FloraIberica R package facilitates access to taxonomic and
distribution data for the c. 6500 vascular plants present in the Iberian
Peninsula and Balearic Islands, based on the AFLIBER
database. This atlas provides the
distribution of each taxon in a 10 x 10 km UTM grid.
remotes::install_github("Pakillo/FloraIberica")library(FloraIberica)is_present(genus = "Laurus", species = c("nobilis", "azorica"))
#> Laurus nobilis Laurus azorica
#> TRUE FALSEis_endemic(genus = "Aconitum", species = "napellus",
subspecies = c("castellanum", "lusitanicum"))
#> Aconitum napellus castellanum Aconitum napellus lusitanicum
#> TRUE FALSEReturns sf or dataframe with the coordinates of the centre of 10 x 10 km UTM grid cells where taxa are present:
get_distribution("Abies", "pinsapo")
#> Simple feature collection with 30 features and 4 fields
#> Geometry type: POINT
#> Dimension: XY
#> Bounding box: xmin: -5.522 ymin: 36.438 xmax: -4.401 ymax: 36.991
#> Geodetic CRS: WGS 84
#> First 10 features:
#> Genus Species Subspecies UTM.cell geometry
#> 213 Abies pinsapo <NA> 30STF76 POINT (-5.519 36.704)
#> 214 Abies pinsapo <NA> 30STF77 POINT (-5.522 36.794)
#> 215 Abies pinsapo <NA> 30STF85 POINT (-5.404 36.616)
#> 216 Abies pinsapo <NA> 30STF86 POINT (-5.407 36.706)
#> 217 Abies pinsapo <NA> 30STF87 POINT (-5.41 36.796)
#> 218 Abies pinsapo <NA> 30STF88 POINT (-5.413 36.887)
#> 219 Abies pinsapo <NA> 30STF93 POINT (-5.287 36.438)
#> 220 Abies pinsapo <NA> 30STF95 POINT (-5.292 36.619)
#> 221 Abies pinsapo <NA> 30STF97 POINT (-5.298 36.799)
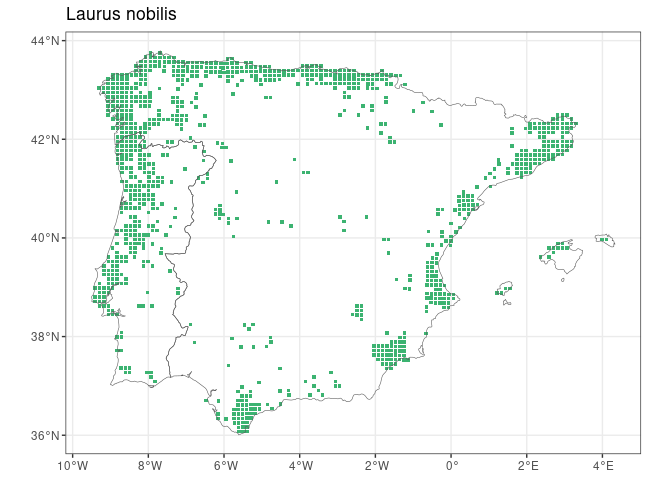
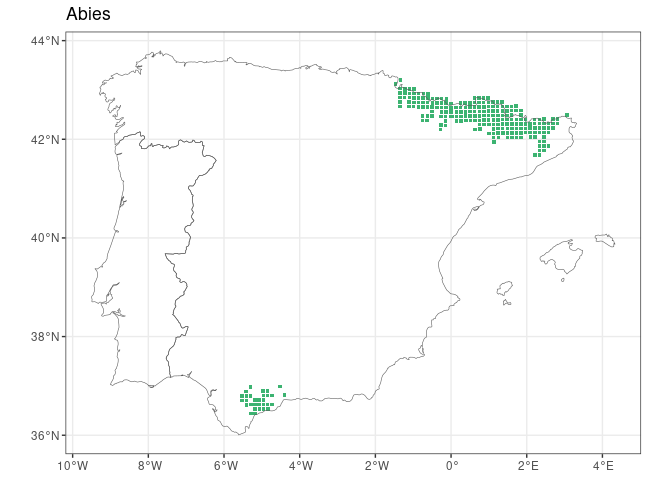
#> 222 Abies pinsapo <NA> 30STF99 POINT (-5.303 36.979)map_distribution(genus = "Laurus", species = "nobilis", size = 0.9)Distribution of Iberian Abies:
abies <- get_distribution("Abies")
map_distribution(abies)You can also get one map per taxon (species):
map_distribution(abies, facet = TRUE, ncol = 1)Or collapse all presences of the entire genus:
map_distribution(abies, taxo.level = "genus", size = 0.9)Another example with Iberian pines:
library(ggplot2)
map_distribution(genus = "Pinus", facet = TRUE, ncol = 2) +
theme(axis.text = element_text(size = 6))If you want to know the plants near a given site, just pass the coordinates to get_checklist:
site <- c(-5, 40)
head(get_checklist(site))
#> Genus Species Subspecies
#> 1 Acer monspessulanum monspessulanum
#> 2 Adenocarpus aureus <NA>
#> 4 Adenocarpus complicatus <NA>
#> 5 Allium scorzonerifolium <NA>
#> 6 Alnus glutinosa <NA>
#> 7 Alyssum fastigiatum <NA>The site can be a polygon, so you can easily obtain a list of the plants present within a given area (e.g. town, province, natural reserve):
cadiz <- mapSpain::esp_get_prov_siane("Cadiz", epsg = "4326")
head(get_checklist(cadiz))
#> Genus Species Subspecies
#> 1 Abies pinsapo <NA>
#> 11 Acer monspessulanum monspessulanum
#> 21 Acer opalus granatense
#> 22 Aceras anthropophorum <NA>
#> 33 Achillea ageratum <NA>
#> 57 Achillea odorata <NA>You can also obtain an sf object rather than a dataframe, so you know
where each plant occurs within or near that polygon (with a resolution
of 10x10 km inherited from the AFLIBER database):
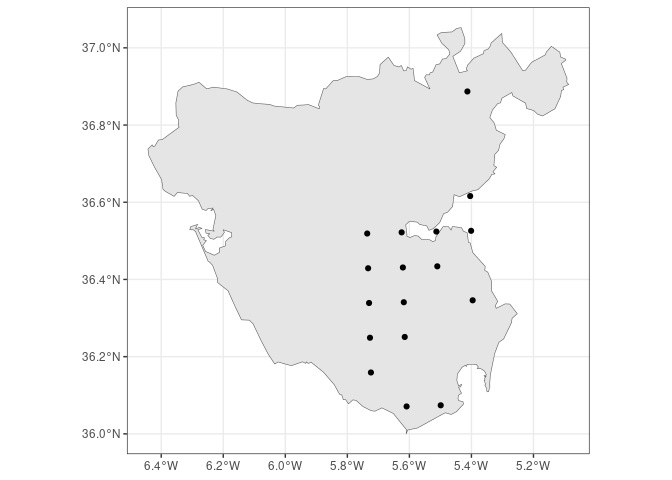
cadiz.qpyr <- get_checklist(cadiz, sf = TRUE) |>
dplyr::filter(Genus == "Quercus", Species == "pyrenaica")
ggplot() +
geom_sf(data = cadiz) +
geom_sf(data = cadiz.qpyr) +
theme_bw()citation("FloraIberica")
If you use FloraIberica, please cite both the data source and the
package as:
Ramos-Gutiérrez I., Lima H., Pajarón S., Romero-Zarco C., Sáez L.,
Pataro L., Molina-Venegas R., Rodríguez M. Á. & Moreno-Saiz J. C.
(2021). Atlas of the vascular flora of the Iberian Peninsula
biodiversity hotspot (AFLIBER). Global Ecology and Biogeography, 30,
1951– 1957. https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.13363
Rodríguez-Sánchez Francisco. 2023. FloraIberica: Taxonomic and
distribution data for the vascular plants of the Iberian Peninsula
and Balearic Islands. https://pakillo.github.io/FloraIberica
To see these entries in BibTeX format, use 'print(<citation>,
bibtex=TRUE)', 'toBibtex(.)', or set
'options(citation.bibtex.max=999)'.The development of this software has been funded by Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional (FEDER) and Consejería de Transformación Económica, Industria, Conocimiento y Universidades of Junta de Andalucía (proyecto US-1381388 led by Francisco Rodríguez Sánchez, Universidad de Sevilla).