This repository contains all code + deployment scripts for the Tailwind Traders Backend.
- Repositories
- Deployment scenarios
- Run Tailwind Traders Backend Services Locally
- Run Tailwind Traderes Backend using Devspaces
- Test image classiffier
- Contributing
For this demo reference, we built several consumer and line-of-business applications and a set of backend services. You can find all repositories in the following locations:
- Tailwind Traders
- Backend (AKS)
- Website (ASP.NET & React)
- Desktop (WinForms & WPF -.NET Core)
- Rewards (ASP.NET Framework)
- Mobile (Xamarin Forms 4.0)
Tailwind Traders supports two deployment scenarios:
- Deploy Tailwind Traders Backend on Azure AKS and Azure resources (CosmosDb and Storage accounts)
- Deploy Tailwind Traders Backend on Windows and Linux containers in AKS
You can deploy all basics scenarios using one script under /Deploy folder.
-
Deploy Tailwind Traders Backend on Azure AKS and Azure resources (CosmosDb and Storage accounts)
Running the following command you can deploy starting with the infrastructure and ending with deploying the images on the storage:
.\Deploy-Unified.ps1 -resourceGroup <resource-group-name> -location <location> -clientId <service-principal-id> -password <service-principal-password> -subscription <subscription-id>
resourceGroup: The name of your resource group where all infrastructure will be createdRequiredlocation: Select where you want to create your resource group, for example:eastusRequiredclientId: Id of the service principal used to create the AKSRequired if your user does not have permissions to create a new onepassword: Password of the service principalRequiredsubscription: Id of your subscription where you are going to deploy your resource groupRequired
The process will take few minutes.
-
Deploy Tailwind Traders Backend on Windows and Linux containers in AKS
Running the following command you can deploy starting with the infrastructure and ending with deploying the images on the storage. This command requires more parameters than Linux scenario because we need to build and deploy a WCF service.
Note For mixed (Windows and Linux containers) scenario we need to deploy Tailwind Traders Rewards before it. Because you are going to need some resources that Tailwind Traders Rewards creates.
.\Deploy-Unified-WinLinux.ps1 -resourceGroup <resource-group-name> -location <location> -clientId <service-principal-id> -password <service-principal-password> -subscription <subscription-id> -deployWinLinux $true -rewardsResourceGroup <resource-group-rewards-name> -rewardsDbPassword <database-rewards-password>
deployWinLinux: Flag needed to execute Windows-Linux scenariocsprojPath: Path location where Tailwind.Traders.Rewards.Registration.Api.csproj is in your machineRequiredmsBuildPath: Path location where MSBuild.exe is, for example:C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2019\Professional\MSBuild\Current\BinrewardsResourceGroup: The name of the resource group where Tailwind Traders Rewards is deployedRequiredrewardsDbPassword: Tailwind Traders Rewards database password (Tailwind Traders Rewards Registration, WCF service, connects to this database)Required
The process will take few minutes, more than Linux scenario, it will create an Azure Kubernetes Service with Windows and Linux nodes.
In addition to the following documentation you can also deploy infrastructure and services step by step.
To run Tailwind Traders you need to create the Azure infrastructure. There are two ways to do it. Using Azure portal or using a Powershell script.
An ARM script is provided so you can automate the creation of the resources required for the backend services just clicking following button:
Azure portal will ask you for the following parameters:
servicePrincipalId: Id of the service principal used to create the AKSservicePrincipalSecret: Password of the service principalaksVersion: AKS version to use (at least 1.14).
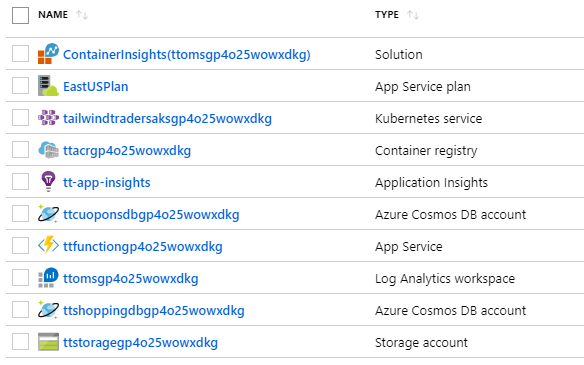
The deployment could take more than 10 minutes, and once finished all needed resources will be created:
You can use the CLI to deploy the ARM script. Open a Powershell window from the /Deploy/powershell folder and run the Deploy-Arm-Azure.ps1 with following parameters:
-resourceGroup: Name of the resource group-location: Location of the resource group
You can optionally pass two additional parameters:
-clientId: Id of the service principal uesd to create the AKS-password: Password of the service principal
If these two parameters are not passed a new service principal will be created.
There is an additional optional parameters to control some aspects of what is created:
-deployAks: If set to$falseAKS and ACR are not created. This is useful if you want to create the AKS yourself or use an existing AKS. Defaults to$true. If this parameter is$truethe resource group can't exist (AKS must be deployed in a new resource group).
Once script finishes, everything is installed. If a service principal has been created, the script will output the service principal details - please, take note of the appId and password properties for use them in the AKS deployment
Pre-requisites for this deployment are to have:
- The AKS and all related resources deployed in Azure
- A terminal with Powershell environment
- Azure CLI 2.0 installed.
- Kubectl installed with the last version (v1.15.0 at this moment).
- Docker installed
A Service Principal is needed for creating the AKS. If you use the CLI for create the resources, you can reuse a SP one passing to the script the id and password as optional parameters; if not, the script will create a new one for you and will print the details (id and password among them).
In case you use Azure Portal for the resources' creation, you can also reuse a SP or create manually a new one for passing the credentials to the template.
From the terminal type:
az loginand follow instructions to log into your Azure.- If you have more than one subscription type
az account list -o tableto list all your Azure subscriptions. Then typeaz account set --subscription <subscription-id>to select your subscription az aks get-credentials -n <your-aks-name> -g <resource-group-name>to download the configuration files thatkubectlneeds to connect to your AKS.
At this point if you type kubectl config current-context the name of your AKS cluster should be displayed. That means that kubectl is ready to use your AKS
Helm is a tool to deploy resources in a Kubernetes cluster in a clean and simple manner. It is composed of two tools, one client-side (the Helm client) that needs to be installed on your machine, and a server component called Tiller that has to be installed on the Kubernetes cluster.
To install Helm, refer to its installation page. Once Helm is installed, Tiller must be deployed on the cluster. For deploying Tiller run the ./Add-Tiller.ps1 (from Powershell).
Once installed, helm commands like helm ls should work without any error.
Before deploying services using Helm, you need to setup the configuration. We refer to the configuration file with the name of gvalues file. This file contains all secrets and connection strings so beware to not commit in your repo accidentally.
An example of this file is in helm/gvalues.yaml. The deployment scripts use this file by default, but do not rely on editing this file. Instead create a copy of it a folder outside the repository and use the -valuesFile parameter of the deployment script.
Note: The folder
/Deploy/helm/__values/is added to.gitignore, so you can keep all your configuration files in it, to avoid accidental pushes.
Note: If you come from the Windows and Linux containers scenario you must add the Rewards database's connection string, in the values file you are using, for example:
inf:
(...)
db:
(...)
rewards:
host: tcp:*****.database.windows.net
port: "1433"
catalog: rewardsdb # you must not modify this name
user: ttuser
pwd: YourPassword
(...)Please refer to the comments of the file for its usage. Just ignore (but not delete) the tls section (it is used if TLS is enabled).
Generating a valid gvalues file can be a bit harder, so there is a Powershell script that can do all work by you. This script assumes that all resources are deployed in the same resource group, and this resource group contains only the Tailwind Traders resources. Also assumes the Azure resources have been created using the tools provided in this repo.
Note The Generate-Config.ps1 uses the application-insights CLI extension to find the application insights id. Install it with
az extension add --name application-insights
To auto-generate your gvalues file just go to /Deploy/powershell folder and from a Powershell window, type the following:
.\Generate-Config.ps1 -resourceGroup <your-resource-group> -outputFile ..\helm\__values\<name-of-your-file>
The parameters that Generate-Config.ps1 accepts are:
-resourceGroup: Resource group where all Azure resources are. Required.-outputFile: Full path of the output file to generate. A good idea is to generate a file in/Deploy/helm/__values/folder as this folder is ignored by Git. If not passed the result file is written on screen.-gvaluesTemplate: Template of the gvalues file to use. The parameter defaults to the/Deploy/helm/gvalues.templatewhich is the only template provided.
The script checks that all needed resources exists in the resource group. If some resource is missing or there is an unexpected resource, the script exits.
If you come from the Windows and Linux containers in AKS scenario and you want to use the rewards registration service you have to pass also the following parameters:
-rewardsResourceGroup: Fill it if you are going to use Rewards DB (this is used, for example in the Windows and Linux containers in AKS scenarios).-rewardsDbPassword: The database password for the administrator user. Required if a rewardsResourceGroup is provided.
Otherwise the script will disable the rewards registration service.
Docker images are stored in a ACR (a private Docker Registry hosted in Azure).
Before deploying anything on AKS, a secret must be installed to allow AKS to connect to the ACR through a Kubernetes' service account.
To do so from a Powershell terminal run the ./Create-Secret.ps1 inside powershell folder with following parameters:
-resourceGroup <group>Resource group where AKS is-acrName <name>Name of the ACR
This will create the secret in AKS using ACR credentials. If ACR login is not enabled you can create a secret by using a service principal. In case that ACR is not created with administrator rights you will have to provide the service principal clientId and secret:
-clientId <id>Client id of the service principal to use-password <pwd>Service principal secret
Please, note that the Service principal must exist. To create a service principal you can run the command az ad sp create-for-rbac.
You can manually use docker-compose to build and push the images to the ACR. If using compose you can set following environment variables:
TAG: Will contain the generated docker images tagREGISTRY: Registry to use. This variable should be set to the login server of the ACR
Once set, you can use docker-compose build and docker-compose push to build and push the images.
Additionaly there is a Powershell script in the Deploy folder, named Build-Push.ps1. You can use this script for building and pushing ALL images to ACR. Parameters of this script are:
resourceGroup: Resource group where ACR is. Required.acrName: ACR name (not login server). Required.dockerTag: Tag to use for generated images (defaults tolatest)dockerBuild: If$true(default value) docker images will be built usingdocker-compose build.dockerPush: If$true(default value) docker images will be push to ACR usingdocker-compose push.isWindows: If$true(default to$false) will use the docker compose file for windows.
This script uses az CLI to get ACR information, and then uses docker-compose to build and push the images to ACR.
To build and push images tagged with v1 to a ACR named my-acr in resource group named my-rg, execute the following command inside /Deploy/powershell
.\Build-Push.ps1 -resourceGroup my-rg -dockerTag v1 -acrName my-acr
To just push the images (without building them before):
.\Build-Push.ps1 -resourceGroup my-rg -dockerTag v1 -acrName my-acr -dockerBuild $false
If you want to deploy the rewards registration image just call this command with the isWindows parameter set to true.
Notes:
- Remember to switch to Windows containers.
- The project needs to be published previously with the already created
FolderProfile.
You can set the CPU and RAM limit and request consumption values for each one of the services, editing the values in its corresponding values.yaml, under the field resources:
resources:
limits:
cpu: "500m"
requests:
cpu: "100m"Tailwind Traders can be deployed with TLS (https) support. For this to work a TLS/SSL certificate must be installed on the Kubernetes cluster. Three options are provided:
- Use staging certificate from Let's Encrypt. Not valid for production scenarios as staging certificates are not trusted.
- Use production certificate from Let's Encrypt. Valid for production scenarios as production certificates are trusted. Should be used only if you have a custom domain (trying to generate a Let's Encrypt certificate from the url generated by http application routing won't probably work).
- Use a custom certificate provided by you.
If Let's Encrypt is choose, then cert-manager is used. Cert-manager allows auto-provisioning of TLS certificates using Let's Encrypt and ACME protocol. The certificate is requested, created and installed on the server without any manual intervention.
Using Let's Encrypt and Cert manager
To enable SSL/TLS support you must do it before deploying your images. The first step is to add cert-manager to the cluster by running ./Add-Cert-Manager.ps1. It has no parameters and use helm to configure cert-manager in the cluster. This needs to be done only once.
Then you should run ./Enable-Ssl.ps1 with following parameters:
-sslSupport: Usestagingorprodto use the staging or production environments of Let's Encrypt-aksName: The name of the AKS to use-resourceGroup: Name of the resource group where AKS is-domain: Domain to use for the SSL/TLS certificates. Is optional and if not used it defaults to the public domain of the AKS. Note that this public domain exists only if Http Application routing is installed on the AKS. Only need to use this parameter if using custom domains.
Output of the script will be something like following:
NAME: tailwindtraders-ssl
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Dec 21 11:32:00 2018
NAMESPACE: default
STATUS: DEPLOYED
RESOURCES:
==> v1alpha1/Certificate
NAME AGE
tt-cert-staging 0s
==> v1alpha1/Issuer
NAME AGE
letsencrypt-staging 0s
You can verify that the issuer object is created using kubectl get issuers:
PS> kubectl get issuers
NAME AGE
letsencrypt-staging 4m
You can verify that the certificate object is created using kubectl get certificates:
PS> kubectl get certificates
NAME AGE
tt-cert-staging 4m
The certificate object is not the real SSL/TLS certificate but a definition on how get one from Let's Encrypt. The certificate itself is stored in a secret, called letsencrypt-staging (or letsencrypt-prod). You should see a secret named tt-letsencrypt-xxxx (where xxxx is either staging or prod).
PS> kubectl get secrets
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
acr-auth kubernetes.io/dockerconfigjson 1 2d
default-token-6tm9t kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 3d
letsencrypt-prod Opaque 1 3h
letsencrypt-staging Opaque 1 4h
tt-letsencrypt-prod kubernetes.io/tls 2 5m
ttsa-token-rkjlg kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 2d
The SSL/TLS secret names are:
letsencrypt-staging: Secret for the staging issuer. This is NOT the SSL/TLS certificatett-letsencrypt-staging: Secret for the staging SSL/TLS certificate.letsencrypt-prod: Secret for the prod issuer. This is NOT the SSL/TLS certificatett-letsencrypt-prod: Secret for the prod SSL/TLS certificate.
At this point the support for SSL/TLS is installed, and you can install Tailwind Traders Backend on the cluster.
Note: You don't need to do this again, unless you want to change the domain of the SSL/TLS certificate. In this case you need to remove the issuer and certificate objects (using
helm delete tailwindtraders-ssl --purgeand then reinstall again)
Remember Staging certificates are not trusted, so browsers will complain about it, exactly in the same way that they complain about a self-signed certificate. The only purpose is to test all the deployment works, but in any production environment you must use the
prodenvironment. In development/test environments is recommended to install the staging certificates and then trust those certificates in the developers' machines. You can download the Let's Encrypt staging certificates from their web.
Another way to validate your certificate deployment is doing a kubectl describe cert tt-cert-staging (or tt-cert-prod). In the Events section you should see that the certificate has been obtained:
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal CreateOrder 10m cert-manager Created new ACME order, attempting validation...
Normal DomainVerified 9m cert-manager Domain "e43cd6ae16f344a093dc.eastus.aksapp.io" verified with "http-01" validation
Normal IssueCert 9m cert-manager Issuing certificate...
Normal CertObtained 9m cert-manager Obtained certificate from ACME server
Normal CertIssued 9m cert-manager Certificate issued successfully
Use custom Certificate
If you already have a TLS certificate from your certificate authority you can deploy it on the server. Using Powershell, run the Enable-Ssl.ps1 script with following parameters:
-sslSupport: Usecustom-aksName: The name of the AKS to use-resourceGroup: Name of the resource group where AKS is-domain: Domain bounded to your AKS. It has to be compatible with the domains allowed by your TLS certificate-tlsCertFile: Certificate file-tlsKeyFile: Certificate key file-tlsSecretName: Name of the Kubernetes secret that will store the certificate. Defaults tott-tls-custom
- The certificate file file with the certificate public key. Usually is a
.certor.crtfile. - The certificate key file is the file with the certificate private key, usually a
.keyfile.
If you have a .pfx file you need to convert it to the separate .crt and .key files:
# Extract encrypted key from pfx file
openssl pkcs12 -in certfile.pfx -nocerts -out keyfile-encrypted.key
# Unencrypt key file
openssl rsa -in keyfile-encrypted.key -out keyfile.key
# Extract certificate file from pfx file
openssl pkcs12 -in certfile.pfx -clcerts -nokeys -out certfile.crtNote: If you want to add SSL/TLS support on the cluster (needed to use https on the web) please read Enabling SSL/TLS on the cluster section before installing the backend.
You can deploy Tailwind Traders using a custom domain or in the domain created by Http Application Routing (if enabled). If you are using a custom domain be sure to:
- Have the ingress public IP linked to custom domain
- Use the parameter
tlsHostwith the value of your custom domain (regardless its name you need to use this parameter even if no TLS is enabled).
If tlsHost is not passed, the script will assume that Http Application Routing is installed in the AKS. If the script has problems detecting the host name verify that the AKS has http_application_routing enabled.
You need to use Powershell and run ./Deploy-Images-Aks.ps1 with following parameters:
-name <name>Name of the deployment. Defaults totailwindtraders-aksName <name>Name of the AKS-resourceGroup <group>Name of the resource group-acrName <name>Name of the ACR-tag <tag>Docker images tag to use. Defaults tolatest-charts <charts>List of comma-separated values with charts to install. Defaults to*(all linux containers)-valuesFile <values-file>: Values file to use (defaults togvalues.yaml)-tlsEnv prod|staging|customIf SSL/TLS support has been installed, you have to use this parameter to enable https endpoints. Value must bestaging,prodorcustomand must be the same value used when you installed SSL/TLS support. If SSL/TLS is not installed, you can omit this parameter.-tlsSecretName: Name of the Kubernetes secret that stores the TLS certificate. Only used iftlsEnviscustom(ignored otherwise) and defaults tott-tls-custom.-tlsHost: Name of the domain bounded to HTTPS endpoints. That is the same value passed to `-autoscale <boolean>: Flag to activate HPA autoscaling. Defaults to$false.
This script will install all services using Helm and your custom configuration from the configuration file set by -valuesFile parameter.
The parameter charts allow for a selective installation of charts. Is a list of comma-separated values that mandates the services to deploy in the AKS. Values are:
prProducts APIcpCoupons APIpfProfiles APIppPopular products APIstStock APIicImage classifier APIctShopping cart APIlgLogin APIrrRewards Registration (not deployed with *)mgwMobile Api GatewaywgwWeb Api Gateway
So, using charts pp,st will only install the popular products and the stock api.
If you want to deploy the whole win-linux environment (with rewards registration pod) use -charts "*,rr.
To deploy the needed images on the Azure Storage account just run the /Deploy/Deploy-Pictures-Azure.ps1 script, with following parameters:
-resourceGroup <name>: Resource group where storage is created-storageName <name>: Name of the storage account
Script will create blob containers and copy the images (located in /Deploy/tailwindtraders-images folder) to the storage account.
This version allows us to deploy Windows and Linux containers. We need to create and Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) with 1.14 version. This AKS version is in preview, so you must execute the following command:
az extension add --name aks-preview
We have added an ARM template so you can automate the creation of the resources required for the backend services.
Click the following button to deploy:
For mixed (Windows and Linux containers) scenario we need to deploy Tailwind Traders Rewards. The data base deployed in Tailwind Traders Rewards is used by a WCF service of this project.
Follow the Step 2: Deploy AKS to deploy the services to AKS.
| Note: In code is important to set RegisterUsers variable true to test all the features.
The easiest way to run your backend services locally is using Compose. To run the services type docker-compose up from terminal located in ./Source folder. This will build (if needed) the Docker images and bring up all the containers.
Note: Only Linux containers are supported currently.
There are some services that connect to a CosmosDb database, hence you require to provide cosmosdb host and key using environment variables, or even better, through an .env file.
To do so, just create a file named .env in the same ./Source folder with following content pointing to your previously created in the Azure portal:
COSMOSDB_HOST=<Url of your CosmosDb>
COSMOSDB_AUTHKEY=<AuthKey of your CosmosDb>
If you are using Windows, you can run the CosmosDb emulator. If using it, you can use following .env file:
COSMOSDB_HOST=https://10.75.0.1:8081/
COSMOSDB_AUTHKEY=C2y6yDjf5/R+ob0N8A7Cgv30VRDJIWEHLM+4QDU5DE2nQ9nDuVTqobD4b8mGGyPMbIZnqyMsEcaGQy67XIw/Jw==
To run the Backend using Visual Studio, just open the Tailwind.Traders.Backend.sln, and set "Docker-compose" as startup project and run the solution. Visual Studio will use the compose file to build and run all the containers.
Tailwind Traders supports Azure Devspaces. Follow the steps in this document to deploy Tailwind traders under devspaces.
Note: There is an end-to-end Devspaces demo.
- AKS with Devspaces enabled
- Devspaces CLI installed
Note Tailwind Traders has been tested with Devspaces CLI version:
Azure Dev Spaces CLI
1.0.20190423.8
API v3.2
First you need to create the parent devspace, using Azure CLI:
> azds space select
Select a dev space or Kubernetes namespace to use as a dev space.
[1] default
Type a number or a new name:
Type the name of the parent devspace in the prompr (like dev):
Dev space 'dev' does not exist and will be created.
Select a parent dev space or Kubernetes namespace to use as a parent dev space.
[0] <none>
[1] default
Type a number:
Type 0 to make the dev devspace a root devspace.
Then the devspace is created. You can check that the devspace is created by typing:
>azds space list
Name DevSpacesEnabled
- ------- ----------------
default False
* dev True
Run Create-Secret.ps1 inside /Deploy/powershell it will create ttsa and ACR secret related to your namespace.
-resourceGroup: Name of the resource group Required for this demo.-acrName: Name of your Azure Container Registry Required for this demo.-clientId: Service Principal Id.-password: Service Principal Password.-namespace: Name of your namespace defined above, default is empty. Required for this demo for exampledev.
It will create pods needed to deploy images, ttsa and acr-secrets pods inside selected namespace.
Like deploying without devspaces you need a configuration file (a gvalues.yml like file) with all the needed configuration (connection strings, storage keys, endpoints, etc). To be used by devspaces this file has to be named gvalues.azds.yaml and has to be located in the /Deploy/helm/ folder.
Note: File
/Deploy/helm/gvalues.azds.yamlis in the.gitignore, so it is ignored by Git.
You should have to copy your configuration file to the /Deploy/helm and rename to gvalues.azds.yaml. The powershell script /Deploy/demos/devspaces/Prepare-Devspaces.ps1 can do it for you:
.\Prepare-Devspaces.ps1 -file \Path\To\My\Config\File.yaml
Example (inside devspaces folder run):
.\prepare-devspaces.ps1 -file ..\..\helm\__values\configFile.yaml
The script just copies the file passed in to the /Deploy/helm folder with the right name. If file already exists is overwritted.
Once you have a valid configuration file, you need to deploy the APIs to the devspaces. You need to go to the root source folder of each API and type:
azds up -v -d
(The root source folder of each API is the one that has the azds.yaml file, like /Source/Services/Tailwind.Traders.Login.Api/ or /Source/ApiGWs/Tailwind.Traders.WebBff/).
APIs that have devspaces enabled are:
- MobileBFF (
/Source/ApiGWs/Tailwind.Traders.Bff) - a Net Core API - WebBFF (
/Source/ApiGWs/Tailwind.Traders.WebBff) - a Net Core API - Cart API (
/Source/Services/Tailwind.Traders.Cart.Api) - a Node.js API - Coupons API (
/Source/Services/Tailwind.Traders.Coupon.Api) - a Node.js API - Login API (
/Source/Services/Tailwind.Traders.Login.Api) - a Net Core API - Popular Products API (
/Source/Services/Tailwind.Traders.PopularProduct.Api) - a Golang API - Profiles API (
/Source/Services/Tailwind.Traders.Profile.Api) - a Net Core API - Stock API (
/Source/Services/Tailwind.Traders.Stock.Api) - a Java API
Once you have all them deployed in Dev Spaces you can check it using azds list-up:
> azds list-up
Name DevSpace Type Updated Status
--------------- -------- ------- ------- -------
cart dev Service 8m ago Running
coupons dev Service 7m ago Running
login dev Service 7m ago Running
mobilebff dev Service 15m ago Running
popularproducts dev Service 5m ago Running
product dev Service 3m ago Running
profile dev Service 2m ago Running
stock dev Service 1m ago Running
webbff dev Service 9m ago Running
Each API has its own ingress created. The command azds list-uris will display all URIs for every service:
> azds list-uris
Uri Status
---------------------------------------------------------------------- ---------
http://dev.tt.xxxxxxxxxs.weu.azds.io/cart-api Available
http://dev.tt.xxxxxxxxxs.weu.azds.io/coupons-api Available
http://dev.tt.xxxxxxxxxs.weu.azds.io/login-api Available
http://dev.tt.xxxxxxxxxs.weu.azds.io/mobilebff Available
http://dev.tt.xxxxxxxxxs.weu.azds.io/popular-products-api Available
http://dev.tt.xxxxxxxxxs.weu.azds.io/product-api Available
http://dev.tt.xxxxxxxxxs.weu.azds.io/profile-api Available
http://dev.tt.xxxxxxxxxs.weu.azds.io/stock-api Available
http://dev.tt.xxxxxxxxxs.weu.azds.io/webbff Available
All pods run in the namespace selected as a Dev Space (dev in our case). Using kubectl get pods will show all running pods:
> kubectl get pods -n dev
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
azds-14223a-dev-tt-popularproducts-79667b6684-75vd8 2/2 Running 0 6m42s
azds-212ef9-dev-tt-products-59f77b8bb6-rbql9 2/2 Running 0 4m2s
azds-26b908-dev-tt-profile-7f97b8d5cb-lwq2k 2/2 Running 0 2m57s
azds-3128d4-dev-tt-login-5b976cf44b-zjkp7 2/2 Running 0 7m59s
azds-312ebd-dev-tt-stock-7b6fb8b87f-wvq62 2/2 Running 0 114s
azds-6ab0d6-dev-tt-cart-574bbf95fb-rvshq 2/2 Running 0 9m17s
azds-70a6e6-dev-tt-coupons-775d47fcf7-rcfq9 2/2 Running 0 8m46s
azds-c16cb7-dev-tt-webbff-cc899c886-sb9bx 2/2 Running 0 10m
azds-c9f588-dev-tt-mobilebff-776cc9f45f-drgdz 2/2 Running 0 13m
Congratulations! You have deployed all APIs in a parent Dev Space
To deploy an API to a child Dev Space just create the child Dev Space (using azds space select), selecting dev as parent devspace. Then deploy again (with azds up -d -v) one of the APIs.
Here Alice is one engineer that need to fix a bug in the Stock API, so first she creates a child devspace for her to use:
> azds space select
Select a dev space or Kubernetes namespace to use as a dev space.
[1] default
[2] dev
Type a number or a new name: alice
Dev space 'alice' does not exist and will be created.
Select a parent dev space or Kubernetes namespace to use as a parent dev space.
[0] <none>
[1] default
[2] dev
Type a number: 2
Creating and selecting dev space 'dev/alice'...2s
An azds space list verifies that she is using the Dev Space alice:
> azds space list
Name DevSpacesEnabled
- --------- ----------------
default False
dev True
* dev/alice True
Fist she must deploy the /Deploy/helm/ttsa.yaml file using kubectl apply. If she fails doing that, the Devspaces deploy will be stuck at "Waiting for container image build..." phase.
She can now deploy her version of Stock API, just going to /Source/Services/Tailwind.Traders.Stock.Api and use azds up -d -v. Once service is deployed a azds list-up shows that, for Alice, all APIs runs on dev but Stock API:
> azds list-up
Name DevSpace Type Updated Status
--------------- -------- ------- ------- -------
cart dev Service 16m ago Running
coupons dev Service 16m ago Running
login dev Service 15m ago Running
mobilebff dev Service 23m ago Running
popularproducts dev Service 13m ago Running
product dev Service 11m ago Running
profile dev Service 10m ago Running
stock alice Service 1m ago Running
webbff dev Service 17m ago Running
If Alice types azds list-uris she will see the URIs for her namespace. These are the uris she has to use:
> azds list-uris
Uri Status
------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ---------
http://alice.s.dev.tt.xxxxxxxxxs.weu.azds.io/cart-api Available
http://alice.s.dev.tt.xxxxxxxxxs.weu.azds.io/coupons-api Available
http://alice.s.dev.tt.xxxxxxxxxs.weu.azds.io/login-api Available
http://alice.s.dev.tt.xxxxxxxxxs.weu.azds.io/mobilebff Available
http://alice.s.dev.tt.xxxxxxxxxs.weu.azds.io/popular-products-api Available
http://alice.s.dev.tt.xxxxxxxxxs.weu.azds.io/product-api Available
http://alice.s.dev.tt.xxxxxxxxxs.weu.azds.io/profile-api Available
http://alice.s.dev.tt.xxxxxxxxxs.weu.azds.io/stock-api Available
http://alice.s.dev.tt.xxxxxxxxxs.weu.azds.io/webbff Available
Next step is deploy the website in the devspaces too.
Note: The web must be deployed in the same AKS that Backend is deployed. Deploy 1st the backend and then the Website.
To test the image classiffier service, you can use the curl to get the suggested products.
The modifier "-v" is for verbose mode.
-
To use the web backend for frontend gateway:
- curl YOUR_URL_OF_BACKEND/webbff/V1/products/imageclassifier -X POST -F "file=@C:\YOUR_PATH_AND_FILENAME_OF_PHOTO_TO_SEARCH" -v
-
To call directly to image classifier service:
- curl YOUR_URL_OF_BACKEND/image-classifier-api/V1/imageclassifier -X POST -F "file=@C:\YOUR_PATH_AND_FILENAME_OF_PHOTO_TO_SEARCH.jpg" -v
The response should be similar to:
- [{"id":57,"name":"Yellow hard hat with tool bag pack","price":46.0,"imageUrl":"YOUR_URL_OF_STORAGE/images/product-list/59890052.jpg"}]* Connection #0 to host localhost left intact
You have sample images to test this feature in:
This project welcomes contributions and suggestions. Most contributions require you to agree to a Contributor License Agreement (CLA) declaring that you have the right to, and actually do, grant us the rights to use your contribution. For details, visit https://cla.microsoft.com.
When you submit a pull request, a CLA-bot will automatically determine whether you need to provide a CLA and decorate the PR appropriately (e.g., label, comment). Simply follow the instructions provided by the bot. You will only need to do this once across all repos using our CLA.
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact opencode@microsoft.com with any additional questions or comments.