Dan MacLean 12 April, 2023
mogo is a package for generating GO analysis using M.oryzae genes
only. You can provide the main function with the list of genes of
interest and it does (most of) the rest!
To install you’ll need the devtools R package. From the R console in
RStudio type
install.packages("devtools")Once devtools is installed you can use that to install mogo
devtools::install_github("TeamMacLean/mogo")The first step is to load our gene expression data file and get a simple list of genes for GO analysis
First read in your gene expression file. You can do that with
read_csv(). Minimally it should contain the gene ID, the log fold
change and the
library(readr)
library(dplyr)
gene_expression <- read_csv(system.file("extdata","sample_gene_expression.csv", package="mogo"))
gene_expression
#> # A tibble: 132 × 3
#> gene_id log2fc p.adj
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 MGG_16981 3.53 0.291
#> 2 MGG_04557 1.51 0.217
#> 3 MGG_03894 -7.03 0.255
#> 4 MGG_09290 -7.19 0.377
#> 5 MGG_01448 2.11 0.174
#> 6 MGG_09589 -3.04 0.183
#> 7 MGG_03476 -0.341 0.199
#> 8 MGG_16442 3.60 0.0434
#> 9 MGG_01048 -3.36 0.309
#> 10 MGG_14883 -4.93 0.157
#> # ℹ 122 more rowsWe can now filter the genes to select only the ones with e.g
filter()
filtered_gene_expression <- filter(gene_expression, p.adj <= 0.05)
filtered_gene_expression
#> # A tibble: 16 × 3
#> gene_id log2fc p.adj
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 MGG_16442 3.60 0.0434
#> 2 MGG_14022 3.51 0.00180
#> 3 MGG_00427 0.462 0.0174
#> 4 MGG_10367 -1.30 0.0215
#> 5 MGG_00015 0.539 0.0398
#> 6 MGG_01295 -4.53 0.0360
#> 7 MGG_05721 -8.60 0.000341
#> 8 MGG_13781 7.58 0.0353
#> 9 MGG_14886 -0.674 0.00469
#> 10 MGG_14863 -1.63 0.0322
#> 11 MGG_01492 -6.62 0.0437
#> 12 MGG_04901 -2.27 0.0440
#> 13 MGG_04562 -1.67 0.0439
#> 14 MGG_00559 0.574 0.0324
#> 15 MGG_14897 5.88 0.00736
#> 16 MGG_03526 -0.932 0.0440We can now extract the gene_id column using the $ syntax
gene_ids <- filtered_gene_expression$gene_id
gene_ids
#> [1] "MGG_16442" "MGG_14022" "MGG_00427" "MGG_10367" "MGG_00015" "MGG_01295"
#> [7] "MGG_05721" "MGG_13781" "MGG_14886" "MGG_14863" "MGG_01492" "MGG_04901"
#> [13] "MGG_04562" "MGG_00559" "MGG_14897" "MGG_03526"The GO enrichment is done in the mogo package. Load that and use the
do_enrich() function, passing it the vector of gene_ids to calculate
the enrichment.
library(mogo)
enrich <- do_enrich(gene_ids)
enrich
#> #
#> # over-representation test
#> #
#> #...@organism UNKNOWN
#> #...@ontology UNKNOWN
#> #...@gene chr [1:16] "MGG_16442" "MGG_14022" "MGG_00427" "MGG_10367" "MGG_00015" ...
#> #...pvalues adjusted by 'BH' with cutoff <0.05
#> #...7 enriched terms found
#> 'data.frame': 7 obs. of 9 variables:
#> $ ID : chr "GO:0032259" "GO:0008168" "GO:0008171" "GO:0001510" ...
#> $ Description: chr "methylation" "methyltransferase activity" "O-methyltransferase activity" "RNA methylation" ...
#> $ GeneRatio : chr "16/16" "16/16" "3/16" "2/16" ...
#> $ BgRatio : chr "132/10114" "136/10114" "18/10114" "10/10114" ...
#> $ pvalue : num 2.78e-31 4.62e-31 2.61e-06 1.05e-04 3.44e-03 ...
#> $ p.adjust : num 7.16e-30 7.16e-30 2.70e-05 8.12e-04 2.13e-02 ...
#> $ qvalue : num 3.65e-30 3.65e-30 1.38e-05 4.14e-04 1.09e-02 ...
#> $ geneID : chr "MGG_16442/MGG_14022/MGG_00427/MGG_10367/MGG_00015/MGG_01295/MGG_05721/MGG_13781/MGG_14886/MGG_14863/MGG_01492/M"| __truncated__ "MGG_16442/MGG_14022/MGG_00427/MGG_10367/MGG_00015/MGG_01295/MGG_05721/MGG_13781/MGG_14886/MGG_14863/MGG_01492/M"| __truncated__ "MGG_14022/MGG_00427/MGG_00015" "MGG_05721/MGG_00559" ...
#> $ Count : int 16 16 3 2 2 2 3
#> #...Citation
#> T Wu, E Hu, S Xu, M Chen, P Guo, Z Dai, T Feng, L Zhou, W Tang, L Zhan, X Fu, S Liu, X Bo, and G Yu.
#> clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data.
#> The Innovation. 2021, 2(3):100141As you can see the enrich object has a lot of information in it. The
result table can be extracted using as.data.frame() to convert the
enrich to a data.frame (note glimpse is a helpful function for
printing out big dataframes).
result_table <- as.data.frame(enrich)
glimpse(result_table)
#> Rows: 7
#> Columns: 9
#> $ ID <chr> "GO:0032259", "GO:0008168", "GO:0008171", "GO:0001510", "G…
#> $ Description <chr> "methylation", "methyltransferase activity", "O-methyltran…
#> $ GeneRatio <chr> "16/16", "16/16", "3/16", "2/16", "2/16", "2/16", "3/16"
#> $ BgRatio <chr> "132/10114", "136/10114", "18/10114", "10/10114", "56/1011…
#> $ pvalue <dbl> 2.781819e-31, 4.617021e-31, 2.612786e-06, 1.048125e-04, 3.…
#> $ p.adjust <dbl> 7.156383e-30, 7.156383e-30, 2.699879e-05, 8.122967e-04, 2.…
#> $ qvalue <dbl> 3.645017e-30, 3.645017e-30, 1.375151e-05, 4.137334e-04, 1.…
#> $ geneID <chr> "MGG_16442/MGG_14022/MGG_00427/MGG_10367/MGG_00015/MGG_012…
#> $ Count <int> 16, 16, 3, 2, 2, 2, 3You can save the result to an excel-compatible csv file with,
write_csv()
write_csv(result_table, "my_GO_results.csv")The enrich object is from the package ClusterProfiler and can be
used directly in most of it’s plot types. See them at the
ClusterProfiler page
http://yulab-smu.top/clusterProfiler-book/chapter12.html#bar-plot
Works ok, but the text can make it a bit unwieldy
library(clusterProfiler)
#> clusterProfiler v4.6.2 For help: https://yulab-smu.top/biomedical-knowledge-mining-book/
#>
#> If you use clusterProfiler in published research, please cite:
#> T Wu, E Hu, S Xu, M Chen, P Guo, Z Dai, T Feng, L Zhou, W Tang, L Zhan, X Fu, S Liu, X Bo, and G Yu. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. The Innovation. 2021, 2(3):100141
#>
#> Attaching package: 'clusterProfiler'
#> The following object is masked from 'package:stats':
#>
#> filter
library(enrichplot)
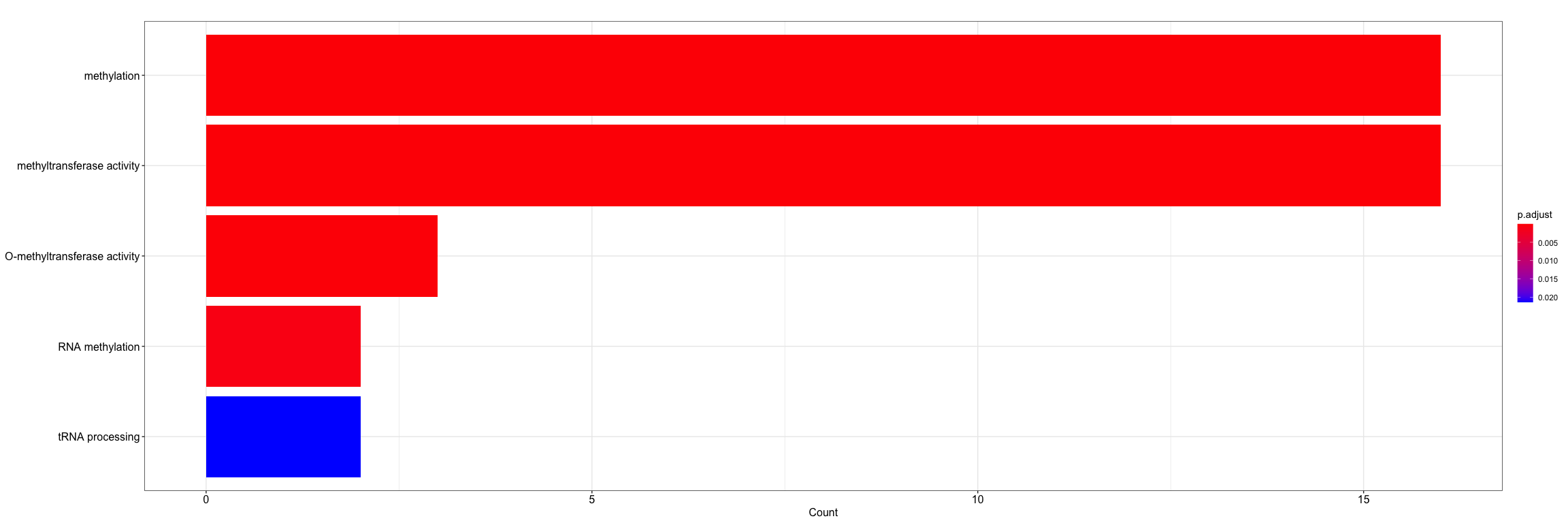
barplot(enrich, showCategory=5)Similar
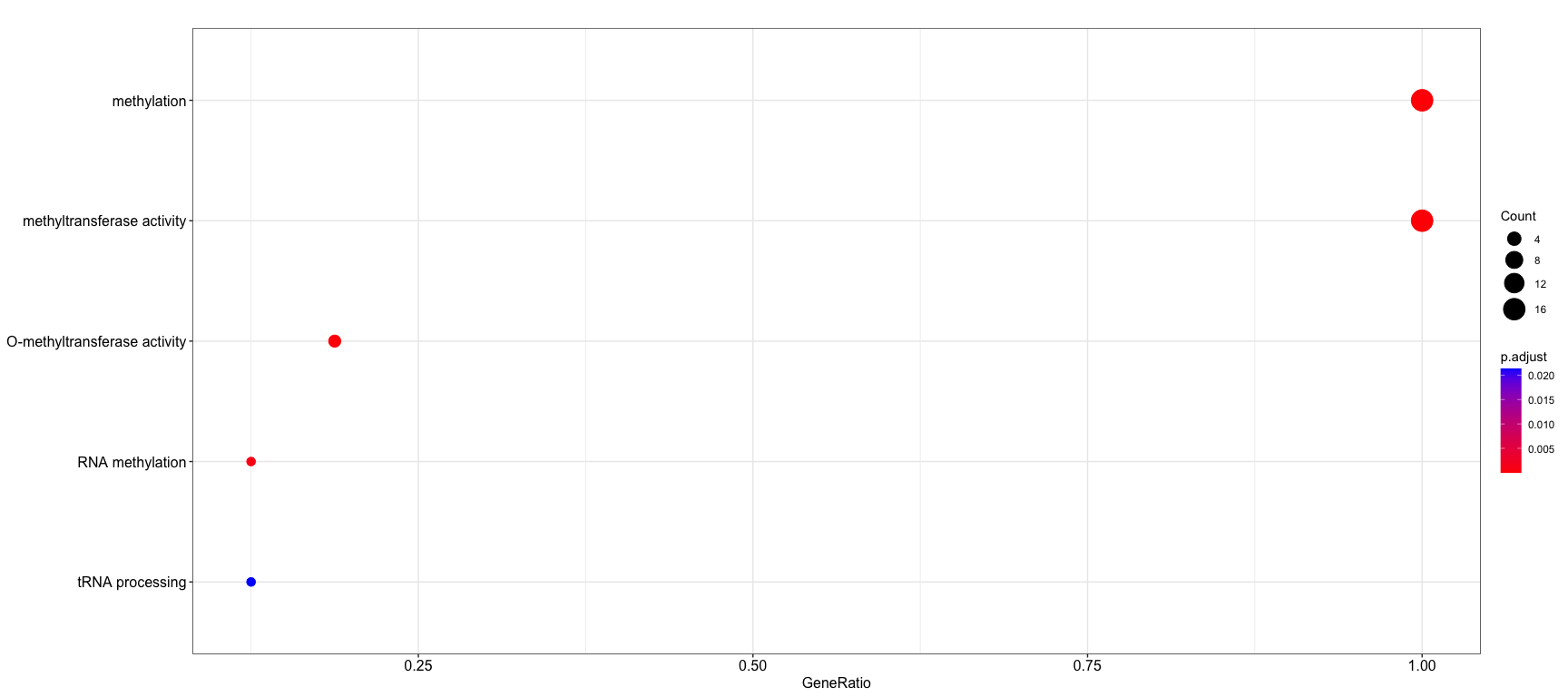
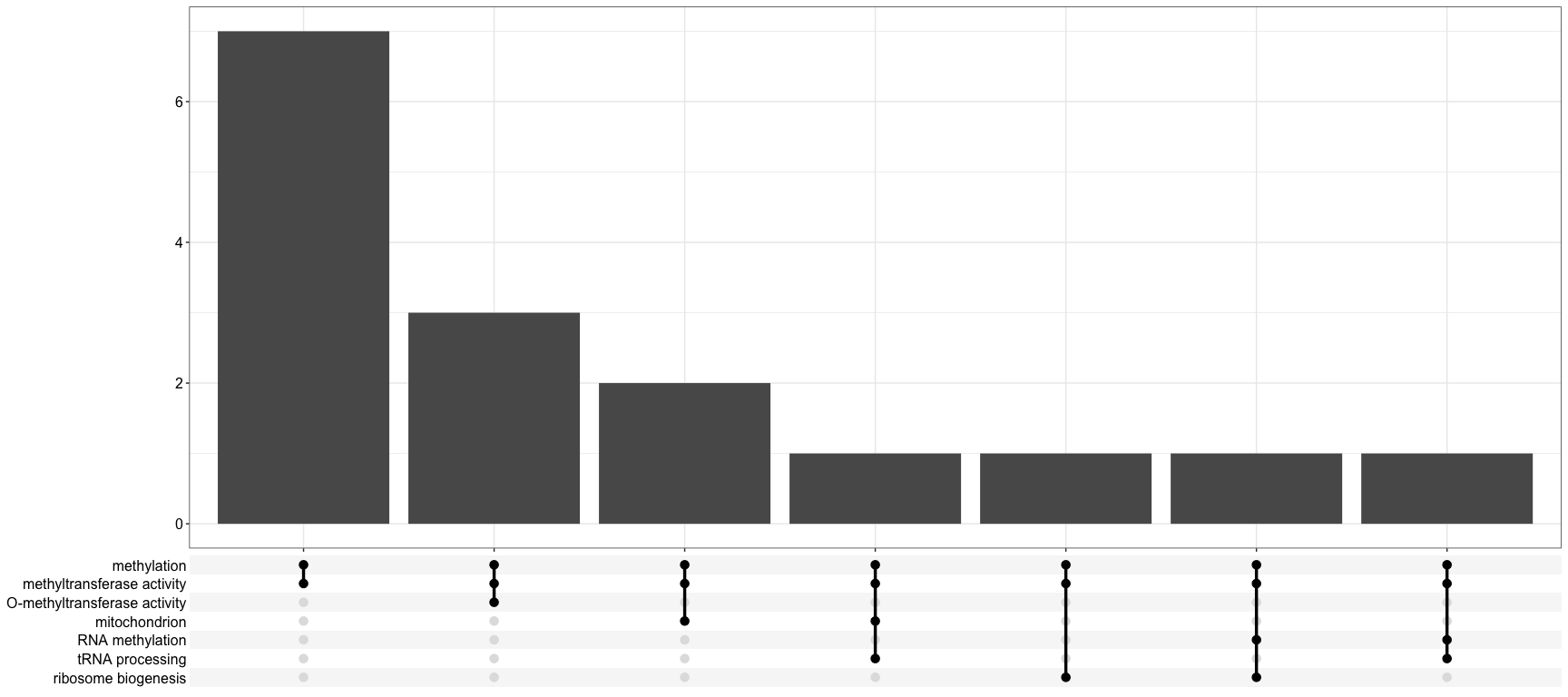
dotplot(enrich, showCategory=5)These are like a really sophisticated Venn/Euler diagram. https://jku-vds-lab.at/tools/upset/
upsetplot(enrich)Plots from the package GoPlot such as bubble plots can be made, but
need you to convert the enrich object to a DAVID compatible object,
and make an accessory data.frame of the expression information. Use
enricher_to_david() for the first part, and the relevant columns of
the gene expression data you created at the beginning for the second
part.
david <- enricher_to_david(enrich)
expr_info <- data.frame(
ID = filtered_gene_expression$gene_id,
logFC = filtered_gene_expression$log2fc
)Then you can convert that to the data format needed for GoPlot
library(GOplot)
#> Loading required package: ggplot2
#> Loading required package: ggdendro
#> Loading required package: gridExtra
#>
#> Attaching package: 'gridExtra'
#> The following object is masked from 'package:dplyr':
#>
#> combine
#> Loading required package: RColorBrewer
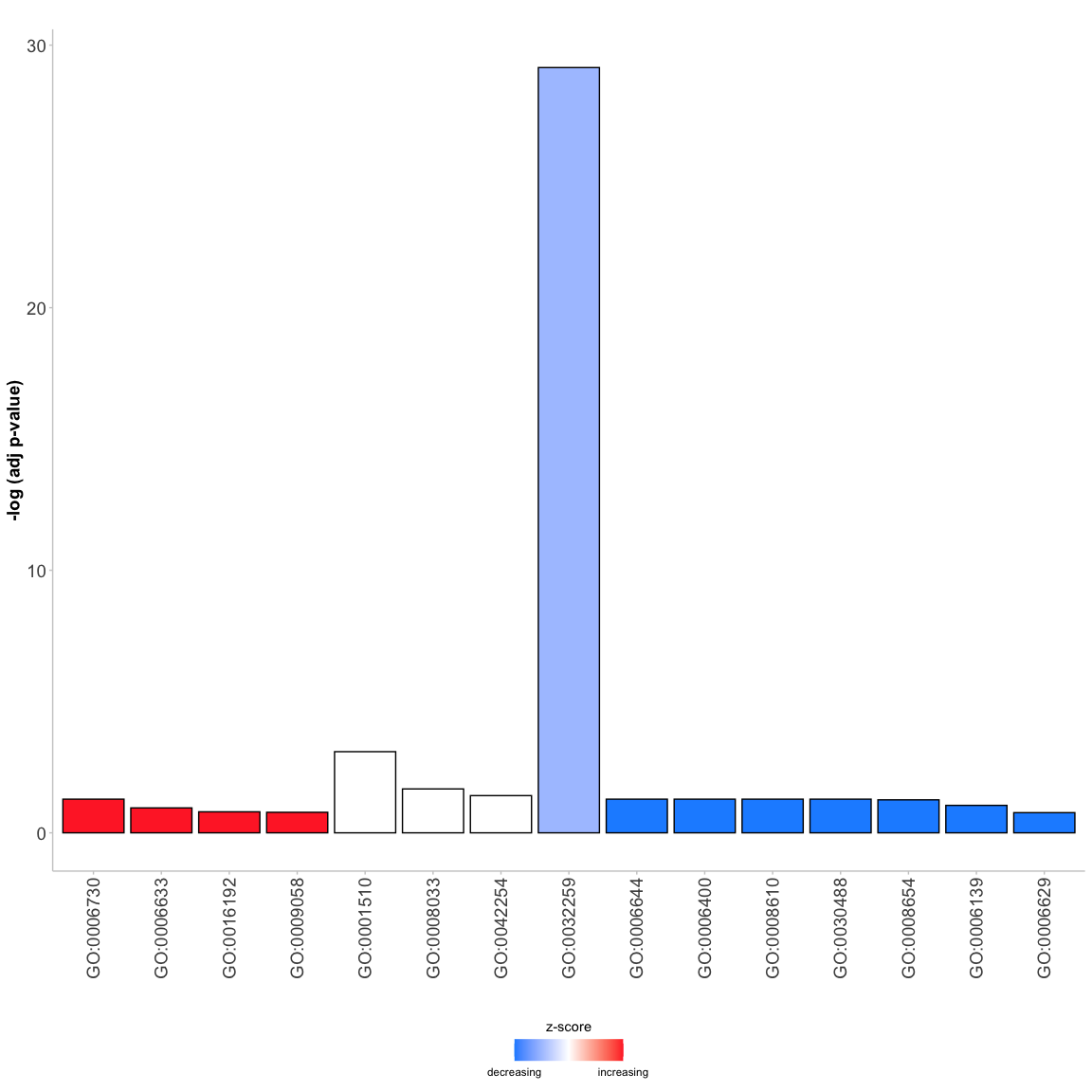
circ <- circle_dat(david, expr_info)A different sort of GO barchart
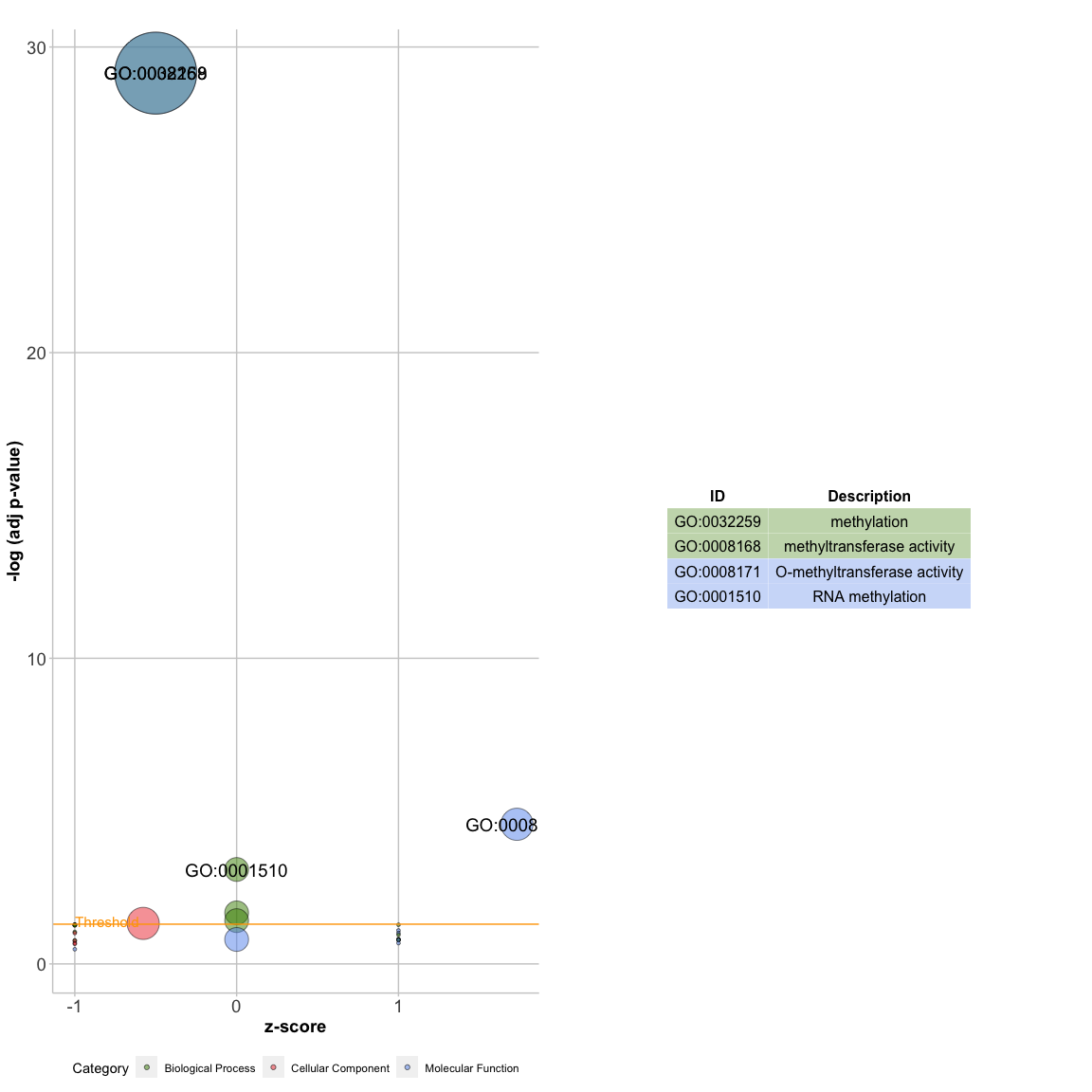
GOBar(subset(circ, category == 'BP'))A plot with bubbles
GOBubble(circ, labels=3)