This is a stm32h7a3 processor, with a single 64mbit qspi ram chip connected over the ospi controller.
A first attempt to use quad spi in memory mapped mode on stm32h7a3 showed occasional data corruption when writing to qspi ram.
Update: Leon Shan has found a way to make memory-mapping an spi ram work.
Steps:
- take an stm32h7 board
- replace the spi flash with pin-compatible spi ram
- replace the stm32h750 processor with a pin-compatible stm32h7a3. The stm32h7a3 supports memory mapping spi ram and flash; the stm32h750 only supports memory-mapping flash.
- port micropython to the stm32h7a3
- add spi ram driver
I'm using two different boards:
- DEVEBOX STM32H7XX
- WeAct MiniSTM32H7xx
These are "Made in Asia" boards in the 10-20$ price range, with a STM32H750VBT6 processor. spi flash is used to store firmware and data. These boards are roughly similar to the OpenMV H7, have connectors for camera and lcd, and run openmv (Open Machine Vision) software.
Replace the Winbond W25Q64JVSSIQ 8 mbyte SPI flash memory with a Espressif ESP-PSRAM64H 8 mbyte SPI pseudo-static RAM.
These two ic's are pin compatible. The ESP-PSRAM64H spi ram is 150 mil wide while the W25Q64 spi flash is 208 mil wide, but you can solder both in the same footprint.
Lyontek LY68L6400SLIT, Espressif ESP-PSRAM64H, APMemory APS6404L-3SQN seem to be pin compatible.
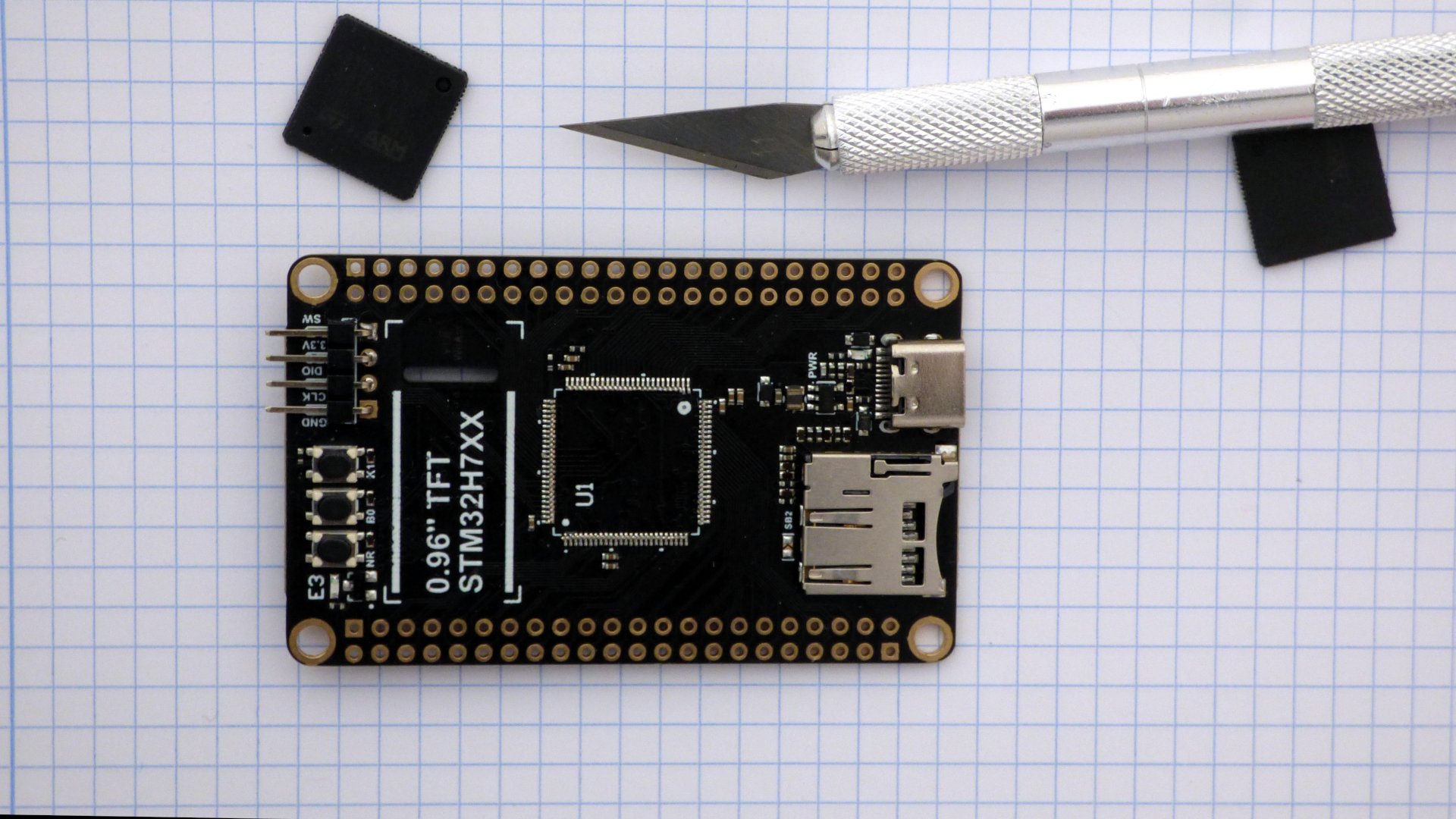
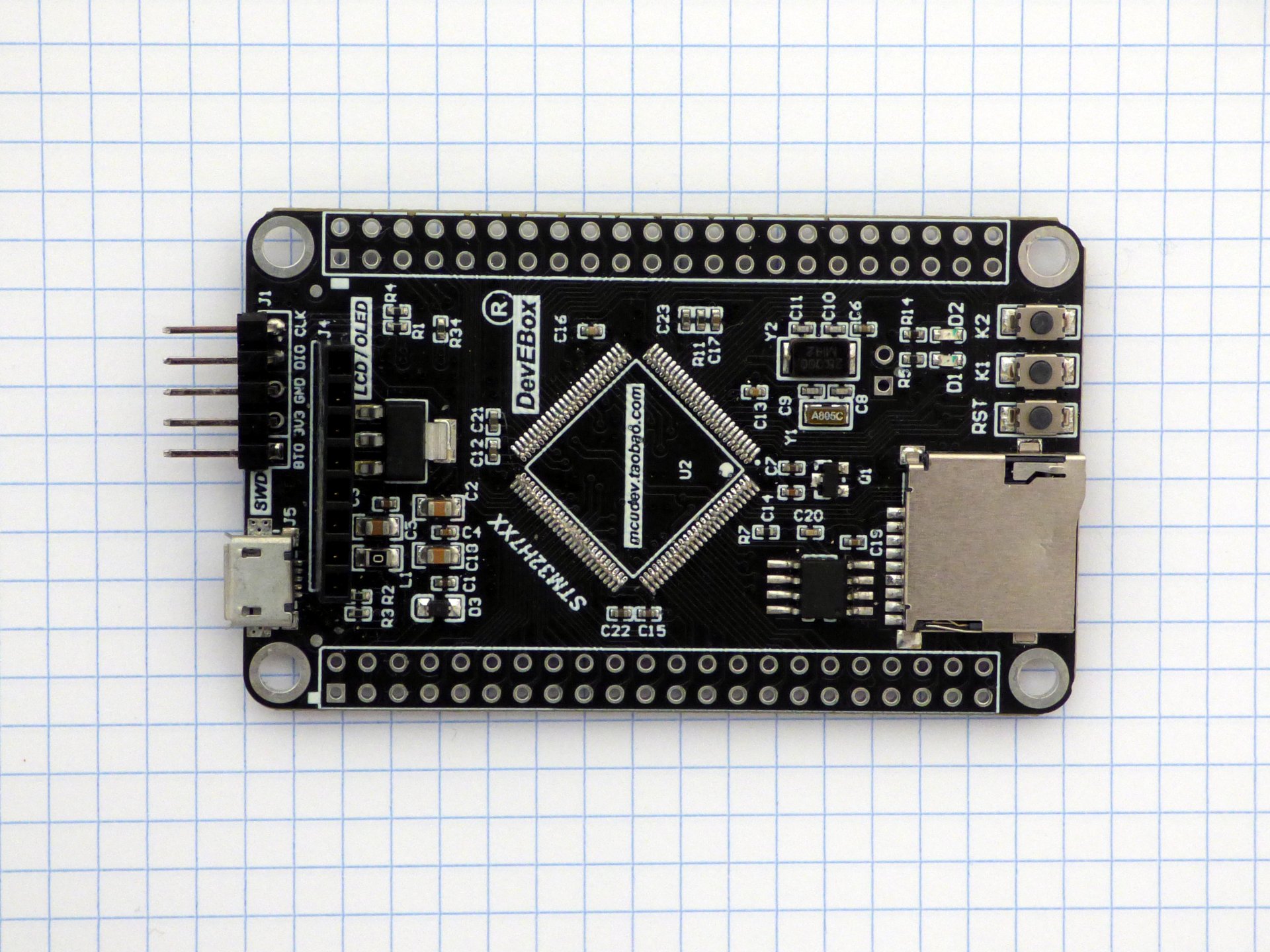
These boards use a STM32H750VBT6 processor in a LQFP100 package. Replace the STM32H750VBT6 with a STM32H7A3VIT6.
The STM32H7A3VIT6 is pin-compatible with STM32H750VBT6, so you do not have to modify the pcb.
The sophisticated way to unsolder is with Chip Quik or Fast Chip solder removal alloy. I do it the unsophisticated way: take a scalpel and cut through the pins, then unsolder the pins one by one. Put kapton tape on the parts of the board you do not wish to solder.
| WeAct | mcudev |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| WeAct | mcudev |
|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
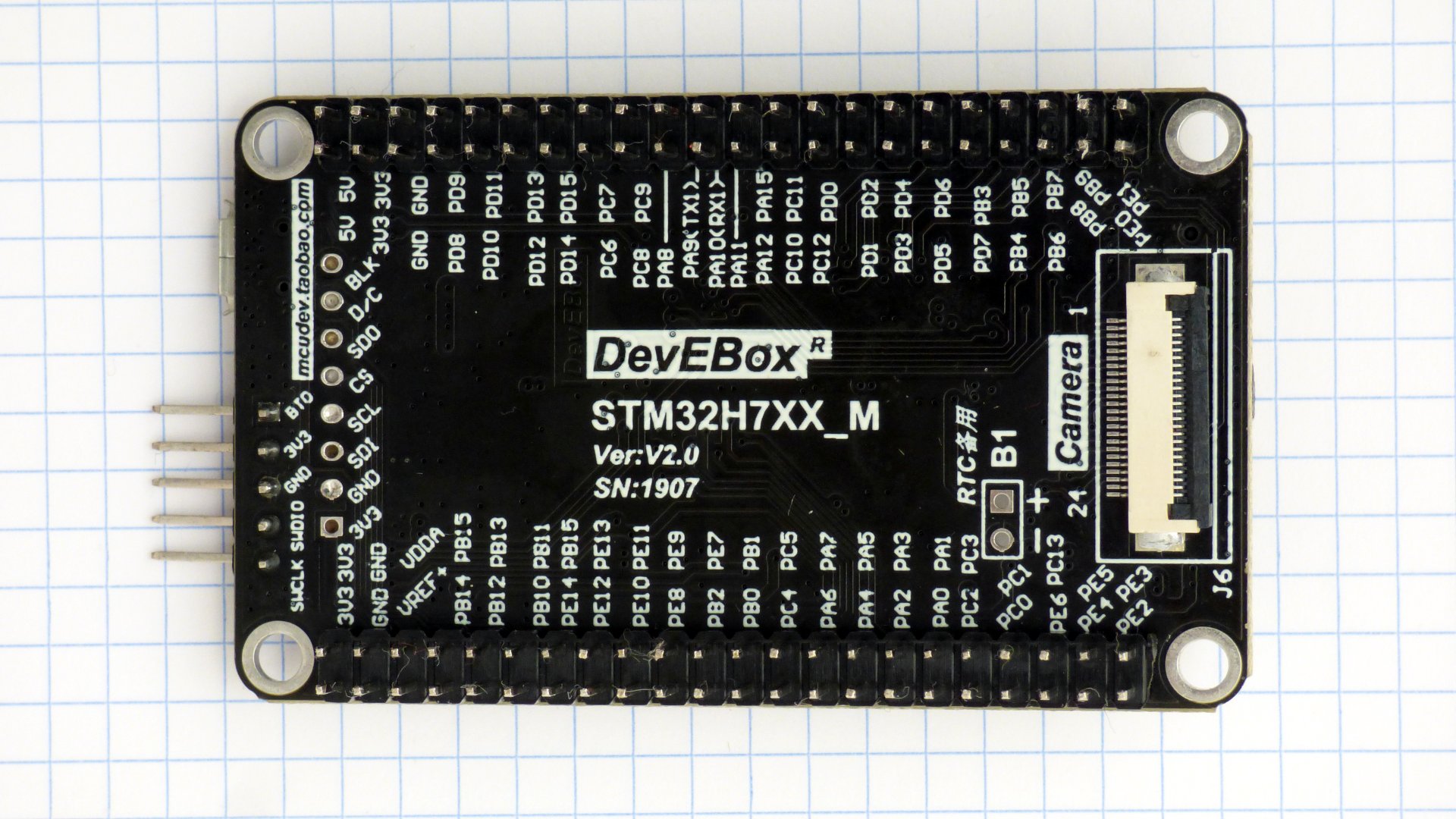 |
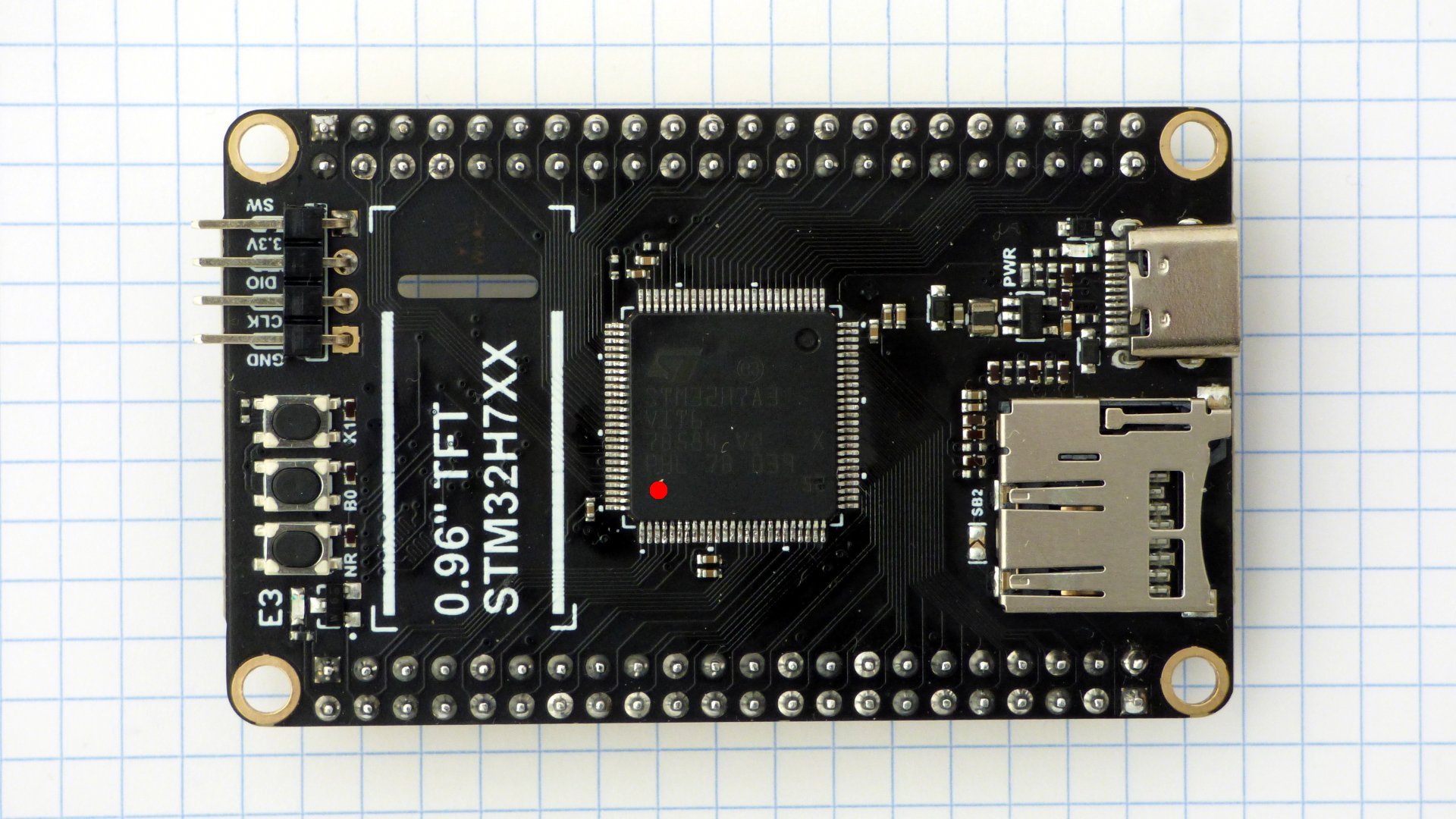
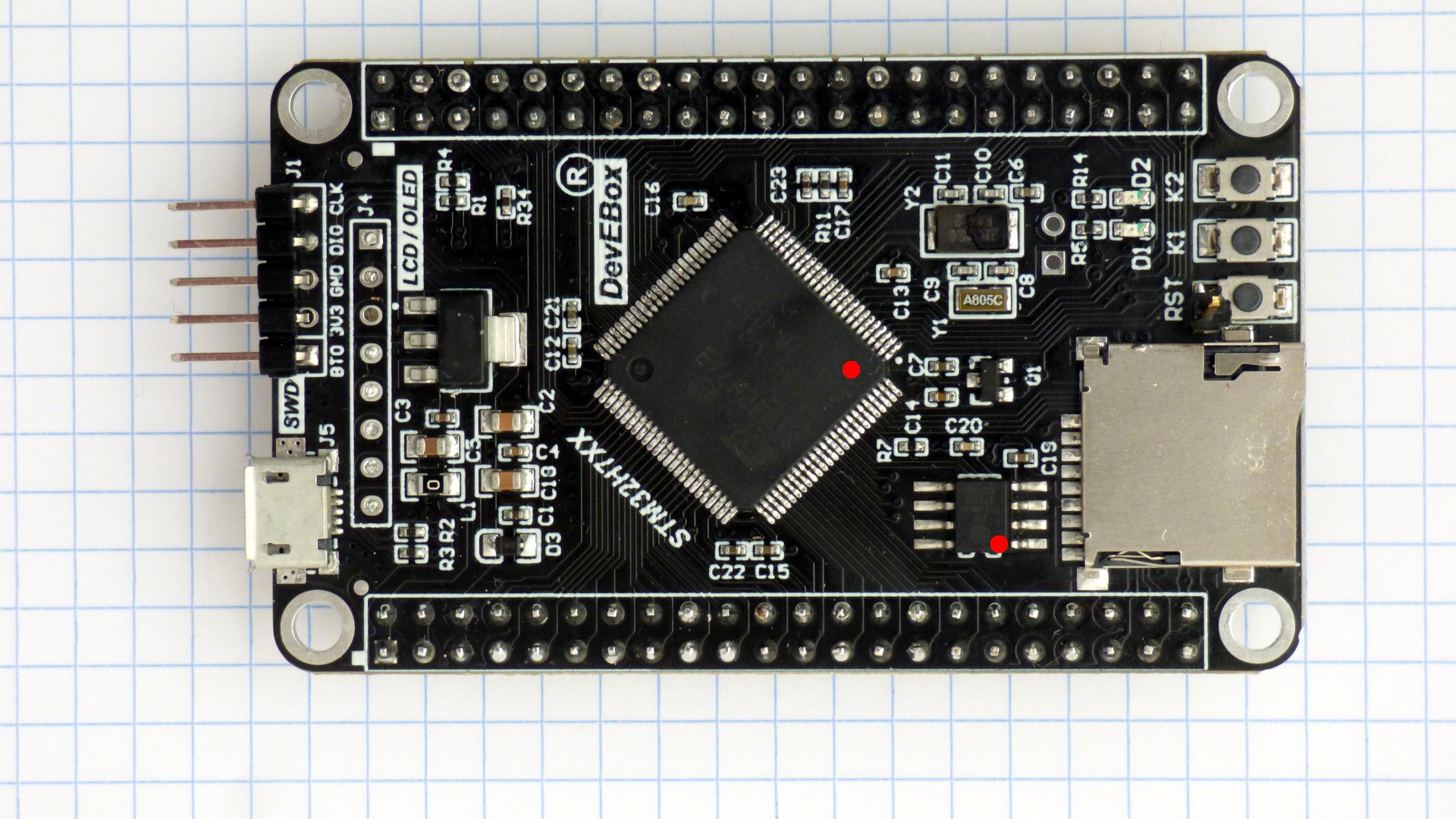
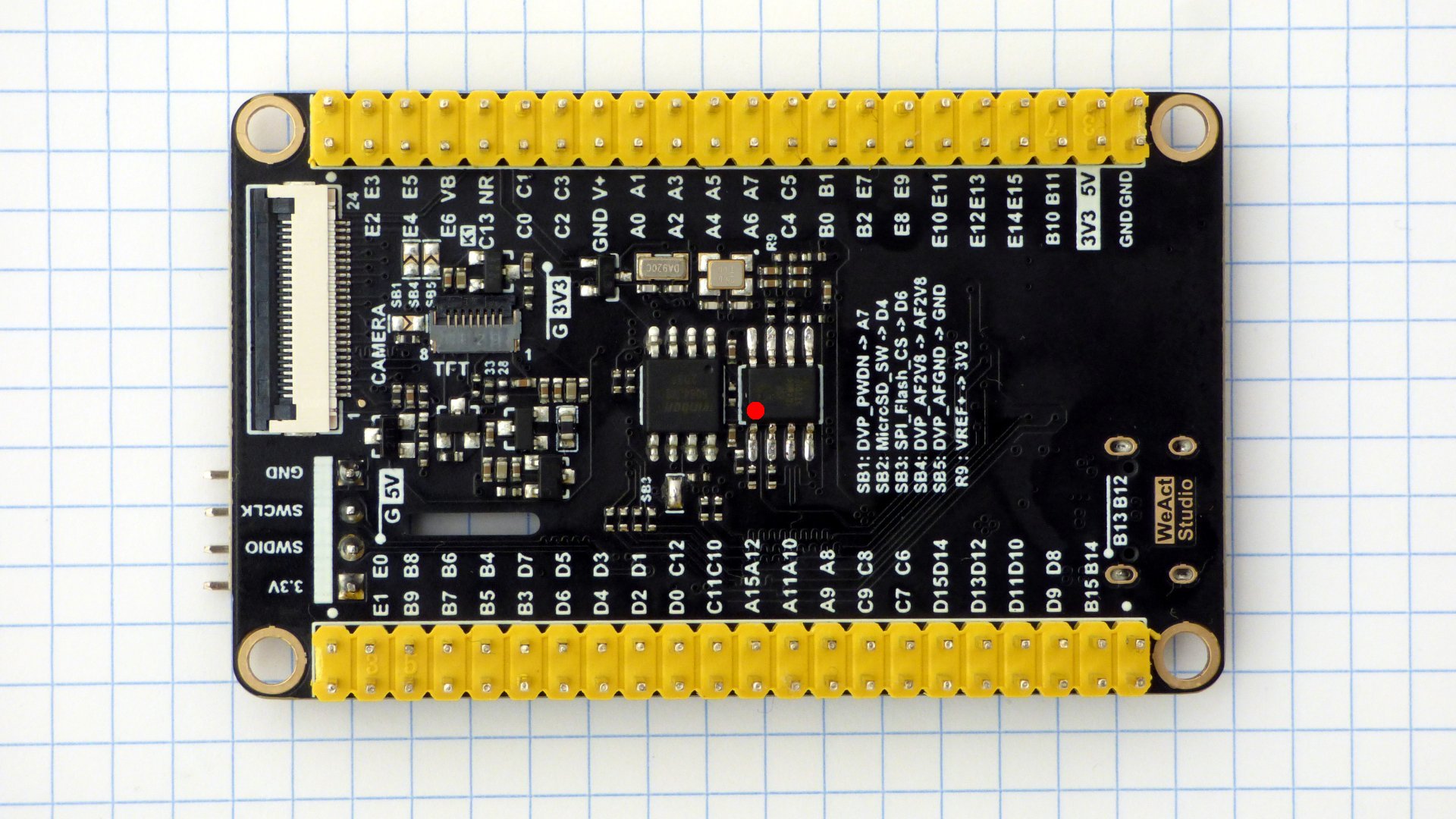
Pictures of the boards. The modified chips are marked with a red dot on pin 1. A pin has been soldered to the DEVEBOARD STM32H7XX reset button. More pictures.
Check the processor responds when connecting a debugger to the SWD port. The debugger needs SWDIO, SWCLK, and NRST. On the WeAct MiniSTM32H7xx the NRST pin is on the DuPont connector. On the DEVEBOX STM32H7XX you need to solder a pin to the RST button. Configure the debugger to assert RST during attach.
Connect usb, and boot in dfu mode. Check dfu-util -l sees device:
$ dfu-util -l
dfu-util 0.9
Found DFU: [0483:df11] ver=0200, devnum=10, cfg=1, intf=0, path="1-1.1", alt=2, name="@OTP Memory /0x08FFF000/01*1024 e", serial="376E356F3339"
Found DFU: [0483:df11] ver=0200, devnum=10, cfg=1, intf=0, path="1-1.1", alt=1, name="@Option Bytes /0x5200201C/01*297 e", serial="376E356F3339"
Found DFU: [0483:df11] ver=0200, devnum=10, cfg=1, intf=0, path="1-1.1", alt=0, name="@Internal Flash /0x08000000/256*08Kg", serial="376E356F3339"
Take the dfu-util output marked "Internal Flash", and in the micropython bootloader ports/stm32/mboot/main.c put :
#define FLASH_LAYOUT_STR "@Internal Flash /0x08000000/256*08Kg" MBOOT_SPIFLASH_LAYOUT MBOOT_SPIFLASH2_LAYOUT
Main differences between H743 and H7A3:
- clock generation
- 1 USB instead of 2
- 2 ADCs instead of 3
- 2 octo-spi (8 wire spi) instead of 1 quad-spi (4 wire spi)
Download schematics. In STM32CubeMX, start a project with processor and pin connections as on the schematic. Set external crystal frequency and do clock tree generation. Hit generate code.
In ports/stm32/boards take board support files for DEVEBOX STM32H743. STM32H7A3 has more ram than STM32H743, modify linker script.
The STM32H7A3 processor is not yet supported in micropython. Browse the code generated by STM32CubeMX and modify micropython accordingly. First patch, still rough.
And we have a REPL prompt:
MicroPython v1.13-237-g8db488963-dirty on 2020-12-07; DEVEBOX STM32H7XX with STM32H7A3
Type "help()" for more information.
>>> import gc
>>> gc.mem_free()
999584
The 1 Mbyte of free memory is the internal memory of the mcu.
- Work in progress *
Configure the ospi controller for spi ram. Modify linker script to put the heap on the external spi ram. Keep stack in internal ram.
To debug ospi, connect logic analyser to ospi pins and lower ospi clock so logic analyser is able to capture clean signals.
spiram eid 0d 5d 52 a2 64 31 91 31
spiram memtest pass
MicroPython v1.13-257-g4bb072268-dirty on 2021-01-21; DEVEBOX STM32H7XX with STM32H7A3
Type "help()" for more information.
>>> import gc
>>> gc.mem_free()
8196192
>>> a=bytearray(8000000)
>>> gc.mem_free()
195728
>>>
The 8 Mbyte of free memory is the external spi ram memory.
I am afraid reading the errata is fruitful on this one.
After experimenting with a single 64Mbit qspi psram on stm32h7a3:
- reading and writing in spi and qspi mode using HAL_OSPI_Command(), HAL_OSPI_Receive(), and HAL_OSPI_Transmit() works fine.
- when memory mapping the spi ram using HAL_OSPI_MemoryMapped(), even though the spi ram does not have a DQS pin, set HAL_OSPI_DQS_ENABLE during write, HAL_OSPI_DQS_DISABLE during read; else hardfault during write. Described in errata "Memory-mapped write error response when DQS output is disabled".
- when memory mapping the spi ram, setting MPU_TEX_LEVEL1, MPU_ACCESS_CACHEABLE, MPU_ACCESS_BUFFERABLE results in occasional data corruption during write.
Terminal ready
spiram eid 0d 5d 52 a2 64 31 91 31
spiram memtest16 fail, address 0x903e2070 written 0x5a5a read 0x0000
MicroPython v1.13-260-g0b108aaa0-dirty on 2021-01-24; DEVEBOX STM32H7XX with STM32H7A3
If I connect a logic analyser to the qspi bus, I see the data going from processor to spi ram is occasionally corrupt: when I do a write, sometimes some bytes still have the value from before the write. This seems to be a cache issue. I'm not aware of a workaround.
This is unfortunate.
- The board has a trace from processor SPI pin to the SPI memory ic, and from processor SPI pin to the board DuPont connectors. At low speeds this is not a problem, but at high speeds the trace to the DuPont connector will cause reflections.
The WeAct git also has code to run STM32H750 from external spi flash.
not truncated