The Robofleet 2.0 Robot Client for ROS
This client serves as the interface between a ROS system and the Robofleet server. It advertises and/or subscribes to ROS topics, services, and actions as specified in a YAML configuration file.
- ROS 2 Humble/Iron
- Qt5WebSockets
- robofleet_client_msgs
Unlike earlier versions of robofleet_client, this release is to be built using colcon as normal for a ROS 2 packages.
Create workspace.
mkdir -p robofleet_client_ws/src && cd robofleet_client_ws/src/Clone packages into src.
git clone --recurse-submodules -j8 git@github.com:UTNuclearRobotics/robofleet_client.git
git clone git@github.com:UTNuclearRobotics/robofleet_client.gitInstall missing dependencies and build in robofleet_client_ws directory.
cd ..
rosdep install --from-paths src -y --ignore-src
colcon buildTo handle ROS messages, the client uses plugin packages. A plugin package provides handler classes and conversion functions that the client needs to pass given messages to and from the server.
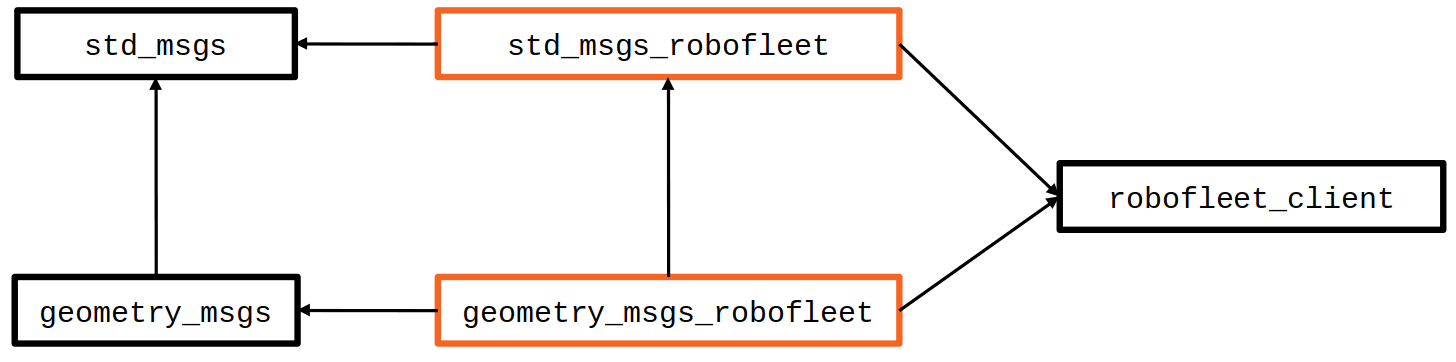 Build dependency graph for some example message plugin packages. The arrows point from dependents to dependencies. Note that, critically, the
Build dependency graph for some example message plugin packages. The arrows point from dependents to dependencies. Note that, critically, the robofleet_client package does not depend on the plugin packages. The client accesses the plugins at runtime only.
For example, to use ROS messages from the geometry_msgs package, you need a corresponding plugin package geometry_msgs_robofleet. You must have plugin packages for all the message types specified in your client's YAML config file.
robofleet_client provides a script which generates your plugin packages for you. It can be run like so:
usage: ros2 run robofleet_client generate_plugin_pkg.py [-h] [-o OUT] [-w] [-i] packages [packages ...]
positional arguments:
packages The msg or srv packages that we want to generate plugins
for. The program will automatically include dependencies
of the listed packages.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-o OUT, --out OUT Specify the output directory. Defaults to
'robofleet_client/scripts/generate/output'
-w, --overwrite If the requested plugin packages already exist in the
output location, they will be deleted and recreated.
-i, --leave-schema Intermediate flatbuffer schema files will not be deleted
during cleanup.
Example: ros2 run robofleet_client generate_plugin_pkg.py geometry_msgs std_srvs
After generating the plugin packages you need, place them in your ROS workspace and build them using colcon.
usage: ros2 run robofleet_client client config_file
positional arguments:
config_file Path to a YAML configuration file which specifies the input and output topics of the client.
See robofleet_client/cfg/example.yaml as a guide. Topic names from the config file are resolved
by the client according to ROS's normal name resolution rules. You must have built plugin
packages for any message types referenced in the configuration. See the example in robofleet_client/cfg/example.yaml
By default, the Robofleet robot client runs a WebSocket client, which connects to an instance of robofleet_server. You can then use robofleet_webviz to connect to the server and interact with connected robots. In some cases, you may not need the features provided by robofleet_server, or you may not want to run the Node.js application. In this case, you can enable "direct mode" in the robot client, which causes it to accept connections as a WebSocket server instead of acting as a WebSocket client. You can then use robofleet_webviz to connect directly to the robot running the robot client, instead of connecting to an intermediary instance of robofleet_server.
Direct mode does not have features such as authentication or subscriptions, nor does it currently support secure WebSockets. It simply broadcasts each incoming message to all other clients, as well as sending messages from local ROS topics as usual.
To switch to direct mode, edit your config file so that host_url is an empty string, and provide values for direct_mode_port and direct_mode_bytes_per_sec. Increase direct_mode_bytes_per_sec to prevent dropped messages or decrease it to prevent time lag when large amounts of message data are sent.