- by Christian Brandt & Mike Marquet
- this tool is under active development,feel free to report issues and add suggestions
- use a release candidate for a stable experience via
-re.g.-r v0.8.0- these are extensively tested release versions of WtP
- releases of WtP are here
What the Phage: A scalable workflow for the identification and analysis of phage sequences
M. Marquet, M. Hölzer, M. W. Pletz, A. Viehweger, O. Makarewicz, R. Ehricht, C. Brandt
- What is this Repo?
- Installation
- Execution / Examples / Help
- Results / Examples
- Under the hood
- Included bioinformatic tools
- WtP is a scalable and easy-to-use workflow for phage identification and analysis. Our tool currently combines 9 established phage identification tools
- An attempt to streamline the usage of various phage identification and prediction tools
- The main focus is stability and data filtering/analysis for the user
- The tool is intended for fasta and fastq reads to identify phages in contigs/reads
- a proper Prophage detection is not implemented (yet) - but a handful of tools report them - so they are mostly identified
- "None informaticians / newcomer to bioinformatics" approach using ubuntu [admin rights required]
- Copy and paste for local, docker usage
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt install -y default-jre
curl -s https://get.nextflow.io | bash
sudo mv nextflow /usr/bin/
sudo apt-get install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
sudo usermod -a -G docker $USER- Restart your computer and go
- Nextflow installation + java runtime
- move or add the nextflow executable to a bin path
- git (should be already installed)
- wget (should be already installed)
- tar (should be already installed)
- Choose one:
- Docker installation
- add docker to your User group via
sudo usermod -a -G docker $USER- Singularity installation
- Restart your computer
- Try out the installation by entering the following (analyses 8 samples ~ 10h runtime)
# for docker (local use)
nextflow run replikation/What_the_Phage -r v0.8.0 --cores 8 -profile test,local,docker
# for singularity (slurm use)
nextflow run replikation/What_the_Phage -r v0.8.0 --cores 8 -profile test,slurm,singularitynextflow run replikation/What_the_Phage -r v0.8.0 --help- Just give me the command god dammit.....
nextflow run \ # calling the workflow
replikation/What_the_Phage \ # WtP Git-Repo
--fasta /path/to/file.fa \ # provide a fasta-file as input
--cores 8 \ # number of cores you want to use
-profile local,docker # choose the environment:local and docker
-r v0.8.0 # WtP release version- e.g.:
nextflow run replikation/What_the_Phage \
--fasta '/path/to/*.fasta' \
-profile local,docker \
--cores 20 \
-r v0.8.0 \
--anno \
--dv \
--vf \
--ma- The order of flags does not matter
- Input examples:
- wildcards need single quotes around the path (
')
- wildcards need single quotes around the path (
--fasta /path/to/phage-assembly.fa # path to your fasta-file
--fasta '/path/to/*.fa' # path to all .fa files in a dir
--fastq /path/to/phage-read.fastq # path to your fastq-file
--fastq '/path/to/*.fastq' # path to all .fastq files in a dir- Turn on/off tools (check
--helpfor more)
--dv # deactivates deepvirfinder
--ma # deactivates marvel
--mp # deactivates metaphinder
--pp # deactivates PPRmeta
--sm # deactivates sourmash
--vb # deactivates vibrant
--vf # deactivates virfinder
--vn # deactivates virnet
--vs # deactivates virsorter
--identify # only phage identification, skips analysis
--annotate # only annotation, skips phage identification- min size of contigs for identification
--filter # min contig size [bp] to analyse- Choose the environment: local, slurm, lsf or ebi
- Choose the engine: docker or singularity
- examples:
-profile local,docker
-profile local,singularity
-profile lsf,docker- A release candidate is a released version of WtP which ensures proper functionality
- version control ensures reproducibility as each tools version is also "locked" within the release candidate
- databases have no automatic version control (they are downloaded from the source)
- if you need version control for databases, just make a copy of the database dir after download
- you can specify the database dir via the
--databaseflag (see below)- WtP only downloads a database if it's missing, it is not "auto-updating" them
- add this flag to your command and a specific release is used instead
-r v0.8.0- WtP handles everything by default
- If you need to change paths use the following commands
- It's useful to specify
--workdirto your current working dir if/tmp(default) has limited space
- It's useful to specify
--workdir /path/to/dir # defines the path where nextflow writes temporary files, default: '/tmp/nextflow-phage-$USER'
--database /path/to/dir # specify download location of databases, default './nextflow-autodownload-databases'
--cachedir /path/to/dir # defines the path where singularity images are cached, default './singularity-images'
--output results # path of the outdir, default './results'--setupskips analysis and just downloads all databases and containers- Needs roughly 30 GB storage for databases, excluding programs
nextflow run replikation/What_the_Phage --setup -r v0.8.0- you can change the database download location via (--database)
- make sure that you specify the database location when executing WtP, if you change the default path
- singularity images sometimes fail during building, just try to re-execute
--setup- WtP attempts to build images up to 3 times, image building is individually skipped if present
Figure 1: This chart (UpSetR plot) quantifies the result-intersections of the phage identification tools, similar to a Venn diagram. The amount of positive phage-sequences identified by each tool is represented on the left barplot in blue. The dot plot shows via line connection(s) which of the tools identified the exact same positive phage sequences. The amount of these shared matches is quantified as a barplot above each corresponding dot pattern.
See Link: The graphical output of the annotation shows an overview of the individual loci of the predicted ORFs and the corresponding genes in the fasta sequences identified as phages. For a better visibility, we have chosen 4 categories tail, capsid, baseplate, and other. This output can be used to verify the identified sequences (if the predicted sequences make sense or not). The annotation results are additionally plotted in an interactive HTML-file and are available as a file for further analysis.
- check CheckV for a detailed explanation
| contig_id | contig_length | genome_copies | gene_count | viral_genes | host_genes | checkv_quality | miuvig_quality | completeness | completeness_method | contamination | provirus |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pos_phage_0 | 146647 | 1 | 243 | 141 | 1 | High-quality | High-quality | 97.03 | AAI-based | 0 | No |
| pos_phage_1 | 58871 | 1 | 97 | 21 | 0 | High-quality | High-quality | 100 | AAI-based | 0 | No |
| pos_phage_2 | 58560 | 1 | 95 | 20 | 0 | High-quality | High-quality | 99.47 | AAI-based | 0 | No |
| pos_phage_3 | 59443 | 1 | 90 | 52 | 0 | High-quality | High-quality | 100 | AAI-based | 0 | No |
| pos_phage_4 | 51290 | 1 | 74 | 44 | 0 | High-quality | High-quality | 100 | AAI-based | 0 | No |
| pos_phage_5 | 43293 | 1 | 69 | 55 | 0 | High-quality | High-quality | 100 | AAI-based | 0 | No |
| pos_phage_6 | 43851 | 1 | 53 | 30 | 0 | High-quality | High-quality | 98.71 | AAI-based | 0 | No |
| pos_phage_7 | 44262 | 1 | 54 | 31 | 0 | High-quality | High-quality | 99.64 | AAI-based | 0 | No |
| pos_phage_8 | 41865 | 1 | 60 | 57 | 0 | High-quality | High-quality | 97.29 | AAI-based | 0 | No |
| pos_phage_9 | 221908 | 1 | 310 | 48 | 9 | High-quality | High-quality | 100 | AAI-based | 0 | No |
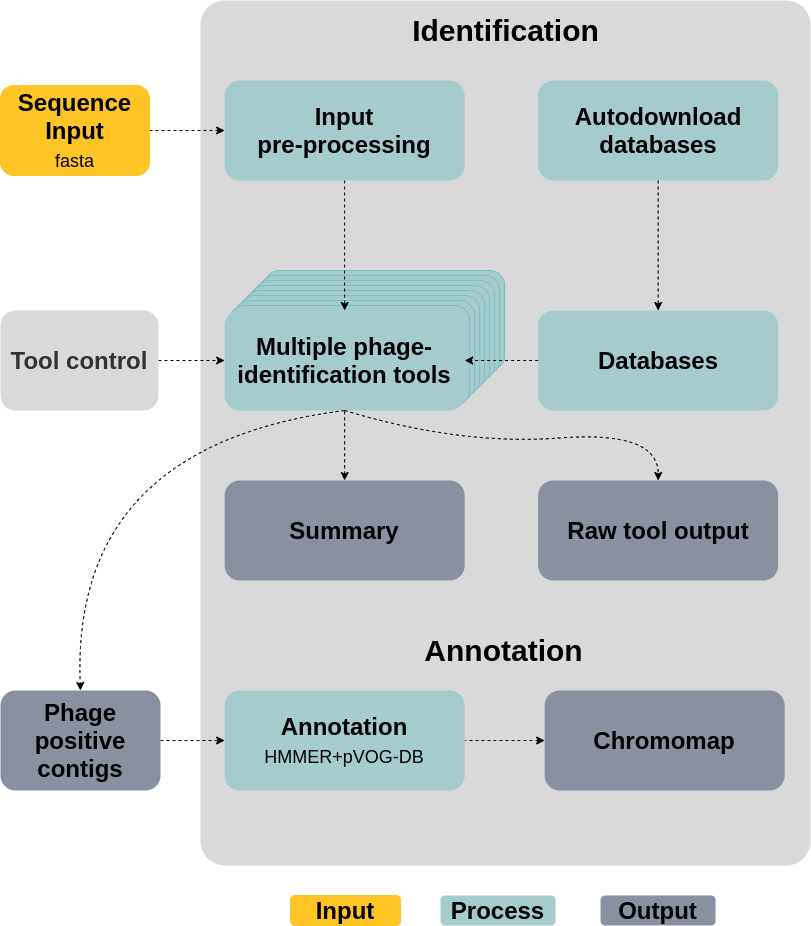
Figure 3: This plot shows a simplified dag-chart of WtP for better understanding of what's going on behind the curtain.
- Please cite the following tools