The ros2_control implementation for any kind of ROBOTIS Dynamixel robots.
dynamixel_hardware: theSystemInterfaceimplementation for the multiple ROBOTIS Dynamixel servos.open_manipulator_x_description: the reference implementation of theros2_controlrobot using ROBOTIS OpenManipulator-X.
The dynamixel_hardware package is hopefully compatible any configuration of ROBOTIS Dynamixel servos thanks to the ros2_control's flexible architecture.
First install ROS 2 Humble on Ubuntu 22.04. Then follow the instruction below.
source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bash
sudo apt update
sudo apt install ros-humble-plotjuggler-ros
pip3 install openpyxl
pip3 install roboticstoolbox-python==0.11.0
pip3 install spatialgeometry==0.2.0 && pip3 install spatialmath-python==0.11
pip3 install colored==1.4.2
mkdir -p ~/ros/humble && cd ~/ros/humble
git clone https://github.com/SamKaiYang/dynamixel_hardware_control.git src
vcs import src < src/dynamixel_control.repos
rosdep update
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src -r -y
colcon build --symlink-install --cmake-args -DCMAKE_EXPORT_COMPILE_COMMANDS=ON
. install/setup.bashH54-200-S500-R Goal Torque unit 16.11328 [mA] H54-100-S500-R Goal Torque unit 16.11328 [mA] H42-20-S300-R Goal Torque unit 4.02832 [mA]
float DynamixelWorkbench::convertValue2Current(uint8_t id, int16_t value)
{
float current = 0;
float CURRENT_UNIT = 2.69f; //Unit : mA, Ref : http://emanual.robotis.com/docs/en/dxl/x/xm430-w350/#goal-current102
model_info = getModelInfo(id);
if (model_info == NULL) return false;
CURRENT_UNIT = 16.11328f;
// current = (int16_t)value * CURRENT_UNIT;
// return current;
// if (getProtocolVersion() == 1.0f)
// {
// current = (int16_t)value * CURRENT_UNIT;
// return current;
// }
// else if (getProtocolVersion() == 2.0f)
// {
// if (strncmp(getModelName(id), "PRO-L", strlen("PRO-L")) == 0 ||
// strncmp(getModelName(id), "PRO-M", strlen("PRO-M")) == 0 ||
// strncmp(getModelName(id), "PRO-H", strlen("PRO-H")) == 0)
// {
// CURRENT_UNIT = 16.11328f;
// current = (int16_t)value * CURRENT_UNIT;
// return current;
// }
// else if (strncmp(getModelName(id), "PRO-PLUS", strlen("PRO-PLUS")) == 0)
// {
// CURRENT_UNIT = 1.0f;
// current = (int16_t)value * CURRENT_UNIT;
// return current;
// }
// else
// {
// CURRENT_UNIT = 16.11328f;
// current = (int16_t)value * CURRENT_UNIT;
// return current;
// }
// }
current = (int16_t)value * CURRENT_UNIT;
return current;
}
float DynamixelWorkbench::convertValue2Current(int16_t value)
{
float current = 0;
const float CURRENT_UNIT = 16.11328f; //Unit : mA, Ref : http://emanual.robotis.com/docs/en/dxl/x/xm430-w350/#goal-current102
// CURRENT_UNIT = 16.11328f;
current = (int16_t)value * CURRENT_UNIT;
return current;
}
MoveIt:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tgAdRwSPZqU Trajectory:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KQFqeoA4rBA&feature=youtu.be
ros2 launch single_arm_6dof_moveit_config demo.launch.py
# open terminal 1
ros2 launch single_arm_6dof_description single_arm_6dof.launch.py
# open terminal 2
ros2 launch my_package traj_action.launch.py
Update the usb_port, baud_rate, and joint_ids parameters on open_manipulator_x_description/urdf/open_manipulator_x.ros2_control.xacro to correctly communicate with Dynamixel motors.
The use_dummy parameter is required if you don't have a real OpenManipulator-X.
Note that joint_ids parameters must be splited by ,.
<hardware>
<plugin>dynamixel_hardware/DynamixelHardware</plugin>
<param name="usb_port">/dev/ttyUSB0</param>
<param name="baud_rate">1000000</param>
<!-- <param name="use_dummy">true</param> -->
</hardware>- Terminal 1
Launch the ros2_control manager for the OpenManipulator-X.
$ ros2 launch open_manipulator_x_description open_manipulator_x.launch.py- Terminal 2
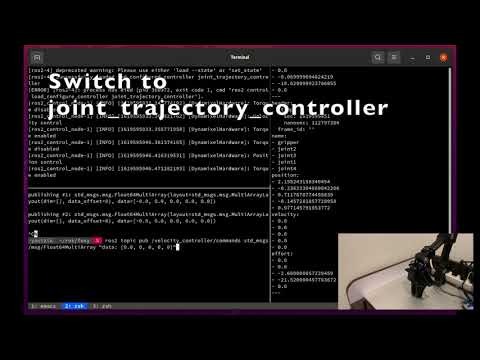
Start the joint_trajectory_controller and send a /joint_trajectory_controller/follow_joint_trajectory goal to move the OpenManipulator-X.
$ ros2 control switch_controllers --activate joint_state_broadcaster --activate joint_trajectory_controller --deactivate velocity_controller
$ ros2 action send_goal /joint_trajectory_controller/follow_joint_trajectory control_msgs/action/FollowJointTrajectory -f "{
trajectory: {
joint_names: [joint1, joint2, joint3, joint4, joint5, joint6],
points: [
{ positions: [0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1], time_from_start: { sec: 2 } },
{ positions: [-0.1, -0.1, -0.1, -0.1, -0.1, -0.1], time_from_start: { sec: 4 } },
{ positions: [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], time_from_start: { sec: 6 } }
]
}
}"If you would like to use the velocity control instead, switch to the velocity_controller and publish a /velocity_controller/commands message to move the OpenManipulator-X.
$ ros2 control switch_controllers --activate joint_state_broadcaster --deactivate joint_trajectory_controller --activate velocity_controller
$ ros2 topic pub /velocity_controller/commands std_msgs/msg/Float64MultiArray "data: [0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0]"The use_dummy parameter is required if you use the dummy OpenManipulator-X.
diff --git a/open_manipulator_x_description/urdf/open_manipulator_x.ros2_control.xacro b/open_manipulator_x_description/urdf/open_manipulator_x.ros2_control.xacro
index c6cdb74..111846d 100644
--- a/open_manipulator_x_description/urdf/open_manipulator_x.ros2_control.xacro
+++ b/open_manipulator_x_description/urdf/open_manipulator_x.ros2_control.xacro
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@
<param name="usb_port">/dev/ttyUSB0</param>
<param name="baud_rate">1000000</param>
- <!-- <param name="use_dummy">true</param> -->
+ <param name="use_dummy">true</param>
</hardware>
<joint name="joint1">
<param name="id">11</param>Then follow the same instruction of the real robot one.
Note that the dummy implementation has no interpolation so far. If you sent a joint message, the robot would move directly to the joints without interpolation.