Authors: Raul Mur-Artal, Juan D. Tardos, J. M. M. Montiel and Dorian Galvez-Lopez (DBoW2)
04 Feb 2019: ORB_SLAM publishes current pose to topics. As of this version, ORB_SLAM2 always needs ROS to compile (one could compile ORB_SLAM2 without compiling its ROS version before). Visualization is default in Rviz (see launch file). There is a service for switching between localization and mapping modes.
- Command line for switching to localization mode (RGBD example):
rosservice call /RGBD/is_mapping_mode false - Command line for switching to mapping mode (RGBD example):
rosservice call /RGBD/is_mapping_mode true
TODO: Possible visualizer optimization: only publish keyframes and graph if there was an update to either of those. We currently publish both at 30Hz (similar to original ORB-SLAM2)
14 Jul 2017: Binary format ORB vocabulary and Map save/load are now supported(See section 10 and 11). See original repository: https://github.com/Alkaid-Benetnash
13 Jan 2017: OpenCV 3 and Eigen 3.3 are now supported.
22 Dec 2016: Added AR demo (see section 7).
ORB-SLAM2 is a real-time SLAM library for Monocular, Stereo and RGB-D cameras that computes the camera trajectory and a sparse 3D reconstruction (in the stereo and RGB-D case with true scale). It is able to detect loops and relocalize the camera in real time. We provide examples to run the SLAM system in the KITTI dataset as stereo or monocular, in the TUM dataset as RGB-D or monocular, and in the EuRoC dataset as stereo or monocular. We also provide a ROS node to process live monocular, stereo or RGB-D streams. The library can no longer be compiled without ROS. ORB-SLAM2 provides a GUI to change between a SLAM Mode and Localization Mode (one can also switch between both using ROS services), see section 9 of this document.
[Monocular] Raúl Mur-Artal, J. M. M. Montiel and Juan D. Tardós. ORB-SLAM: A Versatile and Accurate Monocular SLAM System. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, vol. 31, no. 5, pp. 1147-1163, 2015. (2015 IEEE Transactions on Robotics Best Paper Award). PDF.
[Stereo and RGB-D] Raúl Mur-Artal and Juan D. Tardós. ORB-SLAM2: an Open-Source SLAM System for Monocular, Stereo and RGB-D Cameras. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, vol. 33, no. 5, pp. 1255-1262, 2017. PDF.
[DBoW2 Place Recognizer] Dorian Gálvez-López and Juan D. Tardós. Bags of Binary Words for Fast Place Recognition in Image Sequences. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, vol. 28, no. 5, pp. 1188-1197, 2012. PDF
ORB-SLAM2 is released under a GPLv3 license. For a list of all code/library dependencies (and associated licenses), please see Dependencies.md.
For a closed-source version of ORB-SLAM2 for commercial purposes, please contact the authors: orbslam (at) unizar (dot) es.
If you use ORB-SLAM2 (Monocular) in an academic work, please cite:
@article{murTRO2015,
title={{ORB-SLAM}: a Versatile and Accurate Monocular {SLAM} System},
author={Mur-Artal, Ra\'ul, Montiel, J. M. M. and Tard\'os, Juan D.},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Robotics},
volume={31},
number={5},
pages={1147--1163},
doi = {10.1109/TRO.2015.2463671},
year={2015}
}
if you use ORB-SLAM2 (Stereo or RGB-D) in an academic work, please cite:
@article{murORB2,
title={{ORB-SLAM2}: an Open-Source {SLAM} System for Monocular, Stereo and {RGB-D} Cameras},
author={Mur-Artal, Ra\'ul and Tard\'os, Juan D.},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Robotics},
volume={33},
number={5},
pages={1255--1262},
doi = {10.1109/TRO.2017.2705103},
year={2017}
}
We have tested the library in Ubuntu 12.04, 14.04 and 16.04, but it should be easy to compile in other platforms. A powerful computer (e.g. i7) will ensure real-time performance and provide more stable and accurate results.
We use the new thread and chrono functionalities of C++11.
We use Pangolin for visualization and user interface. Dowload and install instructions can be found at: https://github.com/stevenlovegrove/Pangolin.
We use OpenCV to manipulate images and features. Dowload and install instructions can be found at: http://opencv.org. Required at leat 2.4.3. Tested with OpenCV 2.4.11 and OpenCV 3.2.
Required by g2o (see below). Download and install instructions can be found at: http://eigen.tuxfamily.org. Required at least 3.1.0.
We use modified versions of the DBoW2 library to perform place recognition and g2o library to perform non-linear optimizations. Both modified libraries (which are BSD) are included in the Thirdparty folder.
We provide some examples to process the live input of a monocular, stereo or RGB-D camera using ROS. Building these examples is optional. In case you want to use ROS, a version Hydro or newer is needed.
Map save/load feature needs boost library and more specifically thelibboost_serialization library.
See section 11
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/raulmur/ORB_SLAM2.git ORB_SLAM2
Add the following line to your .bashrc:
export ROS_PACKAGE_PATH=${ROS_PACKAGE_PATH}:PATH/ORB_SLAM2/Examples/ROS
We provide a script build.sh to build the Thirdparty libraries and ORB-SLAM2. Please make sure you have installed all required dependencies (see section 2). Execute:
cd ORB_SLAM2
chmod +x build.sh
./build.sh
This will create libORB_SLAM2.so at lib folder and the executables mono_tum, mono_kitti, rgbd_tum, stereo_kitti, mono_euroc and stereo_euroc in Examples folder.
-
Download a sequence from http://vision.in.tum.de/data/datasets/rgbd-dataset/download and uncompress it.
-
Execute the following command. Change
TUMX.yamlto TUM1.yaml,TUM2.yaml or TUM3.yaml for freiburg1, freiburg2 and freiburg3 sequences respectively. ChangePATH_TO_SEQUENCE_FOLDERto the uncompressed sequence folder.
./Examples/Monocular/mono_tum Vocabulary/ORBvoc.bin Examples/Monocular/TUMX.yaml PATH_TO_SEQUENCE_FOLDER
-
Download the dataset (grayscale images) from http://www.cvlibs.net/datasets/kitti/eval_odometry.php
-
Execute the following command. Change
KITTIX.yamlby KITTI00-02.yaml, KITTI03.yaml or KITTI04-12.yaml for sequence 0 to 2, 3, and 4 to 12 respectively. ChangePATH_TO_DATASET_FOLDERto the uncompressed dataset folder. ChangeSEQUENCE_NUMBERto 00, 01, 02,.., 11.
./Examples/Monocular/mono_kitti Vocabulary/ORBvoc.bin Examples/Monocular/KITTIX.yaml PATH_TO_DATASET_FOLDER/dataset/sequences/SEQUENCE_NUMBER
-
Download a sequence (ASL format) from http://projects.asl.ethz.ch/datasets/doku.php?id=kmavvisualinertialdatasets
-
Execute the following first command for V1 and V2 sequences, or the second command for MH sequences. Change PATH_TO_SEQUENCE_FOLDER and SEQUENCE according to the sequence you want to run.
./Examples/Monocular/mono_euroc Vocabulary/ORBvoc.bin Examples/Monocular/EuRoC.yaml PATH_TO_SEQUENCE_FOLDER/mav0/cam0/data Examples/Monocular/EuRoC_TimeStamps/SEQUENCE.txt
./Examples/Monocular/mono_euroc Vocabulary/ORBvoc.bin Examples/Monocular/EuRoC.yaml PATH_TO_SEQUENCE/cam0/data Examples/Monocular/EuRoC_TimeStamps/SEQUENCE.txt
-
Download the dataset (grayscale images) from http://www.cvlibs.net/datasets/kitti/eval_odometry.php
-
Execute the following command. Change
KITTIX.yamlto KITTI00-02.yaml, KITTI03.yaml or KITTI04-12.yaml for sequence 0 to 2, 3, and 4 to 12 respectively. ChangePATH_TO_DATASET_FOLDERto the uncompressed dataset folder. ChangeSEQUENCE_NUMBERto 00, 01, 02,.., 11.
./Examples/Stereo/stereo_kitti Vocabulary/ORBvoc.bin Examples/Stereo/KITTIX.yaml PATH_TO_DATASET_FOLDER/dataset/sequences/SEQUENCE_NUMBER
-
Download a sequence (ASL format) from http://projects.asl.ethz.ch/datasets/doku.php?id=kmavvisualinertialdatasets
-
Execute the following first command for V1 and V2 sequences, or the second command for MH sequences. Change PATH_TO_SEQUENCE_FOLDER and SEQUENCE according to the sequence you want to run.
./Examples/Stereo/stereo_euroc Vocabulary/ORBvoc.bin Examples/Stereo/EuRoC.yaml PATH_TO_SEQUENCE/mav0/cam0/data PATH_TO_SEQUENCE/mav0/cam1/data Examples/Stereo/EuRoC_TimeStamps/SEQUENCE.txt
./Examples/Stereo/stereo_euroc Vocabulary/ORBvoc.bin Examples/Stereo/EuRoC.yaml PATH_TO_SEQUENCE/cam0/data PATH_TO_SEQUENCE/cam1/data Examples/Stereo/EuRoC_TimeStamps/SEQUENCE.txt
-
Download a sequence from http://vision.in.tum.de/data/datasets/rgbd-dataset/download and uncompress it.
-
Associate RGB images and depth images using the python script associate.py. We already provide associations for some of the sequences in Examples/RGB-D/associations/. You can generate your own associations file executing:
python associate.py PATH_TO_SEQUENCE/rgb.txt PATH_TO_SEQUENCE/depth.txt > associations.txt
- Execute the following command. Change
TUMX.yamlto TUM1.yaml,TUM2.yaml or TUM3.yaml for freiburg1, freiburg2 and freiburg3 sequences respectively. ChangePATH_TO_SEQUENCE_FOLDERto the uncompressed sequence folder. ChangeASSOCIATIONS_FILEto the path to the corresponding associations file.
./Examples/RGB-D/rgbd_tum Vocabulary/ORBvoc.bin Examples/RGB-D/TUMX.yaml PATH_TO_SEQUENCE_FOLDER ASSOCIATIONS_FILE
For a monocular input from topic /camera/image_raw run node ORB_SLAM2/Mono. You will need to provide the vocabulary file and a settings file. See the monocular examples above.
rosrun ORB_SLAM2 Mono PATH_TO_VOCABULARY PATH_TO_SETTINGS_FILE
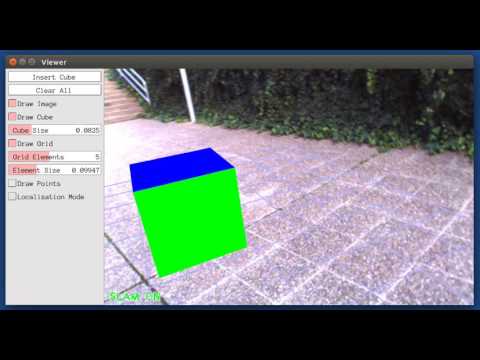
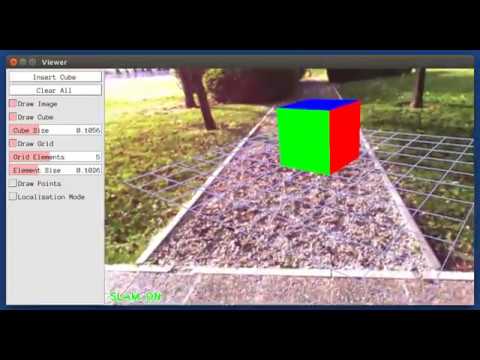
This is a demo of augmented reality where you can use an interface to insert virtual cubes in planar regions of the scene.
The node reads images from topic /camera/image_raw.
rosrun ORB_SLAM2 MonoAR PATH_TO_VOCABULARY PATH_TO_SETTINGS_FILE
For a stereo input from topic /camera/left/image_raw and /camera/right/image_raw run node ORB_SLAM2/Stereo. You will need to provide the vocabulary file and a settings file. If you provide rectification matrices (see Examples/Stereo/EuRoC.yaml example), the node will recitify the images online, otherwise images must be pre-rectified.
rosrun ORB_SLAM2 Stereo PATH_TO_VOCABULARY PATH_TO_SETTINGS_FILE ONLINE_RECTIFICATION
Example: Download a rosbag (e.g. V1_01_easy.bag) from the EuRoC dataset (http://projects.asl.ethz.ch/datasets/doku.php?id=kmavvisualinertialdatasets). Open 3 tabs on the terminal and run the following command at each tab:
roscore
rosrun ORB_SLAM2 Stereo Vocabulary/ORBvoc.bin Examples/Stereo/EuRoC.yaml true
rosbag play --pause V1_01_easy.bag /cam0/image_raw:=/camera/left/image_raw /cam1/image_raw:=/camera/right/image_raw
Once ORB-SLAM2 has loaded the vocabulary, press space in the rosbag tab. Enjoy!. Note: a powerful computer is required to run the most exigent sequences of this dataset.
For an RGB-D input from topics /camera/rgb/image_raw and /camera/depth_registered/image_raw, run node ORB_SLAM2/RGBD. You will need to provide the vocabulary file and a settings file. See the RGB-D example above.
rosrun ORB_SLAM2 RGBD PATH_TO_VOCABULARY PATH_TO_SETTINGS_FILE
You will need to create a settings file with the calibration of your camera. See the settings file provided for the TUM and KITTI datasets for monocular, stereo and RGB-D cameras. We use the calibration model of OpenCV. See the examples to learn how to create a program that makes use of the ORB-SLAM2 library and how to pass images to the SLAM system. Stereo input must be synchronized and rectified. RGB-D input must be synchronized and depth registered.
You can change between the SLAM and Localization mode using the GUI of the map viewer.
This is the default mode. The system runs in parallal three threads: Tracking, Local Mapping and Loop Closing. The system localizes the camera, builds new map and tries to close loops.
This mode can be used when you have a good map of your working area. In this mode the Local Mapping and Loop Closing are deactivated. The system localizes the camera in the map (which is no longer updated), using relocalization if needed.
You can load ORB vocabulary in either text or binary format. The format is determined by suffix(.txt for text format and .bin for binary format).
build.sh will generate a text-to-binary convertor bin_vocabulary in Vocabulary/ . You can also find it as a target in CMakeLists.txt.
bin_vocabulary will convert ./ORBvoc.bin to ./ORBvoc.bin and you can use the new ORBvoc.bin as PATH_TO_VOCABULARY wherever needed.
PS: binary format is loaded faster and text format is more human-readable.
Considering this feature doesn't hurt performance, and it is annonying to deal with conditional compilation flags, so this feature will be enabled unconditionally.
This feature is integrated with class System. The path of mapfile can be set by adding Map.mapfile: map.bin to ORB_SLAM2's settings file. See the last few line of TUM1.yaml for example.
To save a map, you need construct ORB_SLAM2::System with the last parameter (is_save_map) be true. Then the System will save map to mapfile (create if non-existent, overwrite if existent) specified in then setting file when ShutDown (e.g. interrupted by ctrl+c).
With a readable mapfile, map will be loaded automatically and System will run in localization mode at first, but you can change it to SLAM mode later.
mono_tum has been updated as a simple example of this functionality. An extra command line parameter(0 or 1) should be given to indicate whether you want to save map or not.
I use boost_serialization library to serialize Map, MapPoint, KeyFrame,KeyFrameDatabase, cv::Mat, DBoW2::BowVector, DBoW2::FeatureVector. In brief, only the ORBVector isn't serialized.
This feature is tested with boost 1.64 and it works fine mostly. There is still some occasional segmentfault to dig in.
Map Points and KeyFrames seem to not be deleted from Map but only marked as bad instead. So there will be more and more useless data structure residing inside memory and Map size will keep growing.