We're now supporting this project on our group's repository:
We built this to better group FastQC result data across groups where each group is comprised of FASTQs related to an experiment or sequencing batch. Individual samples are grouped into paired-end sets when available and the dashboard's extensibility allows a user to add plots or tables as desired.
Parsing the table and running FastQC is performed with code written for
Python 3. We recommend using Anaconda to
install the FastQC dependency:
conda install -c bioconda fastqc
And if you don't have Python yet:
conda install python
The dashboard reads local files, so install where you will eventually be serving the site.
git clone https://github.com/brwnj/fqc.git
cd fqc
python setup.py install
This installs fqc command-line tool to process FASTQs and create the
dashboard.
Then to deploy a local copy from within the fqc directory, you can run:
python -m http.server
And navigate to localhost:8000.
By default, this will show the test data QC as determined by the data
directory in js/fqc.js:
var filePath = "/fqc/tests/data/qc/plot_data/"
Edit fqc.js to your local path within the fqc directory tree.
The first time this is run, it will build the entire backend of the site. Additional FASTQs being written to the same output directory are added to the backend according to Group ID and UID.
$ fqc qc group_2016 sample1 test_r1.fastq.gz
[2016-07-26 13:24 INFO] Writing data to: plot_data/group_2016/sample1
[2016-07-26 13:24 INFO] Running FastQC
[2016-07-26 13:27 INFO] Extracting data from FastQC archives
[2016-07-26 13:27 INFO] Processing of sample1 complete
fqc qc --r2 test_r2.fastq.gz group_2016 sample2 test_r1.fastq.gz
Located within the plot_data directory, this holds metadata for each group
and samples within the groups:
[
{
"group_id": "group_01",
"uids": [
"test_01"
]
},
{
"group_id": "group_00",
"uids": [
"test_00"
]
}
]
Renders as:
The sample ID and group ID must match the underlying directory tree that is
built by fqc qc and maintained when using fqc batch or fqc add.
And the directory tree of this simple example:
plot_data/
├── group_00
│ └── test_00
│ ├── R1
│ ├── R2
│ └── config.json
├── group_01
│ └── test_01
│ ├── R1
│ ├── R2
│ └── config.json
└── groups.json
Holds metadata for each sample inside the group folder. Each entry must have a tab_name, filename, and chart_properties.
Possible (meaningful) values are pass, fail, and warn, which render respectively as:
Example data:
| Base | Mean | Lower Quartile | Upper Quartile |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 32.193 | 32.0 | 33.0 |
| 2 | 32.365 | 32.0 | 33.0 |
| 3 | 32.570 | 32.0 | 33.0 |
JSON entry:
{
"filename": "R1/Per_base_sequence_quality.csv",
"tab_name": "Quality by Position",
"status": "pass",
"chart_properties": {
"type": "arearange",
"x_label": "Position",
"x_value": "Base",
"y_label": "Quality (Phred score)",
"lower_quartile": "Lower Quartile",
"upper_quartile": "Upper Quartile",
"mean": "Mean"
}
}
There is support for adding zones as well, if you're going for the classic FastQC look and feel:
{
"filename": [
["R1", "R1/Per_base_sequence_quality.csv"],
["R2", "R2/Per_base_sequence_quality.csv"]
],
"tab_name": "Quality by Position",
"status": "warn",
"chart_properties": {
"type": "arearange",
"x_label": "Position",
"x_value": "Base",
"y_label": "Quality (Phred score)",
"lower_quartile": "Lower Quartile",
"upper_quartile": "Upper Quartile",
"mean": "Mean",
"zones": [
{"value": 30, "color": "#e5afb0"},
{"value": 34, "color": "#e6d6b1"},
{"color": "#b0e5b1"}
]
}
}
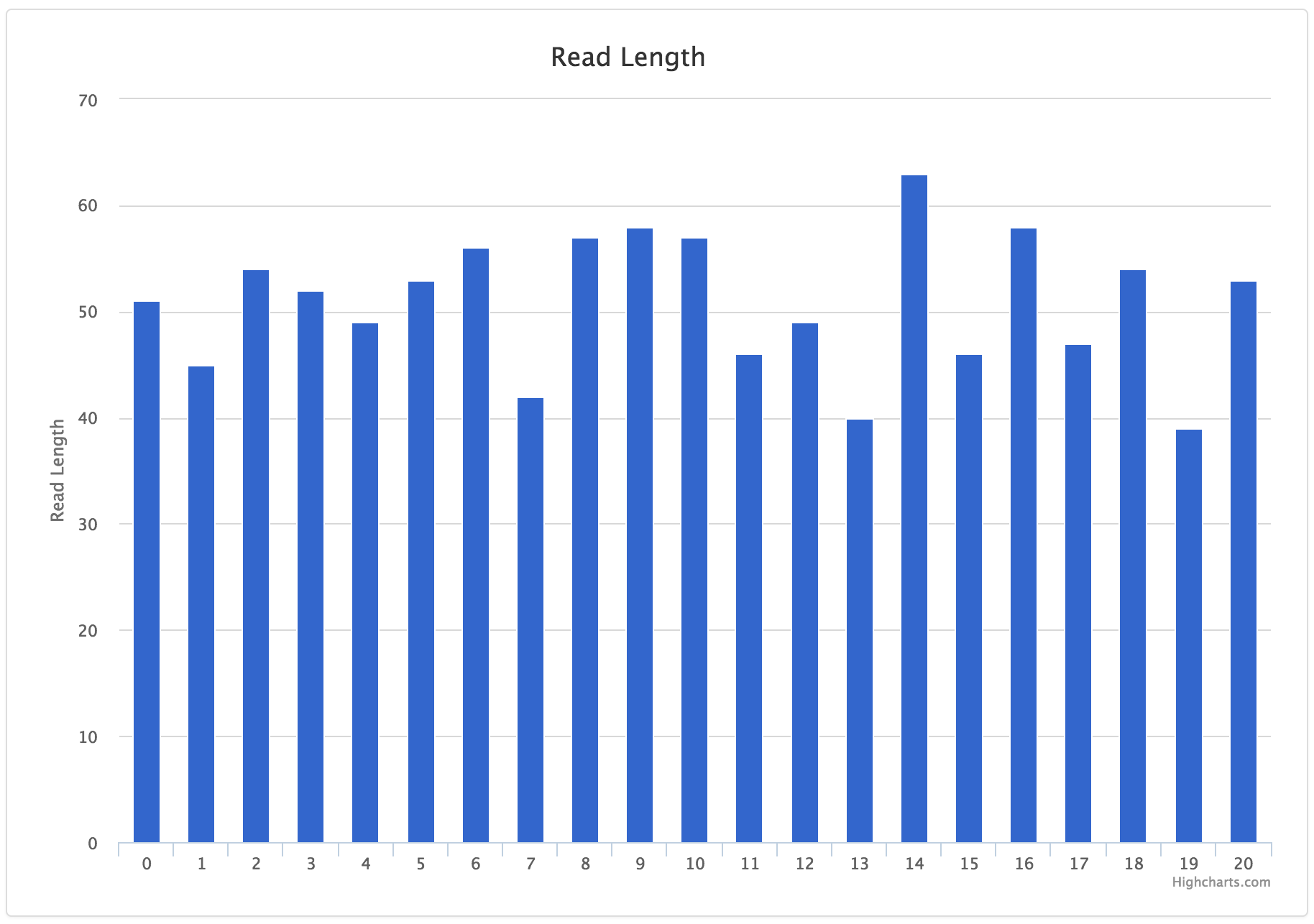
Example data:
| POSITION | READ_LENGTH |
|---|---|
| 0 | 51 |
| 1 | 45 |
| 2 | 54 |
| 3 | 52 |
JSON entry:
{
"tab_name": "Read Length Bar Chart",
"filename": "histogram.csv",
"chart_properties": {
"y_label": "Read Length",
"x_value": "POSITION",
"y_value": [
"READ_LENGTH"
],
"subtitle": "Read Length",
"x_label": "Position",
"type": "bar"
}
}
Example data:
| Tile | Base | Mean |
|---|---|---|
| 1101 | 1 | 0.4305431013906045 |
| 1101 | 2 | 0.1525106635342368 |
| 1101 | 3 | 0.0202493599609709 |
JSON entry:
{
"filename": "R1/Per_tile_sequence_quality.csv",
"tab_name": "Quality by Tile",
"status": "pass",
"chart_properties": {
"type": "heatmap",
"subtitle": "Per Tile Average Quality Deviation",
"x_label": "Position",
"x_value": "Base",
"y_label": "Tile",
"y_value": "Tile",
"shape": "square",
"value": "Mean",
"min": "-10",
"max": "10",
"min_color": "#36c",
"mid_color": "#ffffff",
"max_color": "#dc3912"
}
}
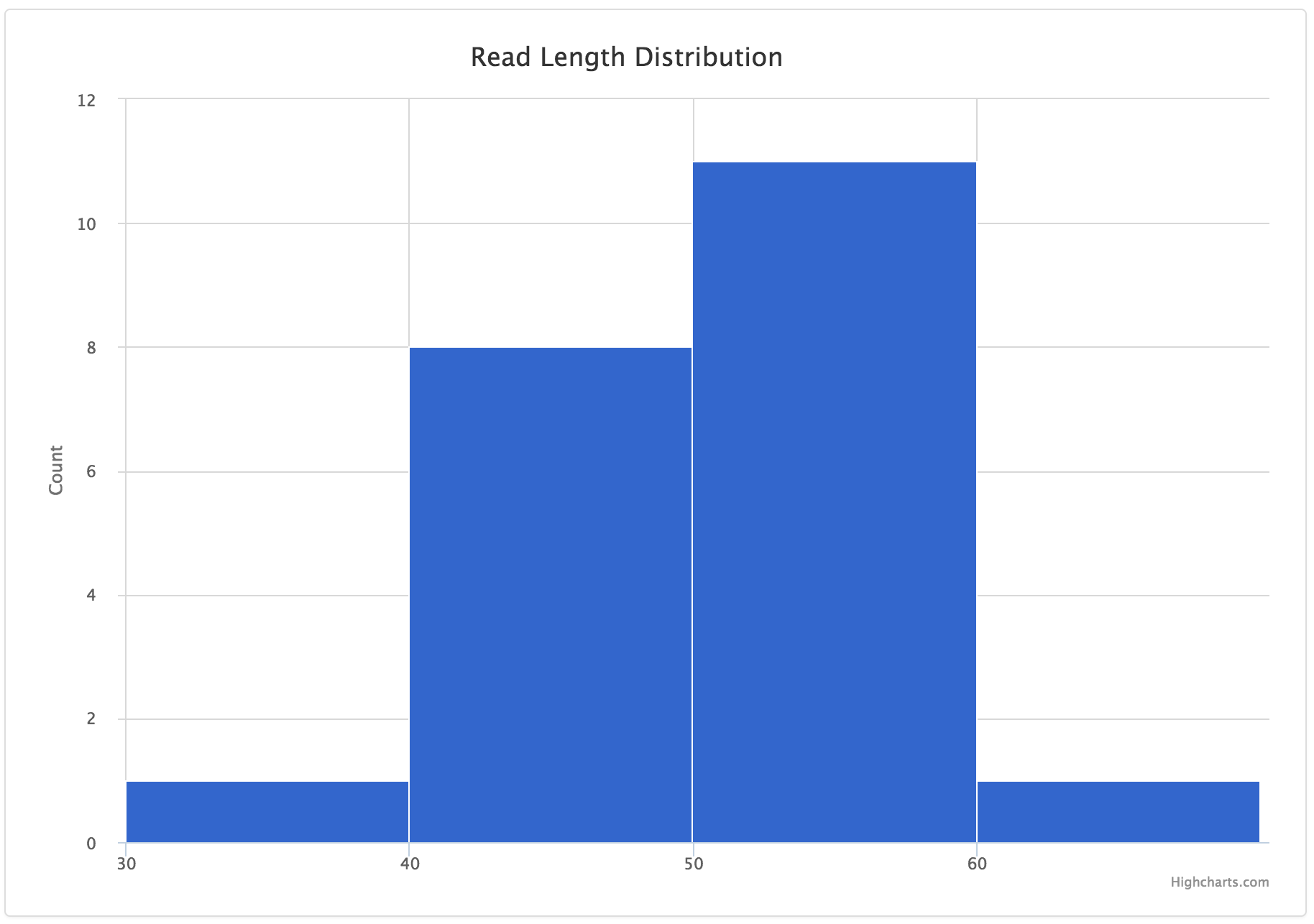
Example data:
| POSITION | READ_LENGTH |
|---|---|
| 0 | 51 |
| 1 | 45 |
| 2 | 54 |
| 3 | 52 |
JSON entry:
{
"tab_name": "Read Length Histogram",
"filename": "histogram.csv",
"chart_properties": {
"y_label": "Count",
"x_value": "POSITION",
"y_value": [
"READ_LENGTH"
],
"step": 10,
"subtitle": "Read Length Distribution",
"x_label": "Read Lengths",
"type": "histogram"
}
}
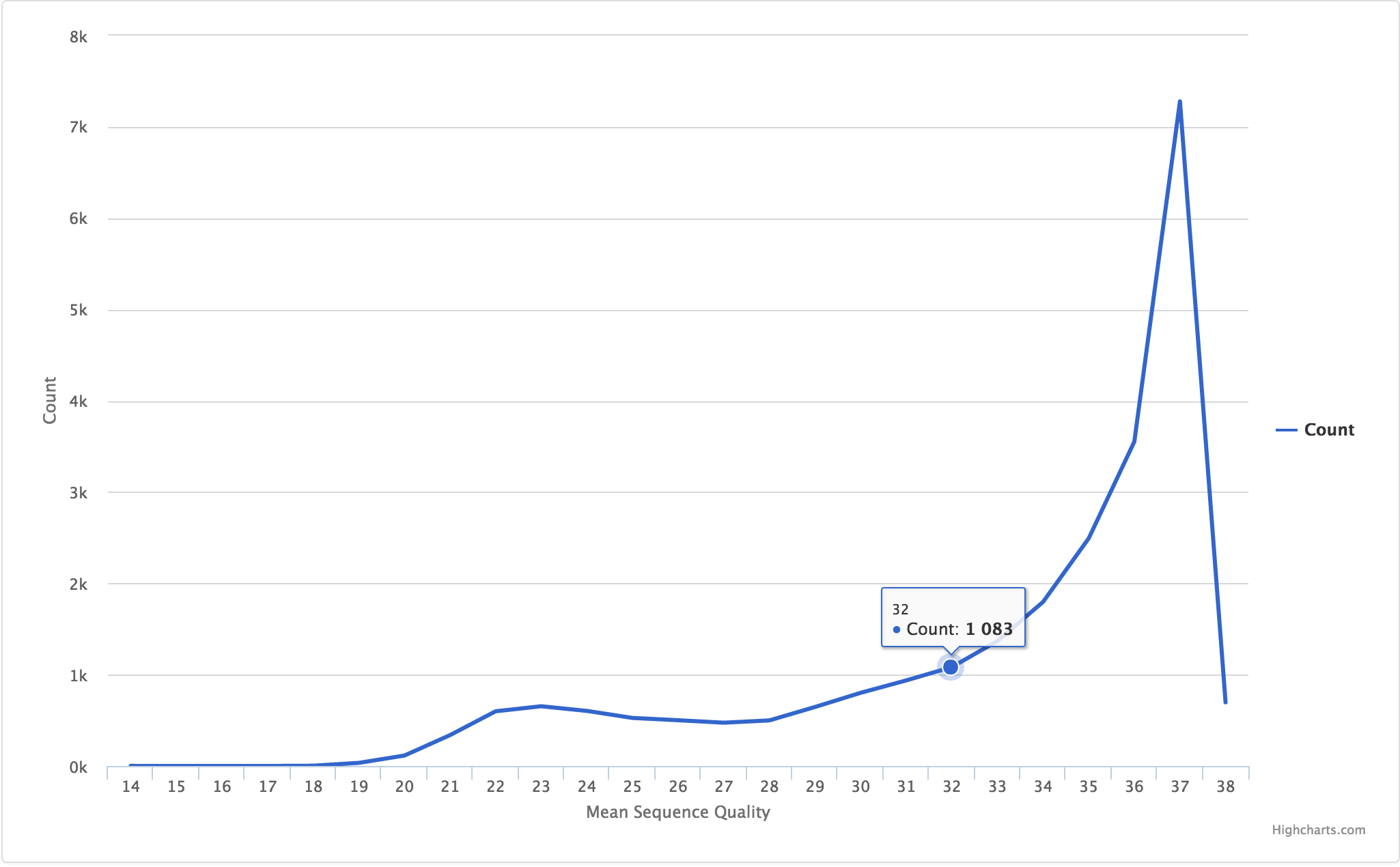
Example data:
| Quality | Count |
|---|---|
| 14 | 1.0 |
| 15 | 0.0 |
| 16 | 0.0 |
JSON entry:
{
"filename": "R1/Per_sequence_quality_scores.csv",
"tab_name": "Quality by Count",
"status": "pass",
"chart_properties": {
"type": "line",
"x_label": "Mean Sequence Quality",
"x_value": "Quality",
"y_label": "Count"
}
}
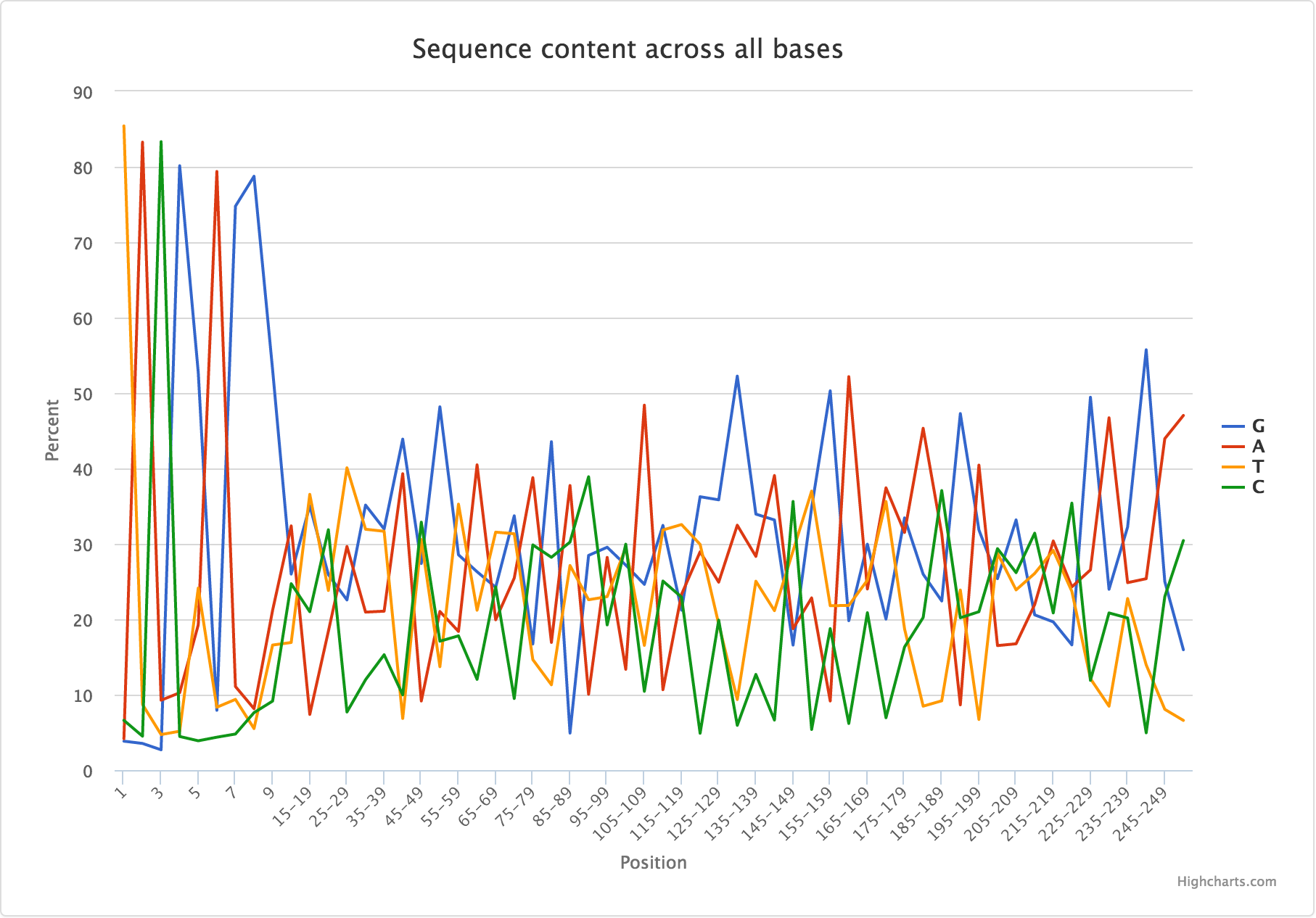
When multiple y-values are being plotted:
| Base | G | A | T | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.832 | 4.148 | 85.424 | 6.596 |
| 2 | 3.531 | 83.268 | 8.704 | 4.496 |
| 3 | 2.692 | 9.264 | 4.712 | 83.332 |
| 4 | 80.14 | 10.252 | 5.152 | 4.456 |
JSON entry:
{
"filename": "R1/Per_base_sequence_content.csv",
"tab_name": "Sequence Content",
"status": "fail",
"chart_properties": {
"type": "line",
"subtitle": "Sequence content across all bases",
"x_label": "Position",
"x_value": "Base",
"y_label": "Percent",
"y_value": [
"G",
"A",
"T",
"C"
]
}
}
A nicely spaced heatmap specifically for showing trends over sample plates. Definitions for colors are optional.
Example data:
| WELL_COL | WELL_ROW | TOTAL_CONTAMINATION | TOTAL_PAIRED_READS | LABEL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | 6 | 205 | |
| 2 | A | 14 | 103 | (+)CTRL |
| 3 | A | 0 | 125 | (-)CTRL |
JSON entry:
{
"filename": [
[
"Plate 1",
"plt1_counts.csv"
],
[
"Plate 2",
"plt2_counts.csv"
]
],
"tab_name": "Plate With Color Defs",
"status": "fail",
"chart_properties": {
"type": "plateheatmap",
"x_value": "WELL_COL",
"y_value": [
"WELL_ROW"
],
"shape": "circle",
"value": "TOTAL_PAIRED_READS",
"label": "LABEL",
"colors": {
"(-)CTRL": "#1f77b4",
"(+)CTRL": "#d62728"
}
}
}
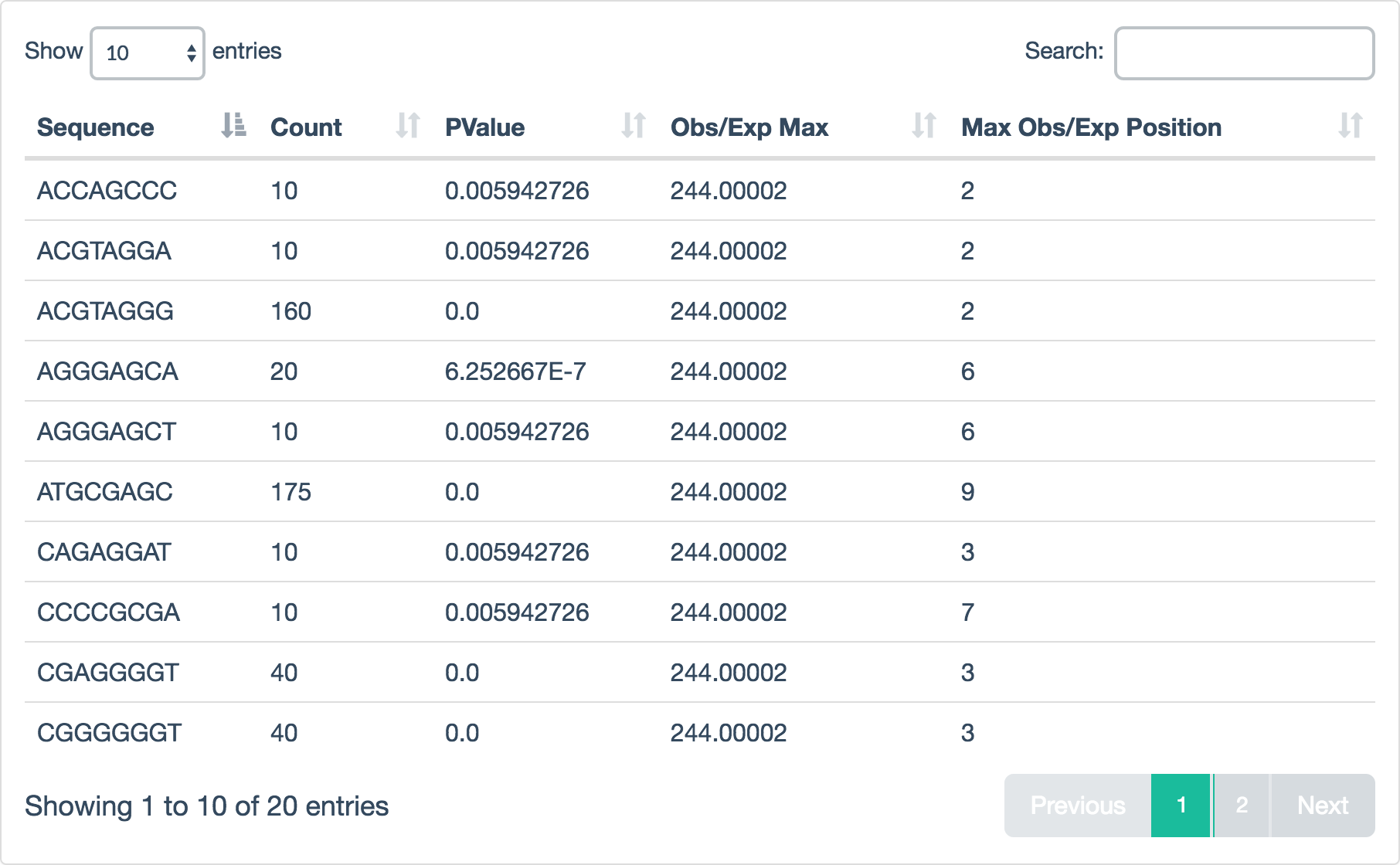
Example data:
| Sequence | Count | PValue | Obs/Exp Max | Max Obs/Exp Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACCAGCCC | 10 | 0.005942726 | 244.00002 | 2 |
| GGGGTTAG | 20 | 6.252667E-7 | 244.00002 | 8 |
| GATGCGAG | 175 | 0.0 | 244.00002 | 8 |
JSON entry:
{
"filename": "R1/Kmer_Content.csv",
"tab_name": "Kmer Content",
"status": "warn",
"chart_properties": {
"type": "table"
}
}
Tabs can be added to the plot area using a list of lists for the filename attribute. The first position is the name of the tab while the second is the file path.
"filename": [
[
"Plate 1",
"plt1_counts.csv"
],
[
"Plate 2",
"plt2_counts.csv"
]
]
Which will render as:
fqc add --x-value WELL_COL \
--y-value WELL_ROW \
--shape circle \
--value TOTAL_PAIRED_READS \
--label "LABEL" \
plot_data/group_00/test_00/config.json \
"Reads by Plate" \
plateheatmap \
"Plate 1",plt1_counts.csv "Plate 2",plt2_counts.csv
This copies data into the necessary local folders and appends the following JSON entry onto plot_data/group_00/test_00/config.json:
{
"filename": [
[
"Plate 1",
"plt1_counts.csv"
],
[
"Plate 2",
"plt2_counts.csv"
]
],
"tab_name": "Reads by Plate",
"chart_properties": {
"type": "plateheatmap",
"x_value": "WELL_COL",
"y_value": [
"WELL_ROW"
],
"shape": "circle",
"value": "TOTAL_PAIRED_READS",
"label": "LABEL"
}
}
Plot data can be added manually to the UID directory by adding the data into a given directory and editting the config.json for that UID. If you're adding a new run, you will have to add it to groups.json.