A small linting and building command line tool for reproducible R analysis with Docker at QBiC.
- Create project from template
- Resolve conda packages from R
sessionInfo - Lint the project against the guidelines
Performing a reproducible analysis with R and share the environment status of an R installation with the necessary packages and all that with the correct version is a very challenging task.
In order to face this issue, under the umbrella of better reproducibility of computational results, we created Rmageddon, a small command-line tool, that assists in the build of Docker container with specified version of R and a dedicated, version-defined package installation. Moreover, Rmageddon provides cookiecutter templates for the easy creation of docker environments for your R analysis.
The container collection is hosted on a different GitHub repository: R-container-lib. All containers there passed the linting and have been build with Rmageddon.
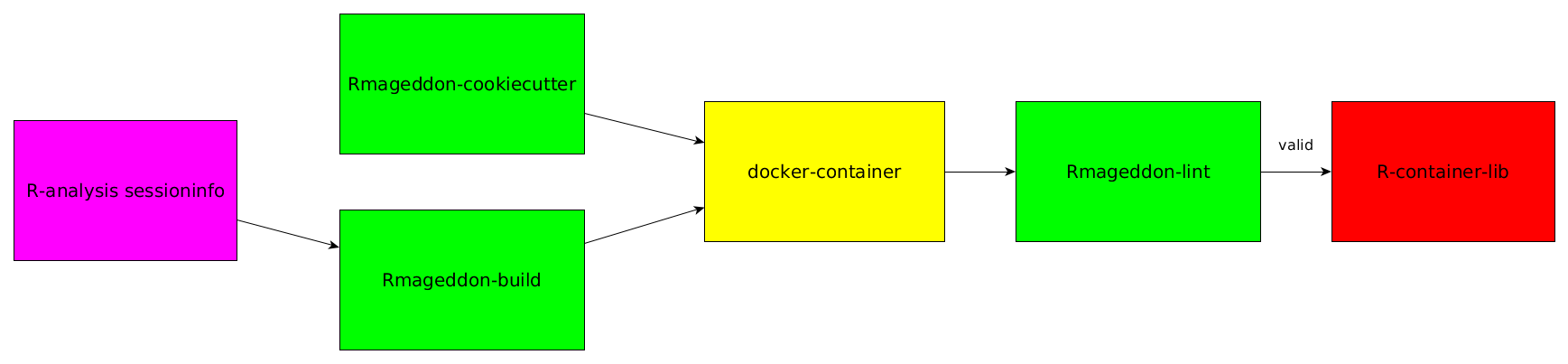
The complete workflow for the creation of a new container for your R-analysis is depicted in the following image:
This README will guide you through the complete process of starting with the sessioninfo of your R-analysis and finally sharing your docker powered R-environment on our R-container-lib.
- Create a sessioninfo from your R-analysis. The official R-documentation explains this process well: Sessioninfo.
- Install Rmageddon. This is explained in the documentation for Rmageddon: Rmageddon documentation
- Create a docker environment using the cookiecutter template. This process is described in the documentation for the Rmageddon-cookiecutter
- Run Rmageddon build on your sessioninfo. This is again explained in the documentation for Rmageddon: Rmageddon documentation, especially in the subcommand build section.
- Ensure that your environment.yml file is now or still in your R-container which you created in step 3
- Add your R-scripts that you used for your analysis to your just created R-container
- Validate your just created R-container: Run Rmageddon lint on it. Please refer to the documentation for Rmageddon: Rmageddon documentation, especially in the subcommand lint section.
- If validation was successful your R-container is now ready to be added to our R-container library. Please refer to the final documentation of the R-container-lib.
- Enjoy!