An open source bipedal robot control framework, based on non-linear MPC and WBC, tailered for EC-hunter80-v01 bipedal robot. For more information refer to the project's Page
# Clone
mkdir -p <catkin_ws_name>/src
cd <catkin_ws_name>/src
git clone https://github.com/bridgedp/hunter_bipedal_control.git
# Build
cd <catkin_ws_name>
catkin init
catkin config -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RelWithDebInfo
catkin build- Run the simulation and load the controller:
roslaunch legged_controllers one_start_gazebo.launch- load the controller
roslaunch legged_controllers one_start_real.launchNotes: After the user starts the simulation, the robot falls down in Gazebo. The user needs to press Ctrl+Shift+R to make the robot stand up. Then, dynamic parameter adjustment is used in the code, and the user needs to set kpposition=100, kdposition=3.
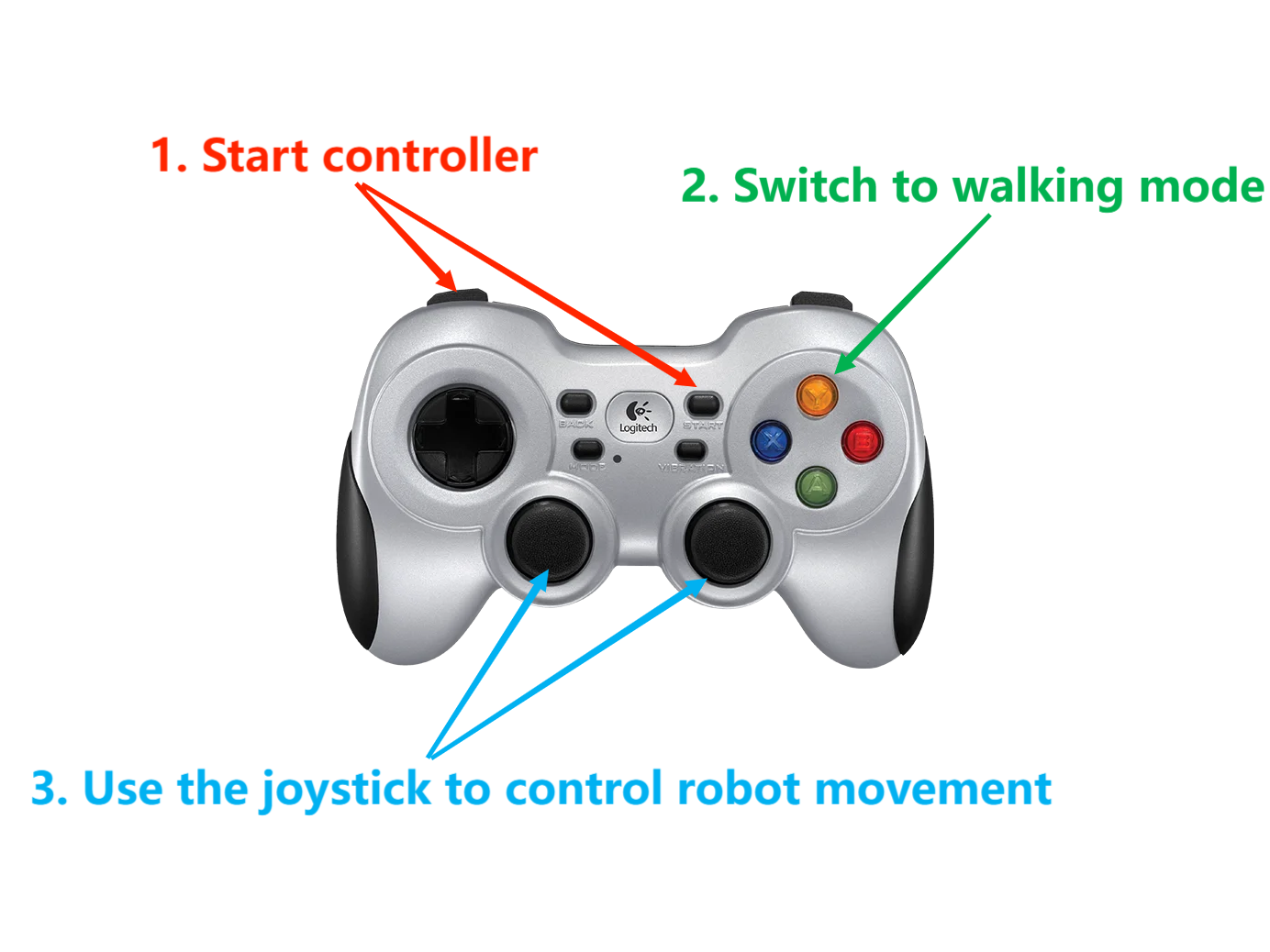
- Start controller
L1 + start
- Switch to walking mode
Y
- Use the joystick to control robot movement
The following is a schematic diagram of the handle operation:
Compilation: Only compile the following packages (and their dependencies), there's no need to compile the entire OCS2.
catkin build legged_controllers legged_hunter_description legged_gazeboExecution: If you don't have a gamepad, you need to send the startup commands in order.
First, set kp_position=100 in rqt and reset the simulation by pressing Ctrl+Shift+R to make the robot stand up. Then, send the following commands:
rostopic pub --once /load_controller std_msgs/Float32 "data: 1.23"
rostopic pub --once /set_walk std_msgs/Float32 "data: 1.23"Before /load_controller, there needs to be a node continuously sending /cmd_vel (10Hz is normal), and it should continue sending during the simulation. Once /cmd_vel stops, the robot may fall.
As a example, here's a Python script that continuously sends /cmd_vel and allows keyboard control. You should start the script before /load_controller.
#!/usr/bin/env python
import rospy
from geometry_msgs.msg import Twist
from pynput import keyboard
import threading
class KeyboardController:
def __init__(self):
self.publisher = rospy.Publisher('/cmd_vel', Twist, queue_size=1)
self.twist_msg = Twist()
self.rate = rospy.Rate(10)
def on_press(self, key):
try:
if key.char == 'q':
rospy.signal_shutdown("Quit")
else:
if key.char == 'w':
self.twist_msg.linear.x = 0.35
elif key.char == 's':
self.twist_msg.linear.x = -0.35
else:
self.twist_msg.linear.x = 0.0
if key.char == 'a':
self.twist_msg.angular.z = 0.35
elif key.char == 'd':
self.twist_msg.angular.z = -0.35
else:
self.twist_msg.angular.z = 0.0
except AttributeError:
pass
def on_release(self, key):
self.twist_msg.linear.x = 0.0
self.twist_msg.angular.z = 0.0
def ros_publish():
while not rospy.is_shutdown():
controller.publisher.publish(controller.twist_msg)
controller.rate.sleep()
if __name__ == '__main__':
rospy.init_node("keyboard_control")
controller = KeyboardController()
thread = threading.Thread(target=ros_publish)
thread.start()
listener = keyboard.Listener(on_press=controller.on_press, on_release=controller.on_release)
listener.start()
while not rospy.is_shutdown():
pass
listener.stop()
listener.join()
thread.join()