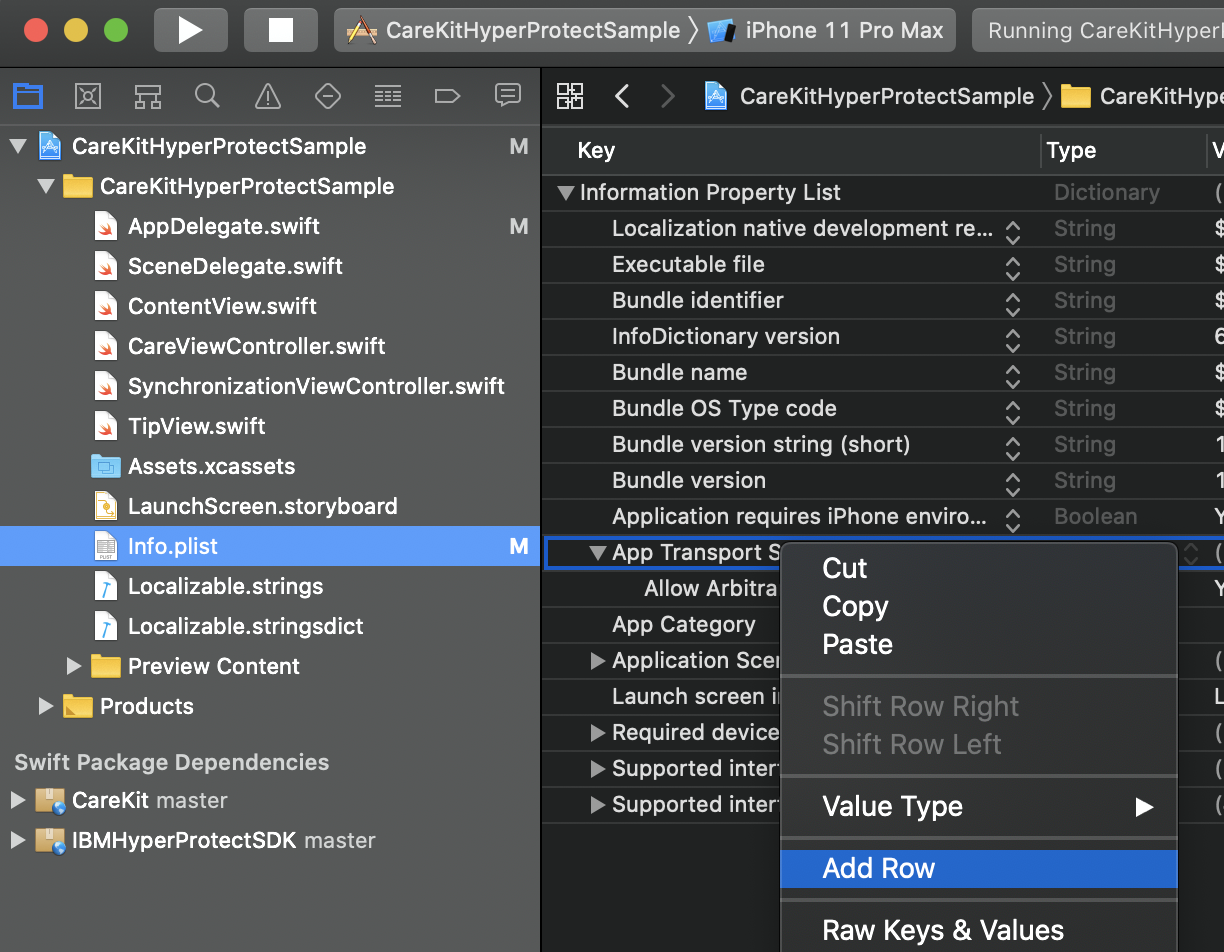
It could also mean you are trying to make a HTTP connection instead of a HTTPS connection and you could add this to Info.plist. Note, you should NEVER do this in production.
<key>NSAppTransportSecurity</key>
<dict>
<key>NSAllowsArbitraryLoads</key>
<true/>
</dict>This can also be done in the GUI, where you add a Row for NSAppTransportSecurity and then add a sub-property NSAllowsArbitraryLoads that you can set to YES.
This code pattern is licensed under the Apache License, Version 2. Separate third-party code objects invoked within this code pattern are licensed by their respective providers pursuant to their own separate licenses. Contributions are subject to the Developer Certificate of Origin, Version 1.1 and the Apache License, Version 2.