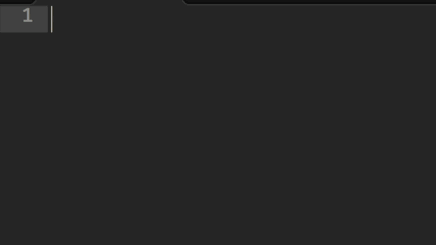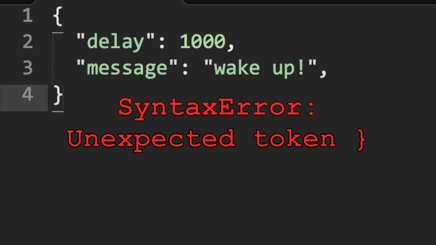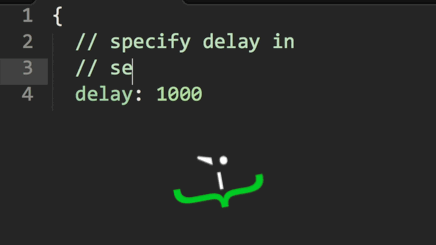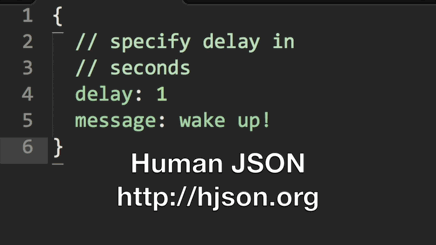
Hjson, the Human JSON. A configuration file format for humans. Relaxed syntax, fewer mistakes, more comments.
{
# specify rate in requests/second (because comments are helpful!)
rate: 1000
// prefer c-style comments?
/* feeling old fashioned? */
# did you notice that rate doesn't need quotes?
hey: look ma, no quotes for strings either!
# best of all
notice: []
anything: ?
# yes, commas are optional!
}
The Java implementation of Hjson is based on minimal-json. For other platforms see hjson.github.io.
You can install the Hjson command line tool by downloading and unpacking the latest hjson.zip.
- run
hjson -hfor help hjson file.jsonwill convert to Hjson.hjson -j file.hjsonwill convert to JSON.
Add a dependency to your build.gradle:
dependencies {
compile 'org.hjson:hjson:3.0.0'
}
Add a dependency to your pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hjson</groupId>
<artifactId>hjson</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0</version>
</dependency>Add a dependency to your ivy.xml:
<dependencies>
<dependency org="org.hjson" name="hjson" rev="3.0.0"/>
</dependencies>You can either
- use this libary directly
- or just convert Hjson to JSON and use it with your favorite JSON library.
// convert Hjson to JSON
String jsonString = JsonValue.readHjson(readerOrHjsonString).toString();
// convert JSON to Hjson
String hjsonString = JsonValue.readHjson(readerOrJSONString).toString(Stringify.HJSON);JsonObject jsonObject = JsonValue.readHjson(string).asObject();
JsonArray jsonArray = JsonValue.readHjson(reader).asArray();JsonValue.readHjson() will accept both Hjson and JSON. You can use JsonValue.readJSON() to accept JSON input only.
String name = jsonObject.get("name").asString();
int age = jsonObject.get("age").asInt(); // asLong(), asFloat(), asDouble(), ...
// or iterate over the members
for (Member member : jsonObject) {
String name = member.getName();
JsonValue value = member.getValue();
// ...
}String name = jsonArray.get(0).asString();
int age = jsonArray.get(1).asInt(); // asLong(), asFloat(), asDouble(), ...
// or iterate over the values
for(JsonValue value : jsonArray) {
// ...
}// Example: { "friends": [ { "name": "John", "age": 23 }, ... ], ... }
JsonArray friends = jsonObject.get("friends").asArray();
String name = friends.get(0).asObject().get("name").asString();
int age = friends.get(0).asObject().get("age").asInt();JsonObject jsonObject = new JsonObject().add("name", "John").add("age", 23);
// -> { "name": "John", "age", 23 }
JsonArray jsonArray = new JsonArray().add("John").add(23);
// -> [ "John", 23 ]jsonObject.set("age", 24);
jsonArray.set(1, 24); // access element by index
jsonObject.remove("age");
jsonArray.remove(1);Writing is not buffered (to avoid buffering twice), so you should use a BufferedWriter.
jsonObject.writeTo(writer);
jsonObject.writeTo(writer, Stringify.HJSON);jsonObject.toString(Stringify.HJSON); // Hjson output
jsonObject.toString(Stringify.FORMATTED); // formatted JSON output
jsonObject.toString(Stringify.PLAIN); // plain JSON output, default
jsonObject.toString(); // plain