This code example demonstrates the implementation of a simple AIROC™ Bluetooth® LE GAP Central - GATT Server with Current Time Service (CTS) using PSoC™ 6 MCU, AIROC™ CYW20829, and ModusToolbox™ software environment.
In this code example, the kit scans for "CTS Client", and after connection with a CTS-based client, sends notifications with Current Time characteristic values derived from the local date and time. The time and date sent as notification are printed on the serial terminal.
This code example along with Bluetooth® LE CTS Client CE Bluetooth® LE CTS Client are low-power-enabled for AIROC™ Bluetooth® LE and can be used to measure the current consumption by PSoC™ 6 (not optimized for power) and CYW43XXX when using the AIROC™ Bluetooth® LE feature. See AN227910: Low-power system design with CYW43012 and PSoC™ 6 MCU to learn about Bluetooth® power optimization techniques and power measurement using this CE.
Provide feedback on this code example.
- ModusToolbox™ v3.2 or later (tested with v3.2)
- Board support package (BSP) minimum required version for:
- PSoC™ 6 MCU: v4.0.0
- CYW920829M2EVK-02: v2.0.0
- CYW989829M2EVB-01: v2.0.0
- CYW989829M2EVB-03: v2.0.0
- Programming language: C
- Associated parts: All PSoC™ 6 MCU with AIROC™ CYW43012 Wi-Fi & Bluetooth® combo chip, AIROC™ CYW4343W Wi-Fi & Bluetooth® combo chip, AIROC™ CYW43438 Wi-Fi & Bluetooth® combo chip, AIROC™ CYW4373 Wi-Fi & Bluetooth® combo chip,AIROC™ CYW43022 Wi-Fi & Bluetooth® combo chip
- GNU Arm® Embedded Compiler v11.3.1 (
GCC_ARM) – Default value ofTOOLCHAIN - Arm® Compiler v6.16 (
ARM) - IAR C/C++ Compiler v9.30.1 (
IAR)
- AIROC™ CYW20829 Bluetooth® LE Evaluation Kit (
CYW920829M2EVK-02) – Default value ofTARGET - AIROC™ CYW89829 Bluetooth® LE Evaluation Kit(
CYW989829M2EVB-01,CYW989829M2EVB-03) - PSoC™ 6 Wi-Fi Bluetooth® Prototyping Kit (
CY8CPROTO-062-4343W) - PSoC™ 6 Wi-Fi Bluetooth® Pioneer Kit (
CY8CKIT-062-WIFI-BT) - PSoC™ 62S2 Wi-Fi Bluetooth® Pioneer Kit (
CY8CKIT-062S2-43012,CY8CEVAL-062S2-CYW955513SDM2WLIPA) - PSoC™ 62S1 Wi-Fi Bluetooth® Pioneer Kit (
CYW9P62S1-43438EVB-01) - PSoC™ 62S1 Wi-Fi Bluetooth® Pioneer Kit (
CYW9P62S1-43012EVB-01) - PSoC™ 62S3 Wi-Fi Bluetooth® Prototyping Kit (
CY8CPROTO-062S3-4343W) - PSoC™ 64 "Secure Boot" Wi-Fi Bluetooth® Pioneer Kit (
CY8CKIT-064B0S2-4343W) - PSoC™ 62S2 Evaluation Kit (
CY8CEVAL-062S2,CY8CEVAL-062S2-LAI-4373M2,CY8CEVAL-062S2-MUR-43439M2,CY8CEVAL-062S2-LAI-43439M2,CY8CEVAL-062S2-MUR-4373EM2,CY8CEVAL-062S2-MUR-4373M2,CY8CEVAL-062S2-CYW43022CUB) - PSoC™ 6 Bluetooth® LE Pioneer Kit (
CY8CKIT-062-BLE) - PSoC™ 6 Bluetooth® LE Prototyping Kit (
CY8CPROTO-063-BLE) - EZ-BLE Arduino Evaluation Board (
CYBLE-416045-EVAL) - PSoC™ 62S2 Wi-Fi Bluetooth® Prototyping Kit (
CY8CPROTO-062S2-43439) - PSoC™ 6 AI Evaluation Kit (
CY8CKIT-062S2-AI)
This example uses the board's default configuration. See the kit user guide to ensure that the board is configured correctly.
Note: The PSoC™ 6 Bluetooth® LE Pioneer Kit (CY8CKIT-062-BLE) and the PSoC™ 6 Wi-Fi Bluetooth® Pioneer Kit (CY8CKIT-062-WIFI-BT) ship with KitProg2 installed. The ModusToolbox™ software requires KitProg3. Before using this code example, make sure that the board is upgraded to KitProg3. The tool and instructions are available in the Firmware Loader GitHub repository. If you do not upgrade, you will see an error like "unable to find CMSIS-DAP device" or "KitProg firmware is out of date".
The AIROC™ CYW20829 Bluetooth® kit (CYW920829M2EVK-02) ships with KitProg3 version 2.21 installed. The ModusToolbox™ software requires KitProg3 with latest version 2.40. Before using this code example, make sure that the board is upgraded to KitProg3. The tool and instructions are available in the Firmware Loader GitHub repository. If you do not upgrade, you will see an error such as "unable to find CMSIS-DAP device" or "KitProg firmware is out of date".
See the ModusToolbox™ tools package installation guide for information about installing and configuring the tools package.
Install a terminal emulator if you don't have one. Instructions in this document use Tera Term.
The ModusToolbox™ tools package provides the Project Creator as both a GUI tool and a command line tool.
Use Project Creator GUI
-
Open the Project Creator GUI tool.
There are several ways to do this, including launching it from the dashboard or from inside the Eclipse IDE. For more details, see the Project Creator user guide (locally available at {ModusToolbox™ install directory}/tools_{version}/project-creator/docs/project-creator.pdf).
-
On the Choose Board Support Package (BSP) page, select a kit supported by this code example. See Supported kits.
Note: To use this code example for a kit not listed here, you may need to update the source files. If the kit does not have the required resources, the application may not work.
-
On the Select Application page:
a. Select the Applications(s) Root Path and the Target IDE.
Note: Depending on how you open the Project Creator tool, these fields may be pre-selected for you.
b. Select this code example from the list by enabling its check box.
Note: You can narrow the list of displayed examples by typing in the filter box.
c. (Optional) Change the suggested New Application Name and New BSP Name.
d. Click Create to complete the application creation process.
Use Project Creator CLI
The 'project-creator-cli' tool can be used to create applications from a CLI terminal or from within batch files or shell scripts. This tool is available in the {ModusToolbox™ install directory}/tools_{version}/project-creator/ directory.
Use a CLI terminal to invoke the 'project-creator-cli' tool. On Windows, use the command-line 'modus-shell' program provided in the ModusToolbox™ installation instead of a standard Windows command-line application. This shell provides access to all ModusToolbox™ tools. You can access it by typing "modus-shell" in the search box in the Windows menu. In Linux and macOS, you can use any terminal application.
The following example clones the "Bluetooth® LE CTS server" application with the desired name "WPSenrollee" configured for the CY8CKIT-062-WIFI-BT BSP into the specified working directory, C:/mtb_projects:
project-creator-cli --board-id CY8CKIT-062-WIFI-BT --app-id mtb-example-btstack-freertos-cts-server --user-app-name CTSserver --target-dir "C:/mtb_projects"
The 'project-creator-cli' tool has the following arguments:
| Argument | Description | Required/optional |
|---|---|---|
--board-id |
Defined in the field of the BSP manifest | Required |
--app-id |
Defined in the field of the CE manifest | Required |
--target-dir |
Specify the directory in which the application is to be created if you prefer not to use the default current working directory | Optional |
--user-app-name |
Specify the name of the application if you prefer to have a name other than the example's default name | Optional |
Note: The project-creator-cli tool uses the
git cloneandmake getlibscommands to fetch the repository and import the required libraries. For details, see the "Project creator tools" section of the ModusToolbox™ tools package user guide (locally available at {ModusToolbox™ install directory}/docs_{version}/mtb_user_guide.pdf).
After the project has been created, you can open it in your preferred development environment.
Eclipse IDE
If you opened the Project Creator tool from the included Eclipse IDE, the project will open in Eclipse automatically.
For more details, see the Eclipse IDE for ModusToolbox™ user guide (locally available at {ModusToolbox™ install directory}/docs_{version}/mt_ide_user_guide.pdf).
Visual Studio (VS) Code
Launch VS Code manually, and then open the generated {project-name}.code-workspace file located in the project directory.
For more details, see the Visual Studio Code for ModusToolbox™ user guide (locally available at {ModusToolbox™ install directory}/docs_{version}/mt_vscode_user_guide.pdf).
Keil µVision
Double-click the generated {project-name}.cprj file to launch the Keil µVision IDE.
For more details, see the Keil µVision for ModusToolbox™ user guide (locally available at {ModusToolbox™ install directory}/docs_{version}/mt_uvision_user_guide.pdf).
IAR Embedded Workbench
Open IAR Embedded Workbench manually, and create a new project. Then select the generated {project-name}.ipcf file located in the project directory.
For more details, see the IAR Embedded Workbench for ModusToolbox™ user guide (locally available at {ModusToolbox™ install directory}/docs_{version}/mt_iar_user_guide.pdf).
Command line
If you prefer to use the CLI, open the appropriate terminal, and navigate to the project directory. On Windows, use the command-line 'modus-shell' program; on Linux and macOS, you can use any terminal application. From there, you can run various make commands.
For more details, see the ModusToolbox™ tools package user guide (locally available at {ModusToolbox™ install directory}/docs_{version}/mtb_user_guide.pdf).
If using a PSoC™ 64 "Secure" MCU kit (like CY8CKIT-064B0S2-4343W), the PSoC™ 64 device must be provisioned with keys and policies before being programmed. Follow the instructions in the "Secure Boot" SDK user guide to provision the device. If the kit is already provisioned, copy-paste the keys and policy folder to the application folder.
-
Connect the board to your PC using the provided USB cable through the KitProg3 USB connector.
-
Open a terminal program and select the KitProg3 COM port. Set the serial port parameters to 8N1 and 115200 baud.
-
Program the board using one of the following:
Using Eclipse IDE
-
Select the application project in the Project Explorer.
-
In the Quick Panel, scroll down, and click <Application Name> Program (KitProg3_MiniProg4).
In other IDEs
Follow the instructions in your preferred IDE.
Using CLI
From the terminal, execute the
make programcommand to build and program the application using the default toolchain to the default target. The default toolchain is specified in the application's Makefile but you can override this value manually:make program TOOLCHAIN=<toolchain>Example:
make program TOOLCHAIN=GCC_ARM -
-
After programming, the application starts automatically. Observe the messages on the UART terminal, and wait for the device to initialize the required components. Use the KitProg3 COM port to view the Bluetooth® stack and application trace messages in the terminal window as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Terminal output when the device is programmed with the CE

-
Use another supported PSoC™ 6 kit and program it with the Bluetooth® LE CTS Client code example.
-
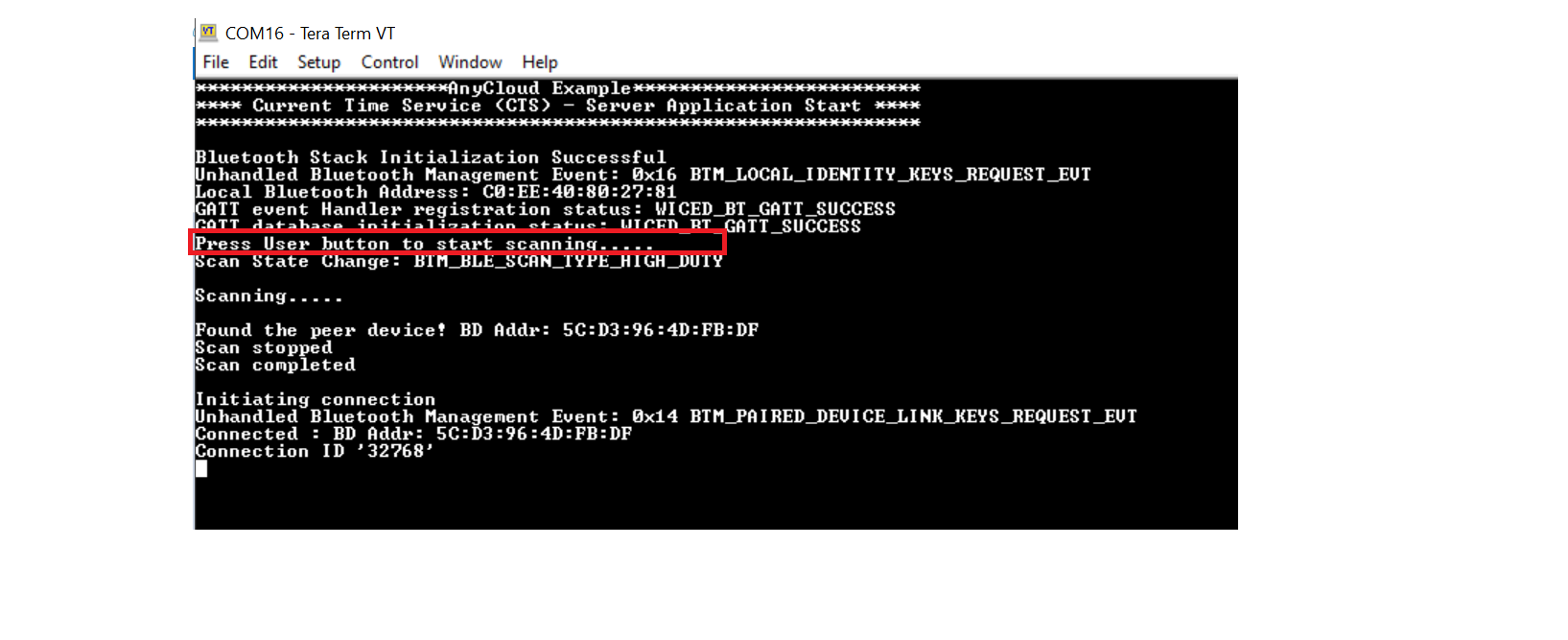
Once both the kits are powered, press the user button (SW2) on the client device to start the advertisement and then press button (SW2) on the server to start the scanning. The application trace messages appear in the terminal window, as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Terminal output - Scanning and connecting
-
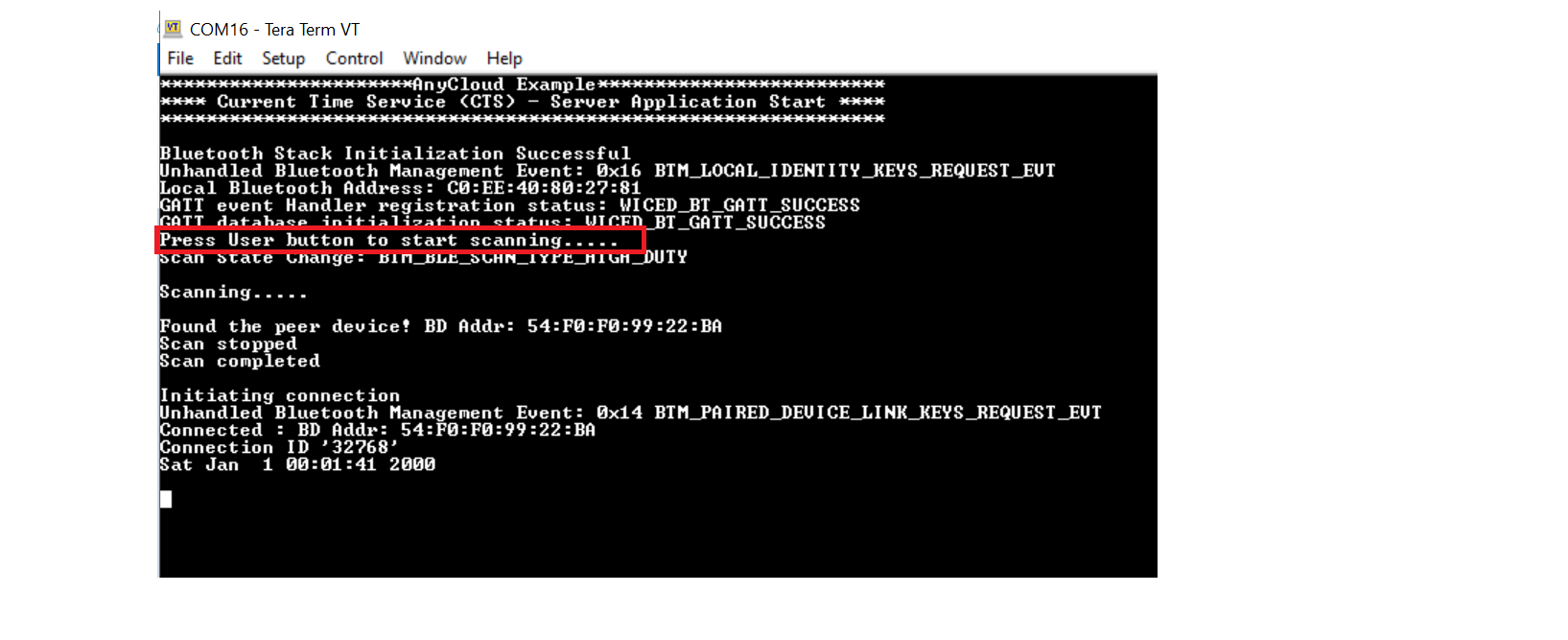
After establishing the connection between the client and server, press the button(SW2) on the client to enable notifications. The server device will start sending notifications with the Current Time characteristic values derived from the device real-time clock. The date and time sent as notification are printed on the serial terminal.
Figure 3. Terminal output - Sending notification
You can debug the example to step through the code.
In Eclipse IDE
Use the <Application Name> Debug (KitProg3_MiniProg4) configuration in the Quick Panel. For details, see the "Program and debug" section in the Eclipse IDE for ModusToolbox™ user guide.
Add the below Note for relevant CEs only, like PSoC 6 MCU based. Remove this note for others.
Note: (Only while debugging) On the CM4 CPU, some code in
main()may execute before the debugger halts at the beginning ofmain(). This means that some code executes twice – once before the debugger stops execution, and again after the debugger resets the program counter to the beginning ofmain(). See KBA231071 to learn about this and for the workaround.
In other IDEs
Follow the instructions in your preferred IDE.
The Bluetooth® LE CTS Server code example configures the device as a Bluetooth® LE GAP Central - GATT Server device. Use this application with the Bluetooth® CTS Client, which is a GAP Peripheral - GATT Client device.
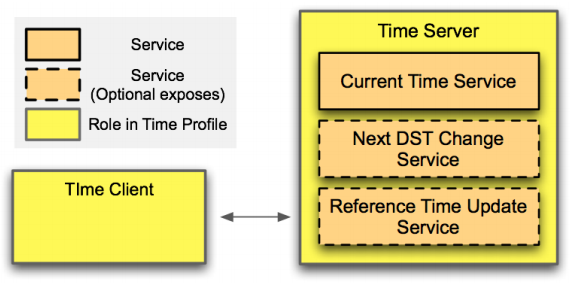
This code example showcases Current Time Service-based time profile. In this CE, the mandatory Current time characteristic with Read and notify properties are implemented. The Time profile defines two roles: Time server (GATT Server) and Time client (GATT Client).
Figure 4. Time profile role and service relationships
The entry point of the application is int main(), which initializes the BSP and Bluetooth® stack. The application-level initializations like RTC and GATT database initialization are handled by the ble_app_init() function. This function starts scanning for the peripheral device by registering a callback using wiced_bt_ble_scan().
This application will specifically scan for advertisement with the Peripheral device name CTS Client and establish a LE GATT connection. All the GATT events are handled in ble_app_gatt_event_handler(). During Read or Notify GATT operations, the fields of the Current Time characteristic are set to values derived from the local date and time and sent as GATT Read response or as notification to the peripheral device. The same data is printed on the serial terminal.
The RTC provides time and date information – second, minute, hour, day of the week, date, month, and year using the RTC driver API. The time and date information are updated every second with automatic leap year compensation performed by the RTC hardware block. The RTC initialization is also done in ble_app_init().
The application uses a UART resource from the Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) to print debug messages on a UART terminal emulator. The UART resource initialization and retargeting of the standard I/O to the UART port is done using the retarget-io library.
This examples enables you to measure power in three different AIROC™ Bluetooth® LE states: Standby, Scanning, and Connected. Do the following to enter each state and measure the power consumption for different kits.
-
Standby state: After programming the device, AIROC™ Bluetooth® LE is initialized and stays in standby state. On the terminal, check for the message 'Bluetooth® stack initialization successful'; you can measure power for standby state.
-
Scanning state: Press the user button (SW2) on your kit to start scanning. Note that the kit with CTS client CE must be advertising when scanning is started. When it discovers the peer device, it sends a connection request. A high duty scan will be performed initially for 30 seconds. Then the device switches to low duty scanning without timeout. High duty scanning of 30 seconds is chosen for faster discovery. If required, this configuration can be changed using the 'bt-configurator' tool that comes with ModusToolbox™ installation.
-
Connected state: Once the scanner finds the advertiser, a connection is established. The terminal displays the message 'Connected : BDA xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx'.
For PSoC™ 6 MCU:
-
Remove J25 to eliminate leakage currents across potentiometer R1.
-
Measure the current at J15 across VTARG and P6_VDD.
For CYW43xxx:
- Measure the current at VBAT across VBAT and VCC_VBAT at J8.
For PSoC™ 6 MCU:
-
Remove J21 to eliminate leakage currents across potentiometer R1.
-
Measure the current at J15 across VTARG and P6_VDD.
For CYW4373E:
- Measure the current at VBAT across VBAT and VCC_VBAT at J11.
For PSoC™ 6 MCU:
-
Remove R65 on the right of the board close to the USB connector of the PSoC™ 6 MCU device.
-
Connect an ammeter between VTARG (J2.32) and P6_VDD (J2.24).
-
Remove R24 at the back of the board, below J1.9, to eliminate the leakage current.
R24 is the pull-up resistor attached to the WL_HOST_WAKE pin P0_4, which leaks approximately 330 µA because P0_4 is driven LOW when there is no network activity. In total, the PSoC™ 6 MCU deep sleep current is approximately 350 µA.
For CYW4343W:
-
Measure the current at VBAT1 and VBAT2 supplies used for powering CYW4343W. VBAT1 and VABT2 are shorted to each other.
-
Remove R87 on the back of the board towards the right and above J2.33.
-
Connect an ammeter between the pads of R87 to measure the current.
For PSoC™ 6 MCU:
- Measure the current by connecting an ammeter to the PWR MON jumper J8.
For CYW4343W:
- Measure the current at WL_VBAT (used for powering CYW4343W) by removing L3 along the right edge of the board close to the CYW4343W module, and connecting an ammeter between the pads of L3.
For PSoC™ 6 MCU:
- Measure the current by removing R59 and connecting an ammeter across VTARG (J2.32) and P6_VDD (J2.31)
For CYW4343W:
- Measure the current by removing R55 and connecting an ammeter between the resistor pads (VCC_3V6 and VBAT_WL).
Table 1 captures the current numbers measured using this CE for two BSPs. The kits have different connectivity devices - CYW43012 and CYW43438. The measurement is not performed in a radio isolated environment. The current consumption by the PSoC™ 6 device is also measured; it was identical across all Bluetooth® states. The following are the average current values:
-
For PSoC™ 6 device in CY8CKIT-062S2-43012: 27 µA
-
For PSoC™ 6 device in CYW9P62S1-43438EVB-01: 620 µA
-
For PSoC™ 6 device in CY8CEVAL-062S2-LAI-4373M2: 23 µA
Table 1. Current consumption
| Bluetooth® state | Setting | CY8CKIT-062S2-43012 | CYW9P62S1-43438EVB-01 | CY8CEVAL-062S2-LAI-4373M2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standby state | Stack initialized | 3.65 mA | 4.21 mA | 10.71 mA |
| High duty scanning | Scan interval: 120 ms | 4.42 mA | 5.67 mA | 7.9 mA |
| Low duty scanning | Scan interval: 2560 ms | 86.23 uA | 111.78 uA | 535.485 uA |
This section explains the ModusToolbox™ resources and their configuration as used in this code example. Note that all the configuration explained in this section has already been done in the code example.
-
Device Configurator: ModusToolbox™ stores the configuration settings of the application in the design.modus file. This file is used by the Device Configurator, which generates the configuration firmware. This firmware is stored in the application’s GeneratedSource folder. By default, all applications in a workspace share the same design.modus file - i.e., they share the same pin configuration. Each BSP has a default design.modus file in the mtb_shared\TARGET_<bsp name>\<version>\COMPONENT_BSP_DESIGN_MODUS directory.
It is not recommended to modify the configuration of a standard BSP directly. To modify the configuration for a single application or to create a custom BSP refer to the ModusToolbox™ user guide. This example uses the default configuration.
For detailed information on how to use the Device Configurator, see the Device Configurator guide.
-
Bluetooth® Configurator: The Bluetooth® peripheral has an additional configurator called the “Bluetooth® Configurator” that is used to generate the AIROC™ Bluetooth® LE GATT database and various Bluetooth® settings for the application. These settings are stored in the file named design.cybt.
Note that unlike the Device Configurator, the Bluetooth® Configurator settings and files are local to each respective application.
For detailed information on how to use the Bluetooth® Configurator, see the Bluetooth® Configurator guide.
Note: For PSoC™ 6 Bluetooth® LE-based BSPs(CY8CKIT-062-BLE, CY8CPROTO-063-BLE, CYBLE-416045-EVAL) with support for AIROC™ BTSTACK, if you want to use the bt-configurator tool, select the AIROC™ BTSTACK with Bluetooth® LE only (CYW20829, PSoC™ 6 with CYW43xxx Connectivity device) option from the dropdown to select the device. Do not use the PSoC™ Bluetooth® LE Legacy Stack (PSoC™ 6-BLE) option because it is not compatible with AIROC™ BTSTACK.
Table 2. Application resources
| Resource | Alias/object | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| UART (HAL) | cy_retarget_io_uart_obj | UART HAL object used by Retarget-IO for Debug UART port |
| GPIO (HAL) | CYBSP_USER_BTN | Start advertisement or enable/disable notification |
| Resources | Links |
|---|---|
| Application notes | AN228571 – Getting started with PSoC™ 6 MCU on ModusToolbox™ software AN215656 – PSoC™ 6 MCU: Dual-CPU system design |
| Code examples | Using ModusToolbox™ on GitHub |
| Device documentation | PSoC™ 6 MCU datasheets PSoC™ 6 technical reference manuals AIROC™ CYW20829 Bluetooth® LE SoC |
| Development kits | Select your kits from the Evaluation board finder. |
| Libraries on GitHub | mtb-pdl-cat1 – PSoC™ 6 Peripheral Driver Library (PDL) mtb-hal-cat1 – Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL) library retarget-io – Utility library to retarget STDIO messages to a UART port |
| Middleware on GitHub | capsense – CAPSENSE™ library and documents psoc6-middleware – Links to all PSoC™ 6 MCU middleware |
| Tools | ModusToolbox™ – ModusToolbox™ software is a collection of easy-to-use libraries and tools enabling rapid development with Infineon MCUs for applications ranging from wireless and cloud-connected systems, edge AI/ML, embedded sense and control, to wired USB connectivity using PSoC™ Industrial/IoT MCUs, AIROC™ Wi-Fi and Bluetooth® connectivity devices, XMC™ Industrial MCUs, and EZ-USB™/EZ-PD™ wired connectivity controllers. ModusToolbox™ incorporates a comprehensive set of BSPs, HAL, libraries, configuration tools, and provides support for industry-standard IDEs to fast-track your embedded application development. |
Infineon provides a wealth of data at www.infineon.com to help you select the right device, and quickly and effectively integrate it into your design.
For PSoC™ 6 MCU devices, see How to design with PSoC™ 6 MCU – KBA223067 in the Infineon Developer Community.
Document title: CE230302 – Bluetooth® LE CTS Server
| Version | Description of change |
|---|---|
| 1.0.0 | New code example |
| 2.0.0 | Major update to support ModusToolbox™ software v2.3.1, This version is not backward compatible with ModusToolbox™ software v2.2 or older versions, Added support for new kits Enabled for CYW43xxx Low power and addition of current numbers |
| 3.0.0 | Added support for 43439 kit Updated BSP to 3.0.0 |
| 4.0.0 | Updated to support ModusToolbox™ software v3.0 and BSPs v4.x |
| 4.1.0 | Added support for CYW920829M2EVB-01, CY8CKIT-062-BLE, CY8CPROTO-063-BLE, and CYBLE-416045-EVAL |
| 4.2.0 | Added support for CY8CEVAL-062S2-LAI-43439M2 and CY8CPROTO-062S2-43439 |
| 4.3.0 | Removed CYW920829M2EVB-01 from supported kits Added support for CYW920829M2EVK-02 |
| 4.4.0 | Added support for CY8CEVAL-062S2-MUR-4373EM2 and CY8CEVAL-062S2-MUR-4373M2 |
| 4.5.0 | Updated error handling and gatt_status |
| 4.6.0 | Update the README with new template and added support for CYW989829M2EVB-01 and CY8CEVAL-062S2-CYW43022CUB |
| 4.7.0 | Added support for BSP CY8CKIT-062S2-AI |
| 5.0.0 | BSP and BTStack-integration major update for BT Firmware as a separate asset and removal of combo devices as doesn't support fw as separate asset |
| 5.1.0 | Added support for CY8CEVAL-062S2-CYW955513SDM2WLIPA |
All referenced product or service names and trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
The Bluetooth® word mark and logos are registered trademarks owned by Bluetooth SIG, Inc., and any use of such marks by Infineon is under license.
© Cypress Semiconductor Corporation, 2020-2024. This document is the property of Cypress Semiconductor Corporation, an Infineon Technologies company, and its affiliates ("Cypress"). This document, including any software or firmware included or referenced in this document ("Software"), is owned by Cypress under the intellectual property laws and treaties of the United States and other countries worldwide. Cypress reserves all rights under such laws and treaties and does not, except as specifically stated in this paragraph, grant any license under its patents, copyrights, trademarks, or other intellectual property rights. If the Software is not accompanied by a license agreement and you do not otherwise have a written agreement with Cypress governing the use of the Software, then Cypress hereby grants you a personal, non-exclusive, nontransferable license (without the right to sublicense) (1) under its copyright rights in the Software (a) for Software provided in source code form, to modify and reproduce the Software solely for use with Cypress hardware products, only internally within your organization, and (b) to distribute the Software in binary code form externally to end users (either directly or indirectly through resellers and distributors), solely for use on Cypress hardware product units, and (2) under those claims of Cypress's patents that are infringed by the Software (as provided by Cypress, unmodified) to make, use, distribute, and import the Software solely for use with Cypress hardware products. Any other use, reproduction, modification, translation, or compilation of the Software is prohibited.
TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW, CYPRESS MAKES NO WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WITH REGARD TO THIS DOCUMENT OR ANY SOFTWARE OR ACCOMPANYING HARDWARE, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. No computing device can be absolutely secure. Therefore, despite security measures implemented in Cypress hardware or software products, Cypress shall have no liability arising out of any security breach, such as unauthorized access to or use of a Cypress product. CYPRESS DOES NOT REPRESENT, WARRANT, OR GUARANTEE THAT CYPRESS PRODUCTS, OR SYSTEMS CREATED USING CYPRESS PRODUCTS, WILL BE FREE FROM CORRUPTION, ATTACK, VIRUSES, INTERFERENCE, HACKING, DATA LOSS OR THEFT, OR OTHER SECURITY INTRUSION (collectively, "Security Breach"). Cypress disclaims any liability relating to any Security Breach, and you shall and hereby do release Cypress from any claim, damage, or other liability arising from any Security Breach. In addition, the products described in these materials may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to deviate from published specifications. To the extent permitted by applicable law, Cypress reserves the right to make changes to this document without further notice. Cypress does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit described in this document. Any information provided in this document, including any sample design information or programming code, is provided only for reference purposes. It is the responsibility of the user of this document to properly design, program, and test the functionality and safety of any application made of this information and any resulting product. "High-Risk Device" means any device or system whose failure could cause personal injury, death, or property damage. Examples of High-Risk Devices are weapons, nuclear installations, surgical implants, and other medical devices. "Critical Component" means any component of a High-Risk Device whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to cause, directly or indirectly, the failure of the High-Risk Device, or to affect its safety or effectiveness. Cypress is not liable, in whole or in part, and you shall and hereby do release Cypress from any claim, damage, or other liability arising from any use of a Cypress product as a Critical Component in a High-Risk Device. You shall indemnify and hold Cypress, including its affiliates, and its directors, officers, employees, agents, distributors, and assigns harmless from and against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses, arising out of any claim, including claims for product liability, personal injury or death, or property damage arising from any use of a Cypress product as a Critical Component in a High-Risk Device. Cypress products are not intended or authorized for use as a Critical Component in any High-Risk Device except to the limited extent that (i) Cypress's published data sheet for the product explicitly states Cypress has qualified the product for use in a specific High-Risk Device, or (ii) Cypress has given you advance written authorization to use the product as a Critical Component in the specific High-Risk Device and you have signed a separate indemnification agreement.
Cypress, the Cypress logo, and combinations thereof, ModusToolbox, PSoC, CAPSENSE, EZ-USB, F-RAM, and TRAVEO are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cypress or a subsidiary of Cypress in the United States or in other countries. For a more complete list of Cypress trademarks, visit www.infineon.com. Other names and brands may be claimed as property of their respective owners.