Video semantic segmentation has a high computational cost and slow speed. It is a feasible way to introduce optical flow to accelerate by utilizing the relationship of video sequence. This repository takes SwiftNet as an example to realize this framework.
Cityscapes leftImg8bit_sequence dataset: log in the official website to view and download If necessary.
Train on training set, and evaluate model on validation set.
- python=3.7
- torch=1.3.0
- training with APEX is optional.
- Configuration of dataset and corresponding model:
./config/cityscapes.py - Configuration of training or evaluating parameters:
./main.py - The format of the input data path refers to the corresponding dataset folder in
./dataset.
python main.py --evaluate 0 --resume 0 --checkname <LOG_SAVE_DIR> --batch-size <BATCH_SIZE> --epoch <EPOCH>
torch.distributed.launchis also available.
python main.py --evaluate 1 --eval-scale 0.75 --ResFolderName <RESULT_SAVE_DIR> --checkname <LOG_SAVE_DIR> --save-res <0 OR 1> --save-seq-res <0 OR 1> --batch-size <BATCH_SIZE>
python main.py --inference 1 --eval-scale 0.75 --ResFolderName <RESULT_SAVE_DIR> --checkname <LOG_SAVE_DIR> --save-seq-res <0 OR 1> --batch-size <BATCH_SIZE>
- The run log and tensorboard log are saved in
f"./logs/run/{args.dataset}/{args.checkname}/ - The network prediction results are saved in
f"./logs/pred_img_res/{args.dataset}/{args.checkname}/{args.ResFolderName}
The evaluation results were calculated on Nvidia Tesla v100 or GTX 1060:
-
frame interval: the number of non-key frames between key frames.
-
input scale: the scale of the network input image relative to the original image resolution.
-
avg. mIoU: the average mIoU of whole video sequence.
-
min.mIoU: the minimum mIoU of whole video sequence, refers to the previous frame of the keyframe, i.e. the last non-keyframe.
-
FPS-T: GPU Tesla v100
-
FPS-G: GPU GTX1060
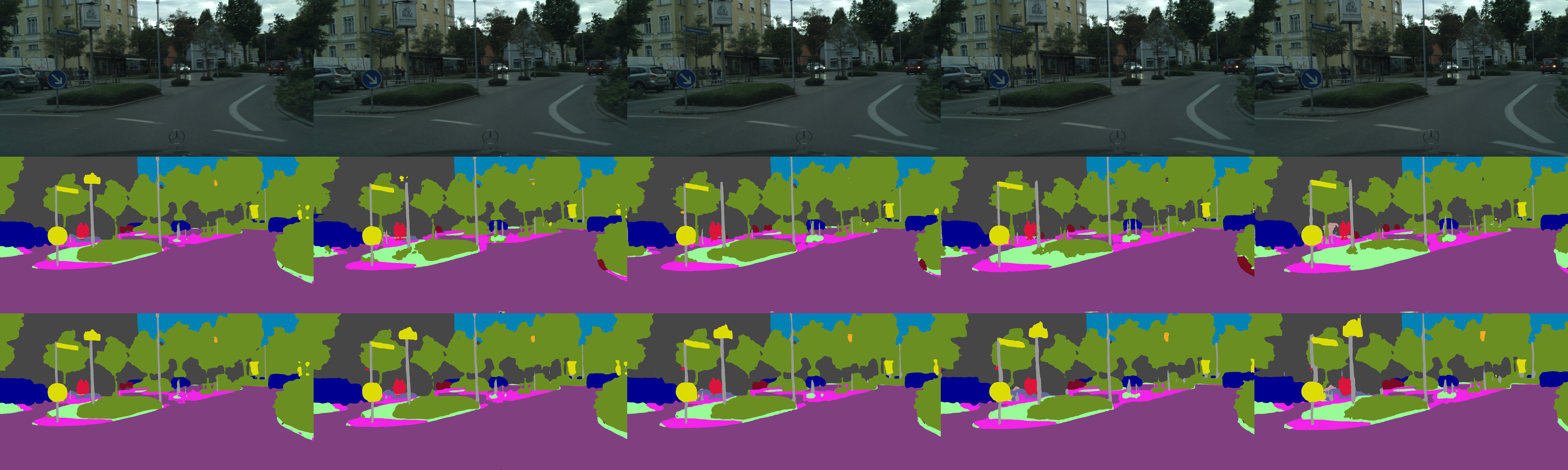
Dataset: cityscapes validation set
Left to right. Key frame k, non-key frame k+1, k+2, k+3, k+4
| Net | frame interval | Input scale | avg mIoU | min IoU w/wo edge |
FPS-G | FPS-T |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Swift Net | i = 0 | 0.75 | 74.4 | 74.4 | 26 | 109 |
| SwNet-seq Net | i = 1 | 0.75 | 73.7 | 73.0/72.6 | 44 | 171 |
| SwNet-seq Net | i = 2 | 0.75 | 72.6 | 70.6/70.1 | 58 | 181 |
| SwNet-seq Net | i = 3 | 0.75 | 71.8 | 69.5/68.8 | 67 | 186 |
| SwNet-seq Net | i = 4 | 0.75 | 70.9 | 67.6/66.8 | 75 | 193 |
| Net | frame interval | Input scale | avg mIoU | min IoU w/wo edge |
FPS-G | FPS-T |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Swift Net | i = 0 | 0.5 | 70.3 | 70.3 | 52 | 180 |
| Swift Net | i = 0 | 0.75 | 74.4 | 74.4 | 26 | 109 |
| Swift Net | i = 0 | 1.0 | 74.6 | 74.6 | 15 | 63 |
| SwNet-seq Net | i = 2 | 0.5 | 69.1 | 67.5/67.0 | 103 | 194 |
| SwNet-seq Net | i = 2 | 0.75 | 72.6 | 70.6/70.1 | 58 | 181 |
| SwNet-seq Net | i = 2 | 1.0 | 73.4 | 72.0/71.3 | 36 | 127 |
Note: Due to device and environment, FPS test results may vary from device to device and are only for relative reference.
Download and put all model weights in ./weights:
SwNet-seq Net: ./weights/cityscapes-swnet_model_best.pth.tar
SwiftNet: ./weights/cityscapes-swnet-R18.pt
FloeNet2S: Weights Download
Reference:
FlowNet2S: Evolution of Optical Flow Estimation with Deep Networks
GSVNet: Guided Spatially-Varying Convolution for Fast Semantic Segmentation on Video