HEAPUtil is an IEEE RA-L & IROS 2021 research paper. In this work, we present a method for unsupervised estimation of the Environment-Specific (ES) and Place-Specific (PS) Utility of unique visual cues in a reference map represented as VLAD clusters. Furthermore, we employ this Utility in a unified hierarchical global-to-local VPR pipeline to enable better place recognition and localization capability for robots, with reduced storage and compute time requirements. This repo contains the official code for estimating the Utility of visual cues and the hierarchical global-to-local VPR pipeline.
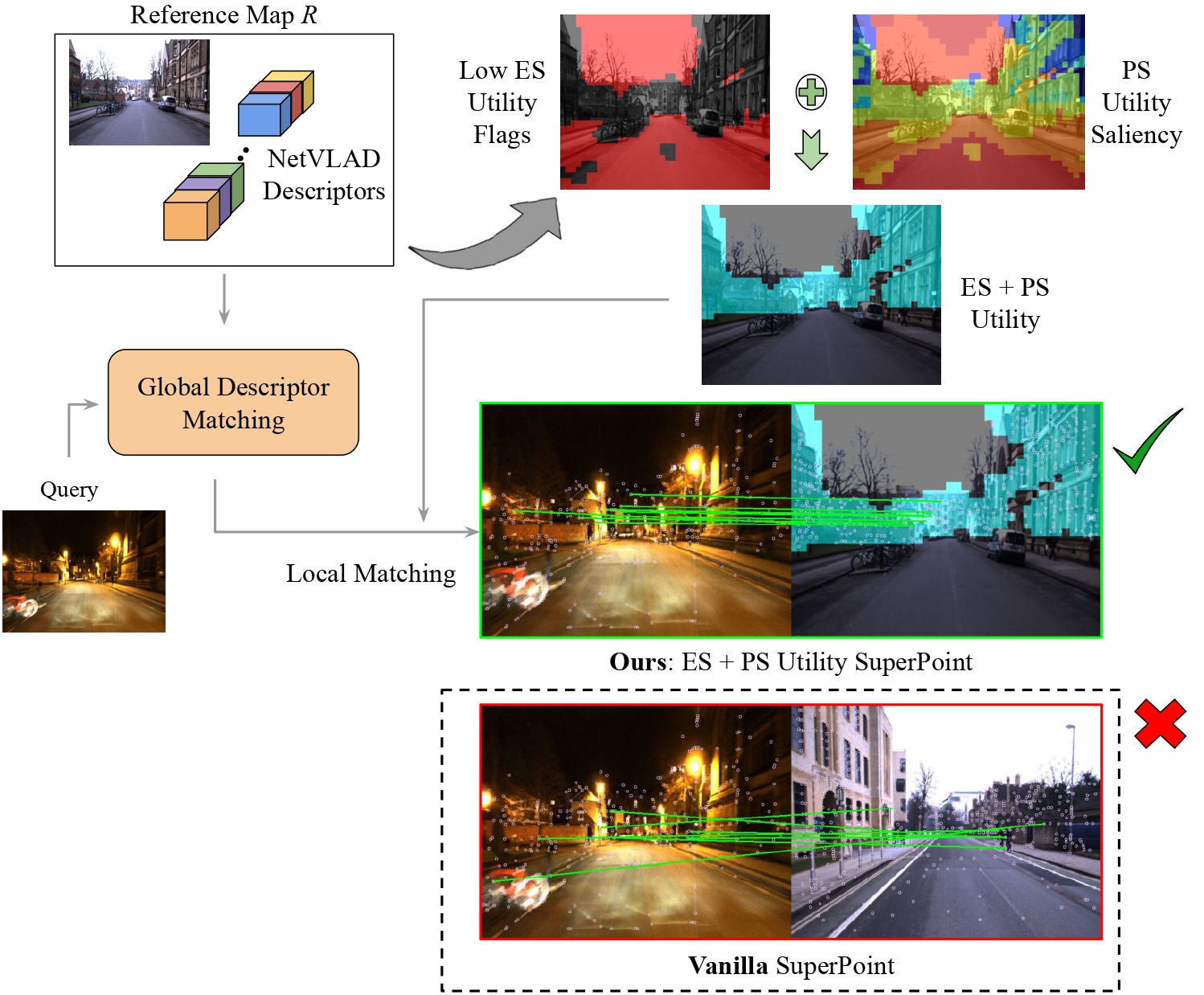
Utility-guided Hierarchical Visual Place Recognition.
For more details, please see:
-
Full paper PDF: A Hierarchical Dual Model of Environment- and Place-Specific Utility for Visual Place Recognition.
-
Authors: Nikhil Varma Keetha, Michael Milford, Sourav Garg
Simply run the following command: pip install -r requirements.txt
conda create -n heaputil python=3.8 mamba -c conda-forge -y
conda activate heaputil
mamba install numpy opencv pytorch matplotlib faiss-gpu scipy scikit-image=0.18.2 torchvision scikit-learn h5py -c conda-forgeFor Data Loading, we use .mat files which contain information regarding Reference Image Paths, Query Image Paths, Ground-truth Co-ordinates for Reference and Query Images, and the Positive Localization Distance Threshold. These .mat files for the Berlin Kudamm, Nordland Summer Vs Winter and Oxford Day Vs Night datasets are present in the ./dataset-mat-files folder.
We provide the Berlin Kudamm Dataset for Inference:
For more details regarding the Berlin Kudamm dataset please refer to this paper.
For all the scripts, apart from SuperPoint Extraction, you may use the --dataset flag to mention the dataset to use. By default, it is set to 'berlin' and the default choices are ['oxford', 'nordland', 'berlin'].
Here's a Colab Notebook to effortlessly run tests on the Berlin Dataset.
Please use the --help flag to see all available arguments for the scripts.
Extract NetVLAD Descriptors, Predictions and Cluster Masks:
python NetVLAD/main.py --resume './data/NetVLAD/netvlad-checkpoint-cc16' --root_dir './data' --save --save_path './data/NetVLAD'Estimate the Environment- and Place-Specific Utility of VLAD Clusters for the Reference Map:
python utility.py --root_dir './data' --netvlad_extracts_path './data/NetVLAD' --save_path './data/Utility' --save_vizYou may use the --save_viz flag to visualize the Environment-Specific and Place-Specific Utility as shown below:


Visualizing ES (left) & PS (right) Utility (Red indicates low utility and blue/gray indicates high utility)
Generate path lists which are required for SuperPoint Extraction & SuperGlue:
python generate_path_lists.py --root_dir './data' --netvlad_predictions './data/NetVLAD' --save_path './data'Extract SuperPoint features for the Reference Map:
python SuperGlue/superpoint_extraction.py --input_images './data/db_list.txt' --split 'db' --input_dir './data' --output_dir './data/SuperPoint'Extract SuperPoint features for the Queries:
python SuperGlue/superpoint_extraction.py --input_images './data/q_list.txt' --split 'query' --input_dir './data' --output_dir './data/SuperPoint'You may use the --viz flag to visualize the best matches as a gif.
Run Vanilla SuperPoint based Local Feature Matching:
python local_feature_matching.py --input_dir './data' --output_dir './data/LFM/Vanilla' \
--netvlad_extracts_path './data/NetVLAD' --superpoint_extracts_path './data/SuperPoint' --utility_path './data/Utility'Run ES-Utility guided Local Feature Matching:
python local_feature_matching.py --input_dir './data' --output_dir './data/LFM/ES_Utility' \
--netvlad_extracts_path './data/NetVLAD' --superpoint_extracts_path './data/SuperPoint' --utility_path './data/Utility' \
--es_utilityRun PS-Utility guided Local Feature Matching:
python local_feature_matching.py --input_dir './data' --output_dir './data/LFM/PS_Utility' \
--netvlad_extracts_path './data/NetVLAD' --superpoint_extracts_path './data/SuperPoint' --utility_path './data/Utility' \
--ps_utilityDefault Number of Top Utility Clusters to use for Local Feature Matching is 10. Please use the --k flag to use a different number of top utility clusters.
Run ES & PS-Utility guided Local Feature Matching:
python local_feature_matching.py --input_dir './data' --output_dir './data/LFM/Utility' \
--netvlad_extracts_path './data/NetVLAD' --superpoint_extracts_path './data/SuperPoint' --utility_path './data/Utility' \
--es_utility --ps_utility --vizDefault Number of Top Utility Clusters to use for Local Feature Matching is X-1 clusters, where X is the number of useful clusters determined by the Environment-Specific system. To use a different number of top utility clusters please use the --non_default_k and --k flags.
We use the --viz flag to visualize the best matches along with utility reference masks as a gif as shown below:
ES & PS Utility-guided Local Feature Matching (Cyan mask represents regions with high utility)
Similar to Local Feature Matching, you may run the superglue_match_pairs.py file for Vanilla SuperGlue & Utility-guided SuperGlue. You may use the --viz flag to visualize all the matches and dump the SuperGlue-style plots.
Run ES & PS-Utility guided SuperGlue:
python superglue_match_pairs.py --input_pairs './data/berlin_netvlad_candidate_list.txt' --input_dir './data' --output_dir './data/SuperGlue/Utility' \
--netvlad_extracts_path './data/NetVLAD' --utility_path './data/Utility' \
--es_utility --ps_utilityIf any ideas from the paper or code from this repo are used, please consider citing:
@article{keetha2021hierarchical,
author={Keetha, Nikhil Varma and Milford, Michael and Garg, Sourav},
journal={IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters},
title={A Hierarchical Dual Model of Environment- and Place-Specific Utility for Visual Place Recognition},
year={2021},
volume={6},
number={4},
pages={6969-6976},
doi={10.1109/LRA.2021.3096751}}The code is licensed under the MIT License.
The authors acknowledge the support from the Queensland University of Technology (QUT) through the Centre for Robotics.
Furthermore, we would like to acknowledge the Pytorch Implementation of NetVlad from Nanne and the original implementation of SuperGlue.
Please check out this collection of related works on place recognition.






