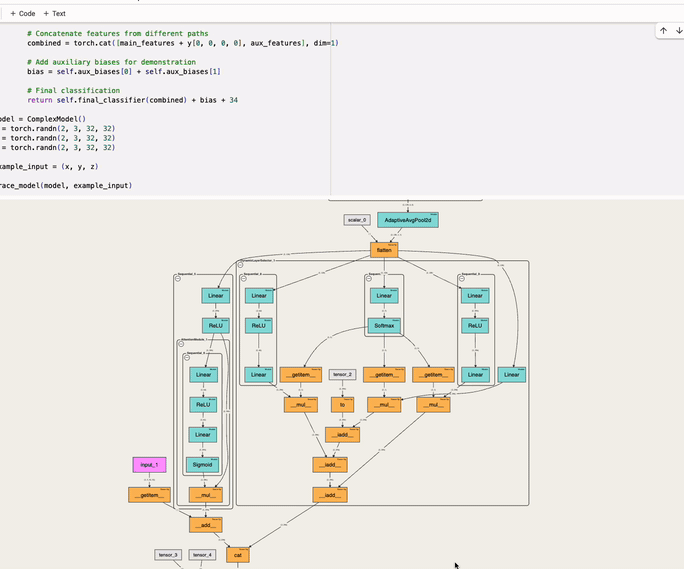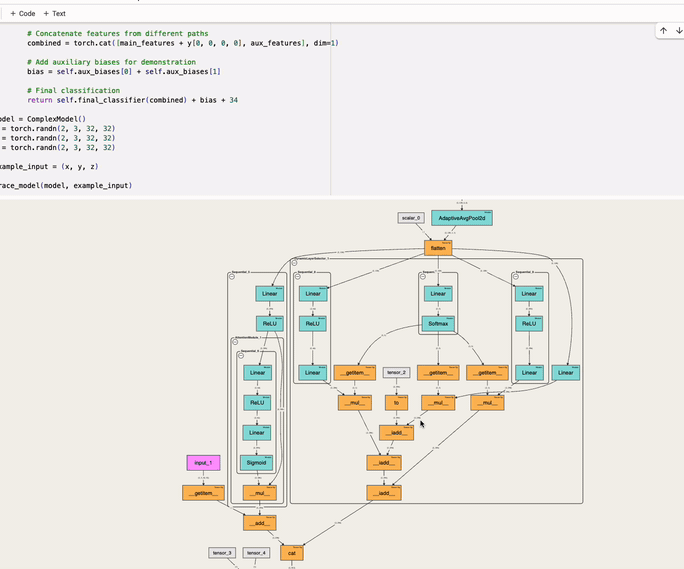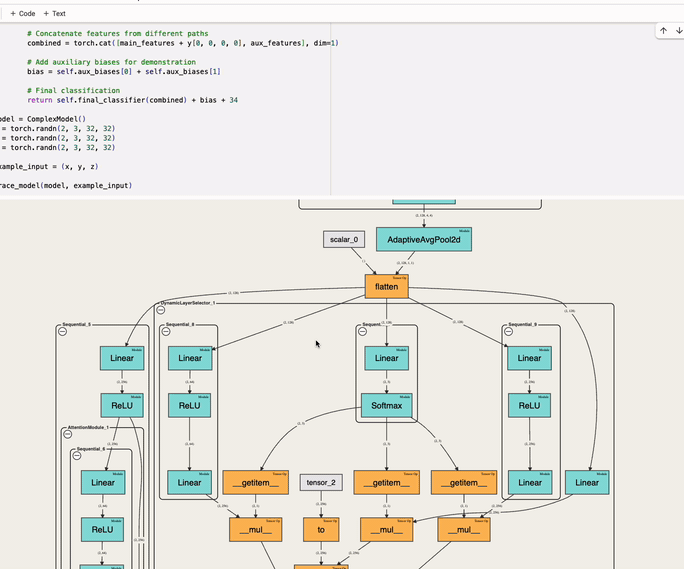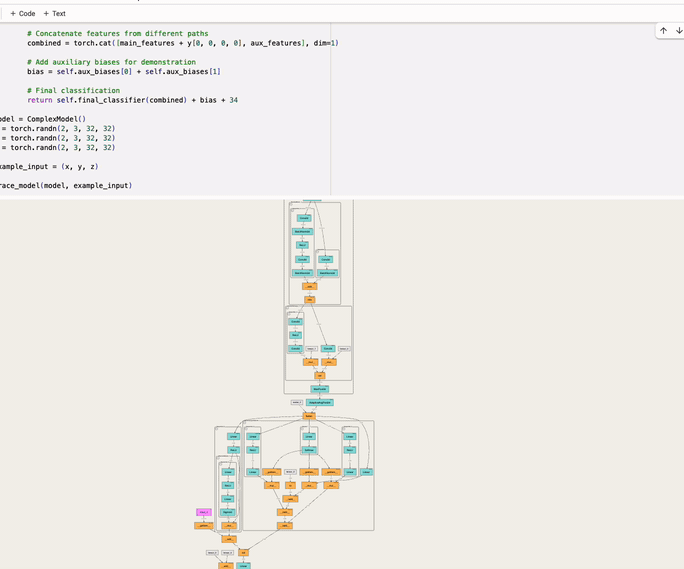
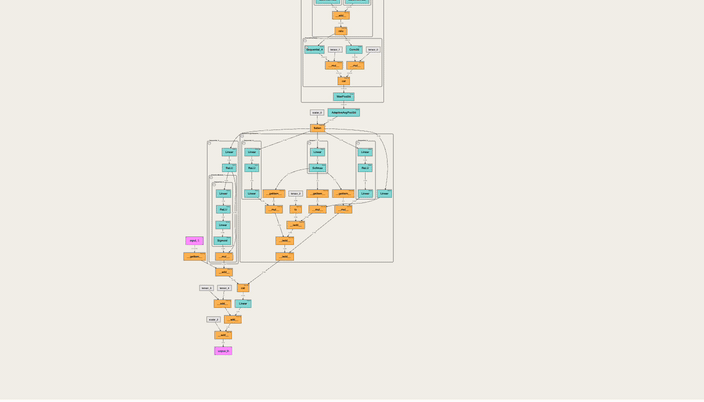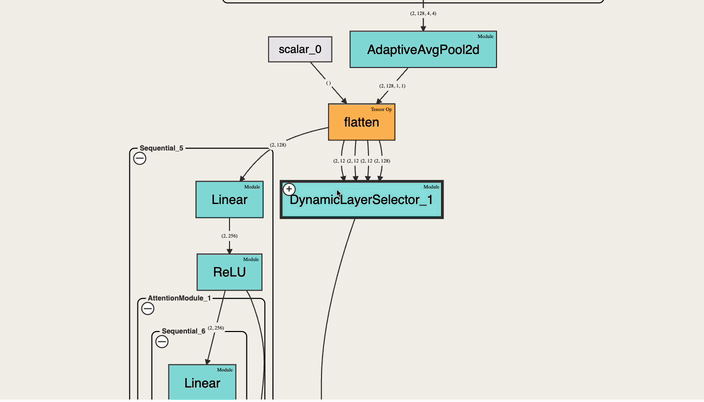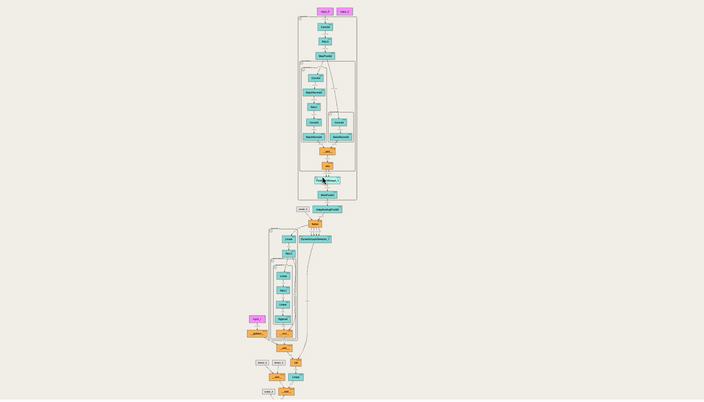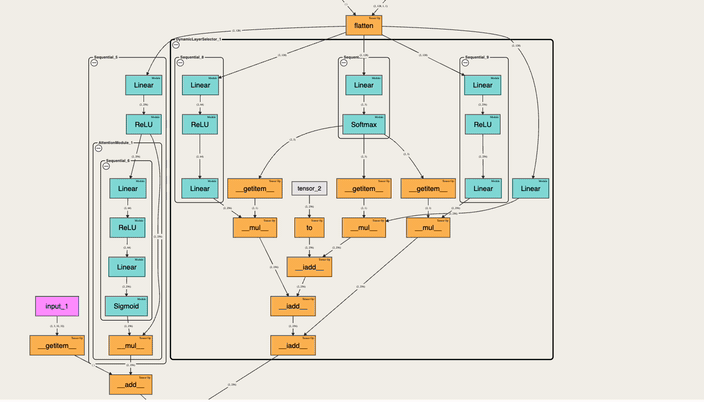
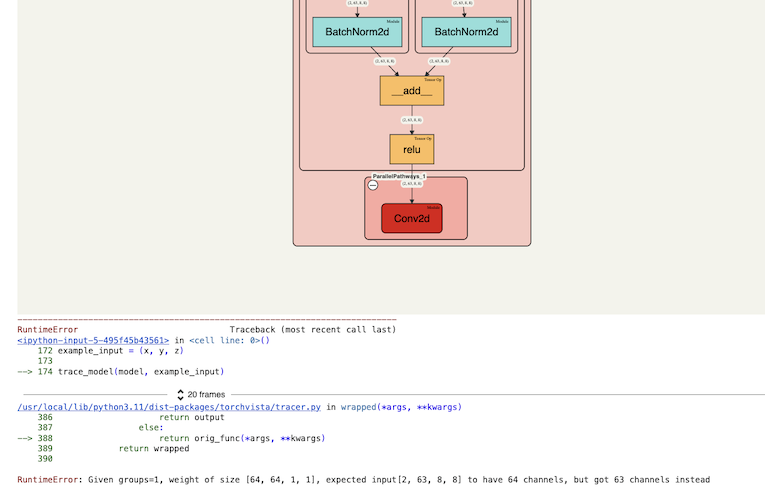
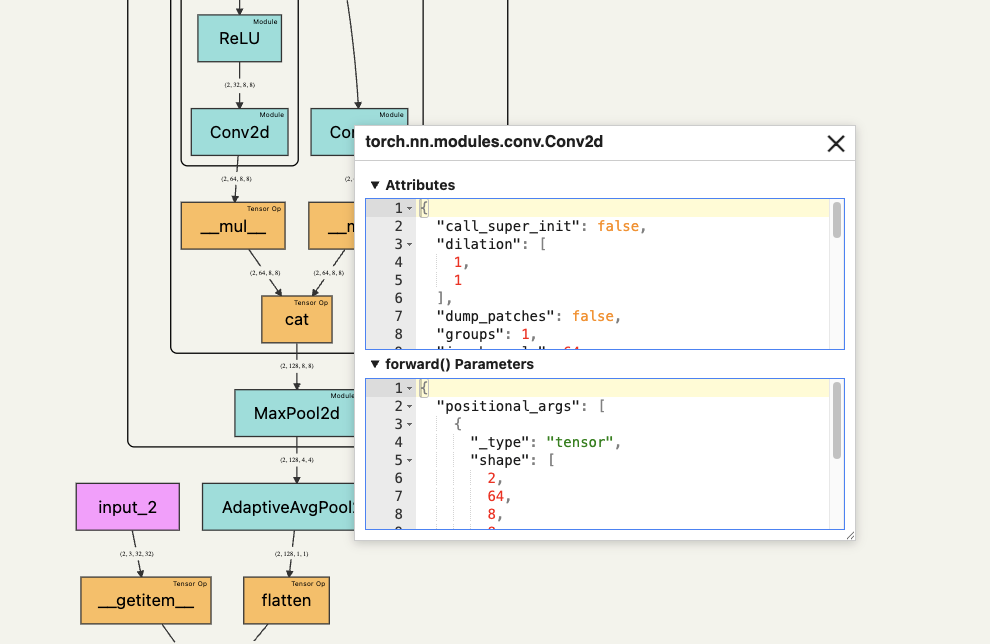
An interactive tool to visualize the forward pass of a PyTorch model directly in the notebook—with a single line of code. Works with web-based notebooks like Jupyter, Google Colab and Kaggle.
(e.g., shape mismatches) for ease of debugging
Install via pip
pip install torchvista
Run from your web-based notebook (Jupyter, Colab, etc)
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# Import torchvista
from torchvista import trace_model
# Define your module
class LinearModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(10, 5)
def forward(self, x):
return self.linear(x)
# Instantiate the module and tensor input
model = LinearModel()
example_input = torch.randn(2, 10)
# Trace!
trace_model(model, example_input)
trace_model(model, inputs, max_module_expansion_depth=3, show_non_gradient_nodes=False)
-
model (torch.nn.Module): The model instance to trace.
-
inputs (Any): Input(s) to be passed to the model. Can be a single input or a tuple of inputs.
-
max_module_expansion_depth (int, optional): Maximum depth for expanding nested modules in the initial view. 0 means everything is collapsed. Default is
3. -
show_non_gradient_nodes (bool, optional): Whether to show nodes for scalars, tensors, and NumPy arrays that are not part of the gradient graph (typically constants passed into operations or modules). Default is
True.