BoT-SORT: Robust Associations Multi-Pedestrian Tracking
Nir Aharon, Roy Orfaig, Ben-Zion Bobrovsky
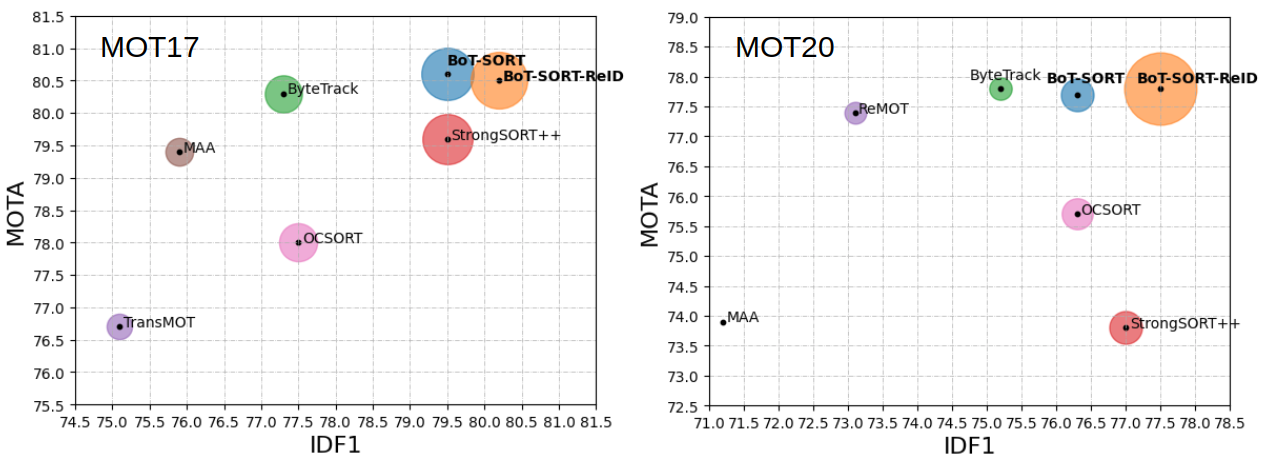
The goal of multi-object tracking (MOT) is detecting and tracking all the objects in a scene, while keeping a unique identifier for each object. In this paper, we present a new robust state-of-the-art tracker, which can combine the advantages of motion and appearance information, along with camera-motion compensation, and a more accurate Kalman filter state vector. Our new trackers BoT-SORT, and BoT-SORT-ReID rank first in the datasets of MOTChallenge [29, 11] on both MOT17 and MOT20 test sets, in terms of all the main MOT metrics: MOTA, IDF1, and HOTA. For MOT17: 80.5 MOTA, 80.2 IDF1, and 65.0 HOTA are achieved.
MOT20-06.mp4
MOT17-14.mp4
| Tracker | MOTA | IDF1 | HOTA |
|---|---|---|---|
| BoT-SORT | 80.6 | 79.5 | 64.6 |
| BoT-SORT-ReID | 80.5 | 80.2 | 65.0 |
| Tracker | MOTA | IDF1 | HOTA |
|---|---|---|---|
| BoT-SORT | 77.7 | 76.3 | 62.6 |
| BoT-SORT-ReID | 77.8 | 77.5 | 63.3 |
The code was tested on Ubuntu 20.04
BoT-SORT code is based on ByteTrack and FastReID.
Visit their installation guides for more setup options.
Step 1. Create Conda environment and install pytorch.
conda create -n botsort_env python=3.7
conda activate botsort_envStep 2. Install torch and matched torchvision from pytorch.org.
The code was tested using torch 1.11.0+cu113 and torchvision==0.12.0
Step 3. Install BoT-SORT.
git clone https://github.com/NirAharon/BoT-SORT.git
cd BoT-SORT
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
python3 setup.py developStep 4. Install pycocotools.
pip3 install cython; pip3 install 'git+https://github.com/cocodataset/cocoapi.git#subdirectory=PythonAPI'Step 5. Others
# Cython-bbox
pip3 install cython_bbox
# faiss cpu / gpu
pip3 install faiss-cpu
pip3 install faiss-gpuDownload MOT17 and MOT20 from the official website. And put them in the following structure:
<dataets_dir>
│
├── MOT17
│ ├── train
│ └── test
│
└── MOT20
├── train
└── test
For training the ReID, detection patches must be generated as follows:
cd <BoT-SORT_dir>
# For MOT17
python3 fast_reid/datasets/generate_mot_patches.py --data_path <dataets_dir> --mot 17
# For MOT20
python3 fast_reid/datasets/generate_mot_patches.py --data_path <dataets_dir> --mot 20Link dataset to FastReID export FASTREID_DATASETS=<BoT-SORT_dir>/fast_reid/datasets. If left unset, the default is fast_reid/datasets
Download and store the trained models in 'pretrained' folder as follow:
<BoT-SORT_dir>/pretrained
-
We used the publicly available ByteTrack model zoo trained on MOT17, MOT20 and ablation study for YOLOX object detection.
-
Ours trained ReID models can be downloaded from MOT17-SBS-S50, MOT20-SBS-S50.
After generating MOT ReID dataset as described in the 'Data Preparation' section.
cd <BoT-SORT_dir>
# For training MOT17
python3 fast_reid/tools/train_net.py --config-file ./fast_reid/configs/MOT17/sbs_S50.yml MODEL.DEVICE "cuda:0"
# For training MOT20
python3 fast_reid/tools/train_net.py --config-file ./fast_reid/configs/MOT20/sbs_S50.yml MODEL.DEVICE "cuda:0"Refer to FastReID repository for addition explanations and options.
By submitting the txt files produced in this part to MOTChallenge website and you can get the same results as in the paper.
Tuning the tracking parameters carefully could lead to higher performance. In the paper we apply ByteTrack's calibration.
- Test on MOT17
cd <BoT-SORT_dir>
python3 tools/track.py <dataets_dir/MOT17> --default-parameters --with-reid --benchmark "MOT17" --eval "test" --fp16 --fuse
python3 tools/interpolation.py --txt_path <path_to_track_result>- Test on MOT20
cd <BoT-SORT_dir>
python3 tools/track.py <dataets_dir/MOT20> --default-parameters --with-reid --benchmark "MOT20" --eval "test" --fp16 --fuse
python3 tools/interpolation.py --txt_path <path_to_track_result>- Evaluation on MOT17 validation set (the second half of the train set)
cd <BoT-SORT_dir>
# BoT-SORT
python3 tools/track.py <dataets_dir/MOT17> --default-parameters --benchmark "MOT17" --eval "val" --fp16 --fuse
# BoT-SORT-ReID
python3 tools/track.py <dataets_dir/MOT17> --default-parameters --with-reid --benchmark "MOT17" --eval "val" --fp16 --fuse- Other experiments
Other parameters can be used without passing --default-parameters flag.
For evaluating the train and validation sets we recommend using the official MOTChallenge evaluation code from TrackEval.
# For all the available tracking parameters, see:
python3 tools/track.py -h cd <BoT-SORT_dir>
python3 tools/demo.py video --path <path_to_video> -f yolox/exps/example/mot/yolox_x_mix_det.py -c pretrained/bytetrack_x_mot17.pth.tar --with-reid --fuse-score --fp16 --fuse --save_resultOur camera motion compensation module is based on the OpenCV contrib C++ version of VideoStab Global Motion Estimation,
which currently does not have a Python version.
Motion files can be generated using the C++ project called 'VideoCameraCorrection' in the GMC folder.
The generated files can be used from the tracker.
In addition, python-based motion estimation techniques are available and can be chosen by passing
'--cmc-method' <files | orb | ecc> to demo.py or track.py.
- Add multi-class support.
- Create OpenCV VideoStab GMC python binding or write Python version.
- Add deployment code.
@article{aharon2022bot,
title={BoT-SORT: Robust Associations Multi-Pedestrian Tracking},
author={Aharon, Nir and Orfaig, Roy and Bobrovsky, Ben-Zion},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.14651},
year={2022}
}
A large part of the codes, ideas and results are borrowed from ByteTrack, StorngSORT, FastReID and YOLOX. Thanks for their excellent work!