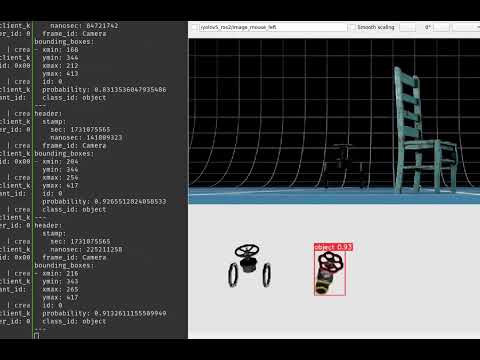
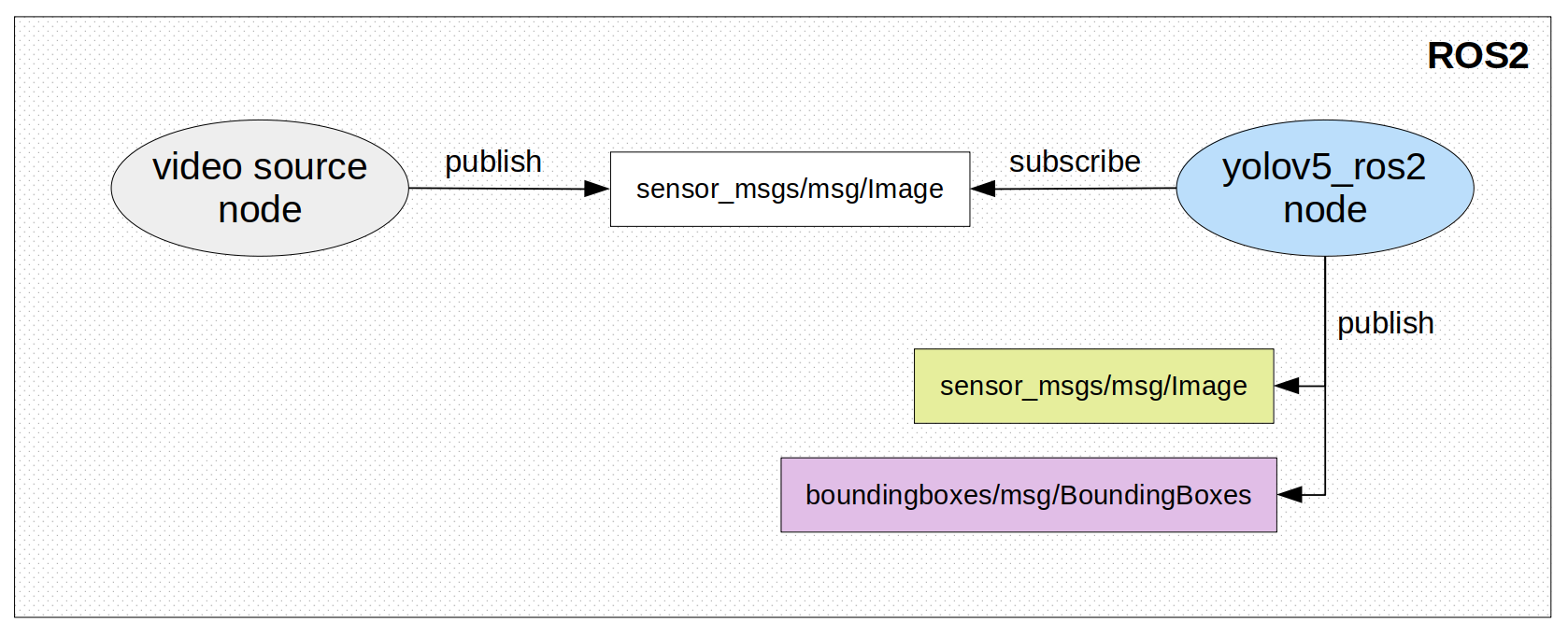
State-of-the-art object detection technique, YOLOv5 is now compatible with ROS2
Subscribed Topic:
- Input image-stream
sensor_msgs/msg/Image
Published Topic:
- Image-stream with bounding box around detected objects
sensor_msgs/msg/Image - Bounding boxes (manually created message type)
boundingboxes/msg/BoundingBoxes
Note: Published image and boundingbox topics are assigned same time-stamp as that of subscribed image topic, so that input and output can be matched frame-by-frame if required for further processing.
- Install ROS2 from the official ROS2 website
For Ubuntu Linux - Focal Fossa (20.04): ROS Foxy installation guide - Strictly necessary YOLOv5 related libraries and packages:
Run the following command in terminal for yolov5_strict_requirements.txt file:
pip install -r yolov5_strict_requirements.txt
Download the docker from RAICAM-EU-Project/isaac_ros_common and follow the instructions to build the image.
Mount the workspace (~/yolo_ws/) to the docker using the run_dev.sh
Run the following commands in terminal:
# clone repo
git clone https://github.com/SasaKuruppuarachchi/yolov5_ros2_pkg.git
# create directory
mkdir -p ~/yolo_ws/src
# build workspace
cd ~/yolo_ws
colcon build --symlink-install
Here we are using webcam for testing purpose. You can also use any other video source (like Intel d435). Open terminal shell and run the following command to initialize webcam node:
ros2 run image_tools cam2image
Note: the above command will start publishing image-stream with topic name '/image'
Now we will start our yolov5_ros2 node to perform object detection on input image-stream Open another shell in terminal and run the following commands:
# move to our workspace directory
cd ~/yolo_ws
# source ws
. install/setup.bash
# run launch file to initialize yolov5_ros2 node
# provide the input image-stream topic name as argument (in our case, its '/image')
# also provide the weight file that you want to use (default: best.pt)
ros2 launch yolov5_ros2 yolov5_ros2_node.launch.py sub_topic:='/image' weights:='yolov5s.pt'